
National and Global Islamic Financial Architecture:
Problems and Possible Solutions for the OIC Member Countries
212
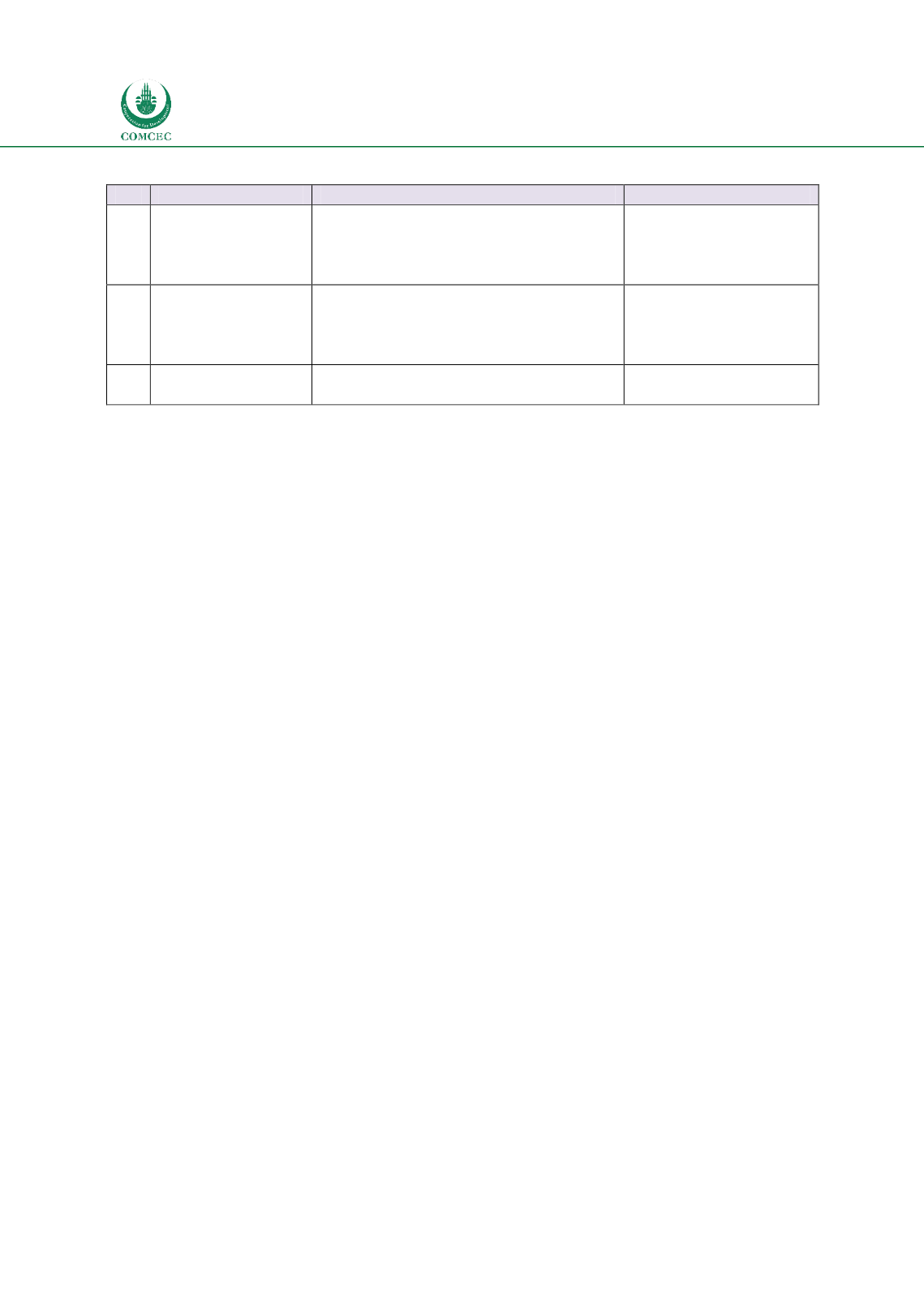
Table
7.4: Liquidity Infrastructure
No. Recommendations Specific Steps
Implemented by
4.1
Shariah compliant
liquidity
instruments
Issue government sponsored Islamic
liquidity instruments
Issue private sector sukuk issues
Government
(Ministry of finance)
Central bank
Financial institutions
4.2
Islamic money
market
Develop infrastructure for secondary
markets for Islamic instruments
Develop a framework for inter-bank
money market
Central bank
Regulator (capital
markets)
Financial institutions
4.3
Lender of the last
resort
Shariah complaint liquidity facilities
for Islamic financial institutions
Central bank
There is also a need to develop an active money market that would use some of these
instruments to meet the short-term liquidity needs in an organized way. This platform can be
established by the government in the countries where Islamic finance is in the initial stages of
development. Finally, Shariah complaint lender of the last resort would be required so that
Islamic financial institutions can benefit from the liquidity facility in case of emergencies.
7.1.5. Information Infrastructure
As some features of Islamic financial transactions require using specific accounting and
auditing treatments, there is a need to require Islamic banks to use accounting standards that
reflect these. In this regard, countries need to either adopt AAOIFI accounting and auditing
standards or introduce changes in the domestic accounting and auditing standards to
accommodate features of Islamic financial transactions. There is a need also to come up with
disclosure and transparency requirements that are relevant for Islamic finance. Some of these
disclosure requirements are identified in AAOIFI standards and the IFSB also has published
standards on the topic. One of the key issues that should be disclosed is the Shariah compliance
related issues to enhance the confidence of the customers. Not only should the structure of
products be disclosed but also the basis of Shariah rulings for them. While the domestic Islamic
accounting and disclosure standards need to be developed by the national accounting
standards setting board, their implementation would be required by the regulators.
Credit information services and ratings agencies provide relevant information to different
stakeholders that can be used to make financial decisions. While the former relates to the
clients of financial institutions, the latter provides an assessment of organizations and
instruments. However, most of the credit information and rating agencies provide assessments
relating to credit worthiness for debt based financing. As Islamic finance emphasizes both debt
and equity based financing, the credit information services and rating agencies should be able
to provide both perspectives. Thus there is a need to have public and private institutions that
provide relevant information on clients, organizations and instruments dealing with the
Islamic financial sector.
















