
National and Global Islamic Financial Architecture:
Prolems and Possible Solutions for the OIC Member Countries
209
7.
Policy Recommendations
Chapter 6 showed the status of different infrastructural institutions in different countries for
Islamic finance. While a few countries have sound and mature financial architecture for the
Islamic financial sector, the institutions are weak and underdeveloped in some other countries.
In this chapter, the policies that can be undertaken to strengthen the financial architecture for
Islamic finance are identified. The policies are presented in line with the architectural elements
discussed in previous chapters. It should be noted that the order in which the
recommendations are arranged for each of the architectural elements shows the priority in
terms of their importance.
68
7.1. Policies at the National Level
7.1.1. Legal Infrastructure
A key element in the legal infrastructure is to have supporting laws for different Islamic
financial sectors. Thus, governments need to come up with supporting Islamic financial laws to
give legal foundations for different segments of the Islamic financial industry. The tax laws
related to income (profit, withholding), transactions (capital gains and stamp duties) and
goods and services (value-added tax) need to be accommodated for tax neutrality and to level
the playing field of Islamic and conventional financial sectors.
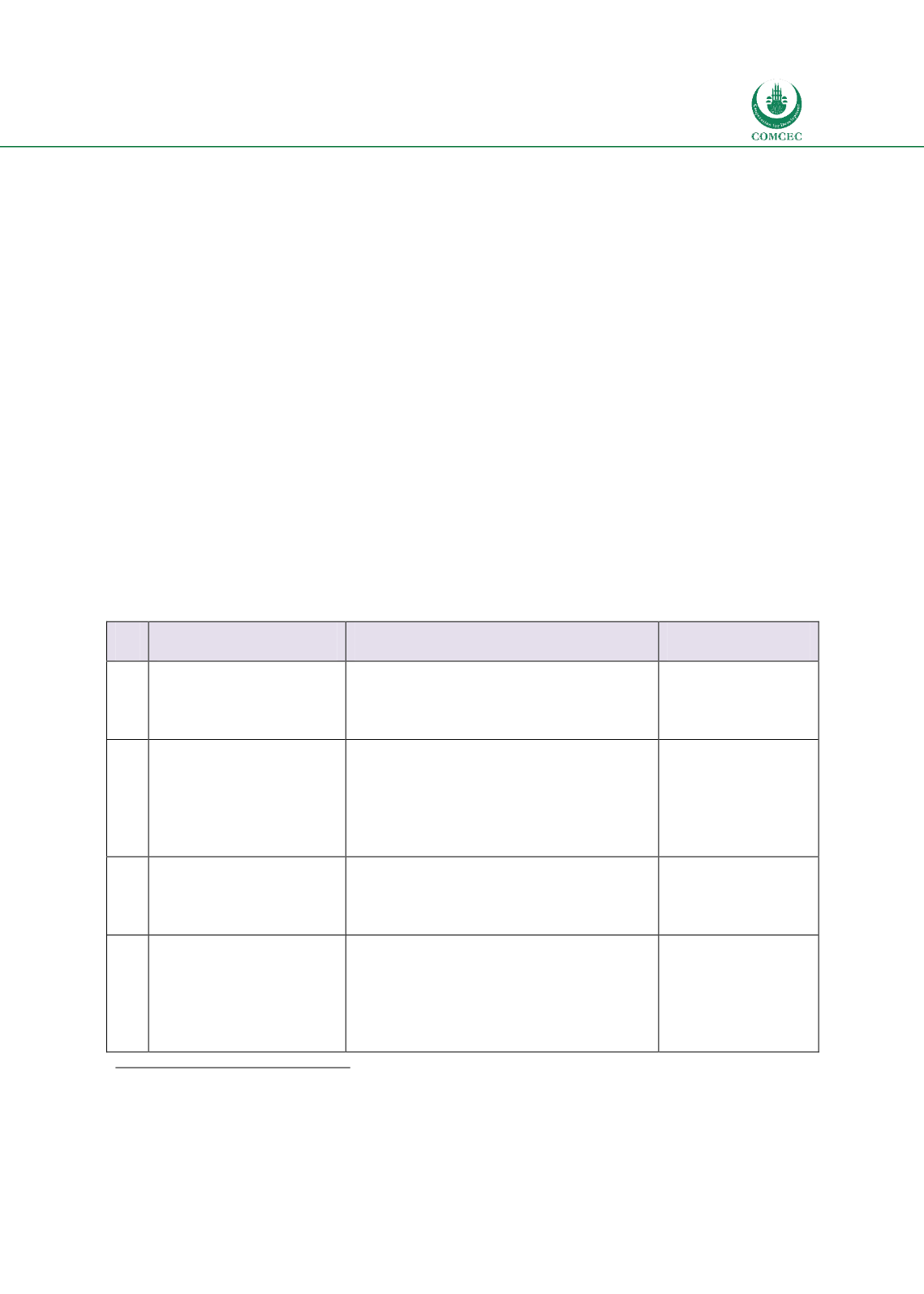
Table
7.1: Policy Recommendations for Legal Infrastructure
No. Recommendations
Specific Steps
Implemented by
1.1 Adopt Islamic financial
laws
Islamic banking law
Takaful law
Islamic capital markets law
Government
(Ministry of
Law/ Legal
Affairs)
1.2 Adopt Supporting Tax
Laws
for
Islamic
Financial sector
Change/accommodate tax neutrality
issues to level the playing field of
Islamic banking and conventional
banks
Change/accommodate tax neutrality
issues for sukuk issuance
Government
(Ministry of
Finance)
1.3 Appropriate
dispute
resolution framework
Arrangement in civil courts to
adjudicate Islamic finance disputes
Specific Islamic arbitration centers
Government
(Ministry of
Law/ Legal
Affairs)
1.4 Bankruptcy Framework
and Resolution of banks
Develop a general Islamic bankruptcy
framework for corporate sector
Develop specific framework of
resolution of Islamic banks
Shariah
scholars/board
Government
(Ministry of
Law/ Legal
Affairs)
68
Note that one of the criteria used to assess the priority of recommendations is the prevalence and frequency with which
they affect the Islamic financial sector. For example, for legal infrastructure ‘adoption of Islamic finance laws’ is given
priority as it is necessary for not only establishing new Islamic financial institutions but also governing their operations at all
times. An appropriate dispute resolution framework is applicable only when disputes arise.
















