
Improving Public Debt Management
In the OIC Member Countries
51
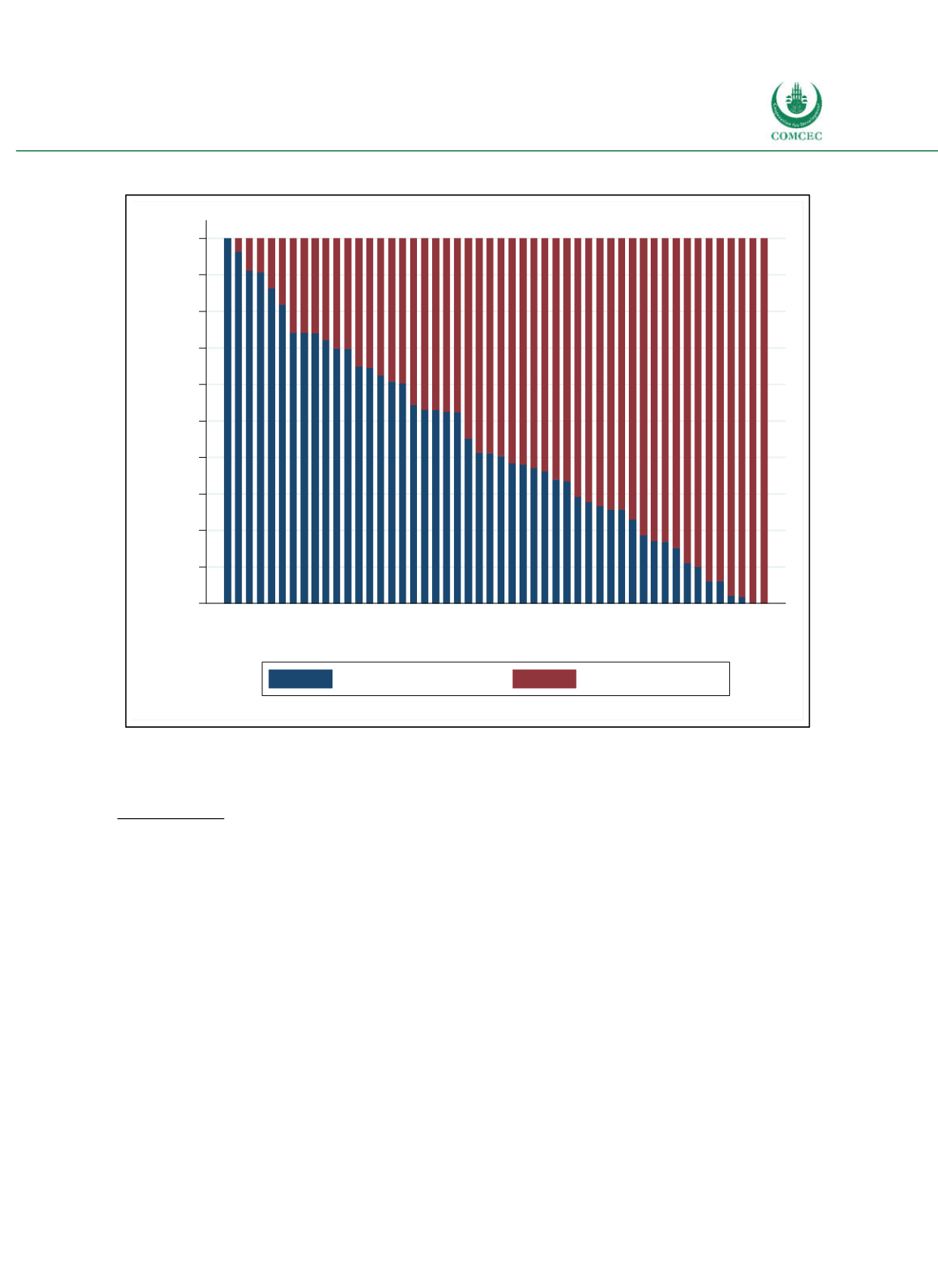
Figure 3-7: Creditor Structure of Public Debt by Country (2015)
Note: Data for Brunei Darussalam, Kuwait, Libya, Palestine, Somalia, Turkmenistan, and UAE is not available.
Sources: IMF Country Reports (see 4.1 Case Countries), national central banks, national Ministries of Finance,
Moody’s, World Bank (2016) International Debt Statistics, calculations by the Ifo Institute.
Grant Element
Figure 38 shows the grant element of loans, defined as the grant equivalent as a percentage of
the amount committed. The average grant element in OIC countries has been about 50% since
2006, similar to the worldwide average. Grants are primarily extended by official creditors,
while private credit contracts have a small grant element. Grants to lowincome countries are
more generous than to middleincome countries (see lower left panel of Figure 38). The grant
element is particularly high in the African group (see lower right panel of Figure 38).
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Share of total public debt (in %)
Saudi Arabia
Bahrain
Egypt
Iran
Lebanon
Nigeria
Syria
Qatar
Kazakhstan
Yemen
Pakistan
Maldives
Turkey
Guinea-Bissau
Jordan
Bangladesh
Malaysia
Guinea
Togo
Albania
Suriname
Morocco
Gambia
Indonesia
Chad
Oman
Côte d'Ivoire
Tunisia
Uganda
Benin
Iraq
Cameroon
Senegal
Sierra Leone
Burkina Faso
Guyana
Niger
Mali
Algeria
Gabon
Mozambique
Tajikistan
Sudan
Comoros
Mauritania
Djibouti
Kyrgyz Republic
Azerbaijan
Afghanistan
Uzbekistan
Domestic creditors
External creditors
















