Financial Outlook of the OIC Member Countries 2016
14
3
CHARACTERIZATION AND FUNCTIONING OF FINANCIAL SYSTEMS
Previous two chapters cover banking and capital markets individually among OIC member
countries with available data. The effort shows that the data is difficult to obtain and inference
on them should be cautious. It also shows that the size of bank and capital markets is greatly in
parallel to the size of the economy and economic development.
This chapter makes use of World Bank Global Financial Development Database. Cihak,
Demirgüç-Kunt, Feyen and Levine (2012) introduce this database and explain that the
database measures and benchmarks financial systems, allows cross-country and regional
comparison, and time series trends.
The database has varying coverage of data among countries. With this limitation and the fact
that economic development could be used to aggregate and represent income-level group
countries, this Financial Outlook categorizes OIC Member States in four major groups
according to the World Bank Income Grouping Methodology (according to their GDP per capita
levels), which is globally used in current financial and economic researches. According to this
categorization, 15 countries are in OIC-Low Income Group (OIC-LIG); 19 are in OIC Lower
Middle Income Group (OIC-LMIG); 16 are in OIC-Upper Middle Income Group (OIC-UMIG), and
7 are in OIC-High Income Group (OIC-HIGH) as shown in Table 4.
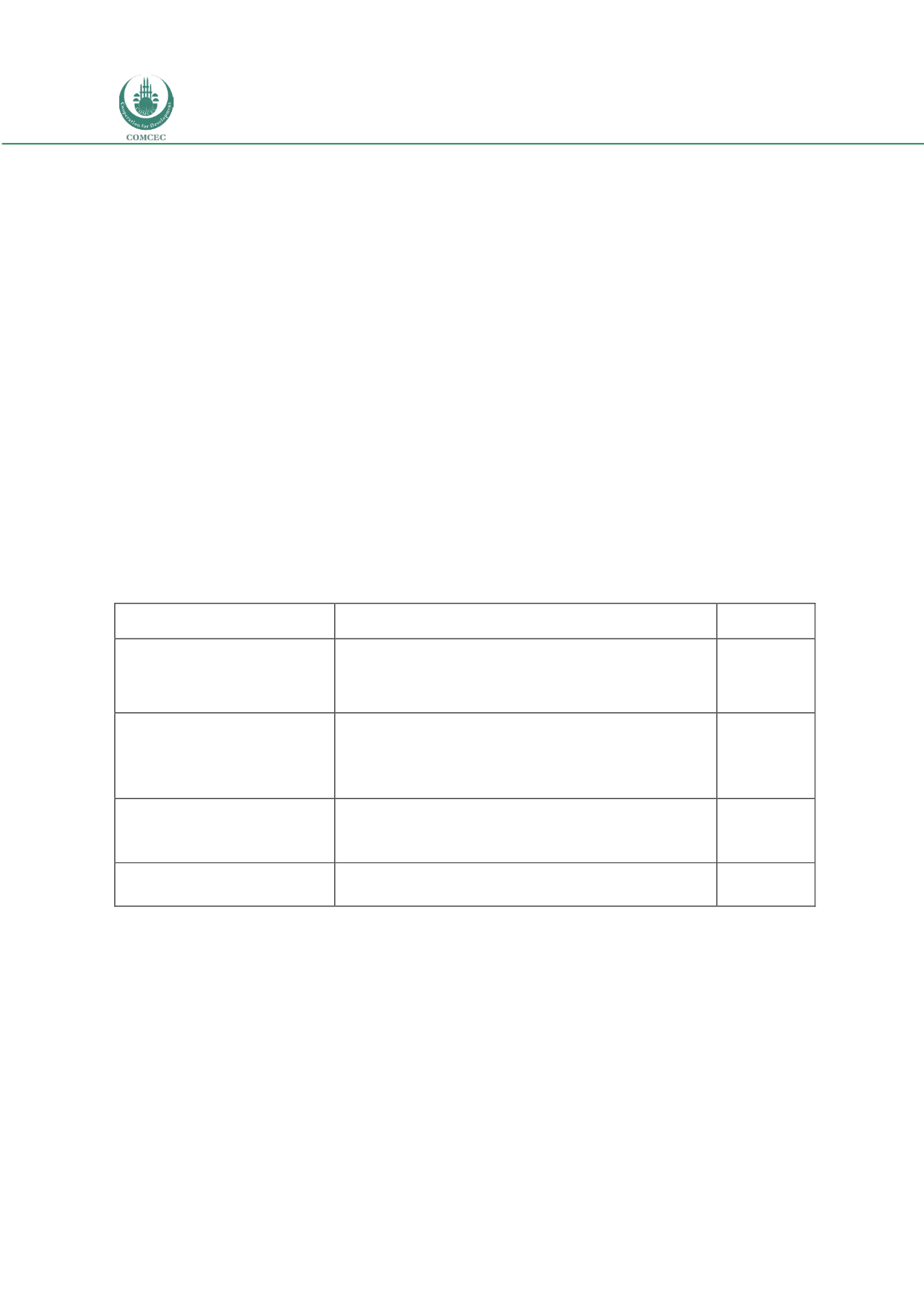
Table 4: Categorization of OIC Member States as of Calendar Year 2014
Categories
Countries
Number of
Countries
OIC-Low income group
1,045 USD or less
Afghanistan, Benin, Burkina Faso, Chad, Comoros, Guinea,
Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Sierra Leone,
Somalia, Gambia The, Togo, Uganda
15
OIC-Lower middle income group
1,046 USD to 4,125 USD
Bangladesh, Cameroon, Cote d'Ivoire, Djibouti, Egypt, Arab
Rep., Guyana, Indonesia, Kyrgyz Republic, Mauritania,
Morocco, Nigeria, Pakistan, Palestine, Senegal, Sudan,
Syrian Arab Republic, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Yemen
19
OIC-Upper middle income
4,126 USD to 12,735 USD
Albania, Algeria, Azerbaijan, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Jordan,
Kazakhstan, Lebanon, Libya, Malaysia, Maldives, Suriname,
Tunisia, Turkey, Turkmenistan
16
OIC-High income group 12,736
USD or more
Bahrain, Brunei Darussalam, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi
Arabia, United Arab Emirates
7
Note: World Bank (2016a) names West Bank and Gaza rather than Palestine.
Source: World Bank (2016a)
Cihak et al. (2012:3) collect measures of financial systems in four broad characteristics: “(a)
the size of financial institutions and markets (financial depth), (b) the degree to which
individuals can and do use financial institutions and markets (access), (c) the efficiency of
financial institutions and markets in providing financial services (efficiency), and (d) the
stability of financial institutions and markets (stability).”
Table 5 shows the selected financial measures within these four characteristics to study how
well financial institutions and markets of OIC Member States perform. Among four
characteristics there are many measures given in World Bank (2016b). Selected measures in