
National and Global Islamic Financial Architecture:
Prolems and Possible Solutions for the OIC Member Countries
203
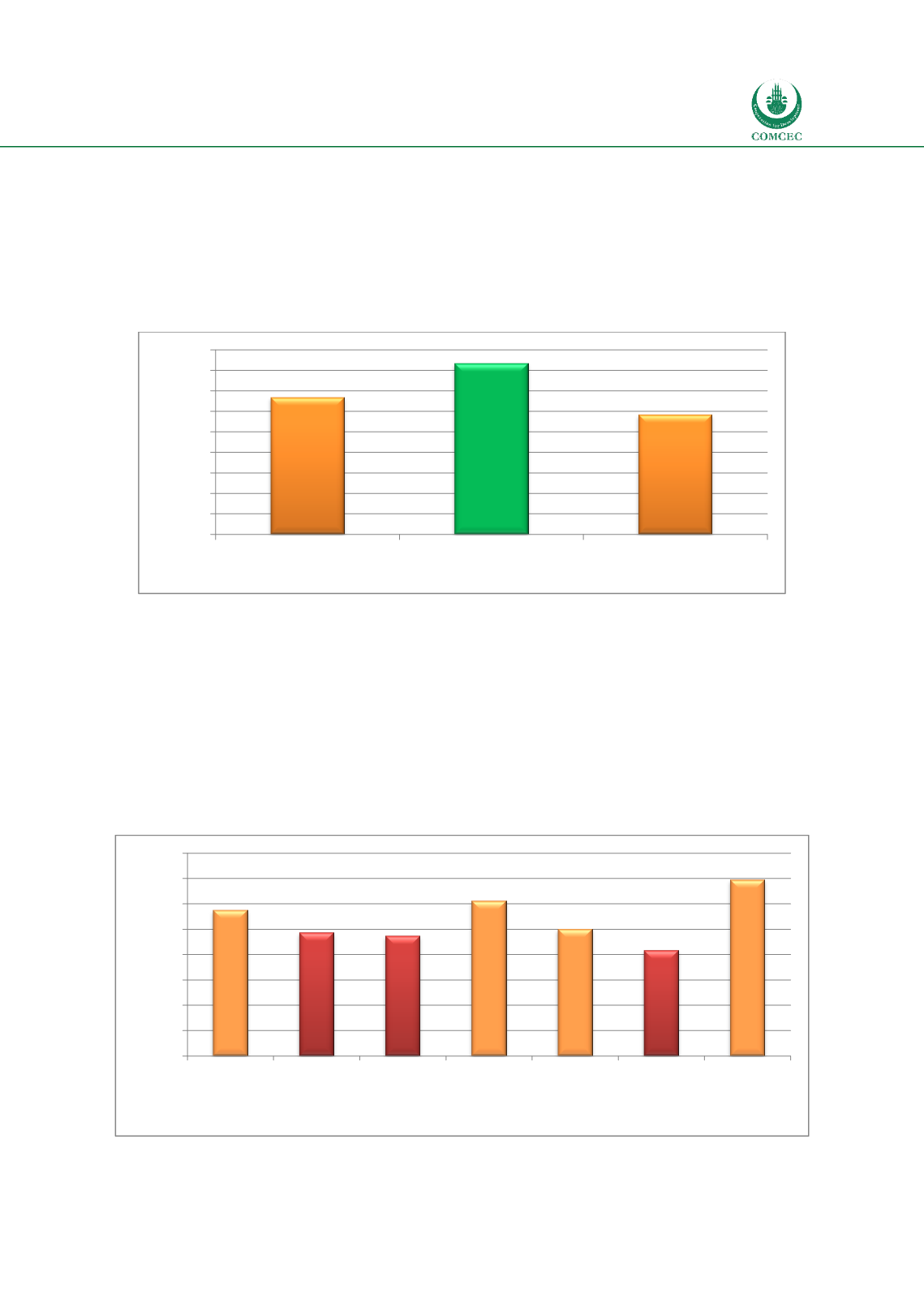
same. In an overwhelming 83.3% of the countries, universities and academic institutions are
providing education in the discipline. Thus, while the initiative for human capital and
knowledge development is ‘developed’ at the academic level, it has a status of ‘developing’ for
public bodies, the private sector and nonprofits. Note that one of the key gaps in human capital
in Islamic finance exists in public bodies such as regulators and the judiciary. Some countries
are unable to come up with appropriate policies for the industry due to a lack of knowledge
and skills related to the Shariah principles and practices of Islamic finance.
Chart
6.11: Human Capital and Knowledge Development
Chart 6.12 shows the overall averages of different Islamic finance infrastructure institutions
for sample case-study countries arrived at by averaging the different elements of each
infrastructural component. The chart shows that while some of the infrastructural institutions
have the status of ‘developing’, others are ‘underdeveloped’. Specifically, the legal, liquidity and
information infrastructures, and human capital and knowledge development aspects of the
Islamic financial sector can be ranked as ‘developing’; and regulations and supervision, Shariah
governance framework, and consumer protection and financial literacy are ‘underdeveloped’.
As none of the architectural elements show a ‘developed’ status on average, there is a room for
the development of all aspects of the infrastructural institutions, particularly in the latter
types.
Chart
6.12: Overall Averages of Infrastructural Institutions for Sample Countries
66,7
83,3
58,3
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
Initiatives by public
bodies
Initiatives by academic
institutions/universities
Private sector intiatives
including NGOs
Percentage of total
57,5
48,6
47,3
61,1
50,0
41,6
69,4
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
Legal
Infrastructure
Regulation &
Supervision
Shariah
Governance
Framework
Liquidity
Infrastructure
Information
Infrastructure
Consumer
Protection &
Financial
Literacy
Human Capital
and
Knowledge
Development
Percentage of total
















