
Improving Public Debt Management
In the OIC Member Countries
29
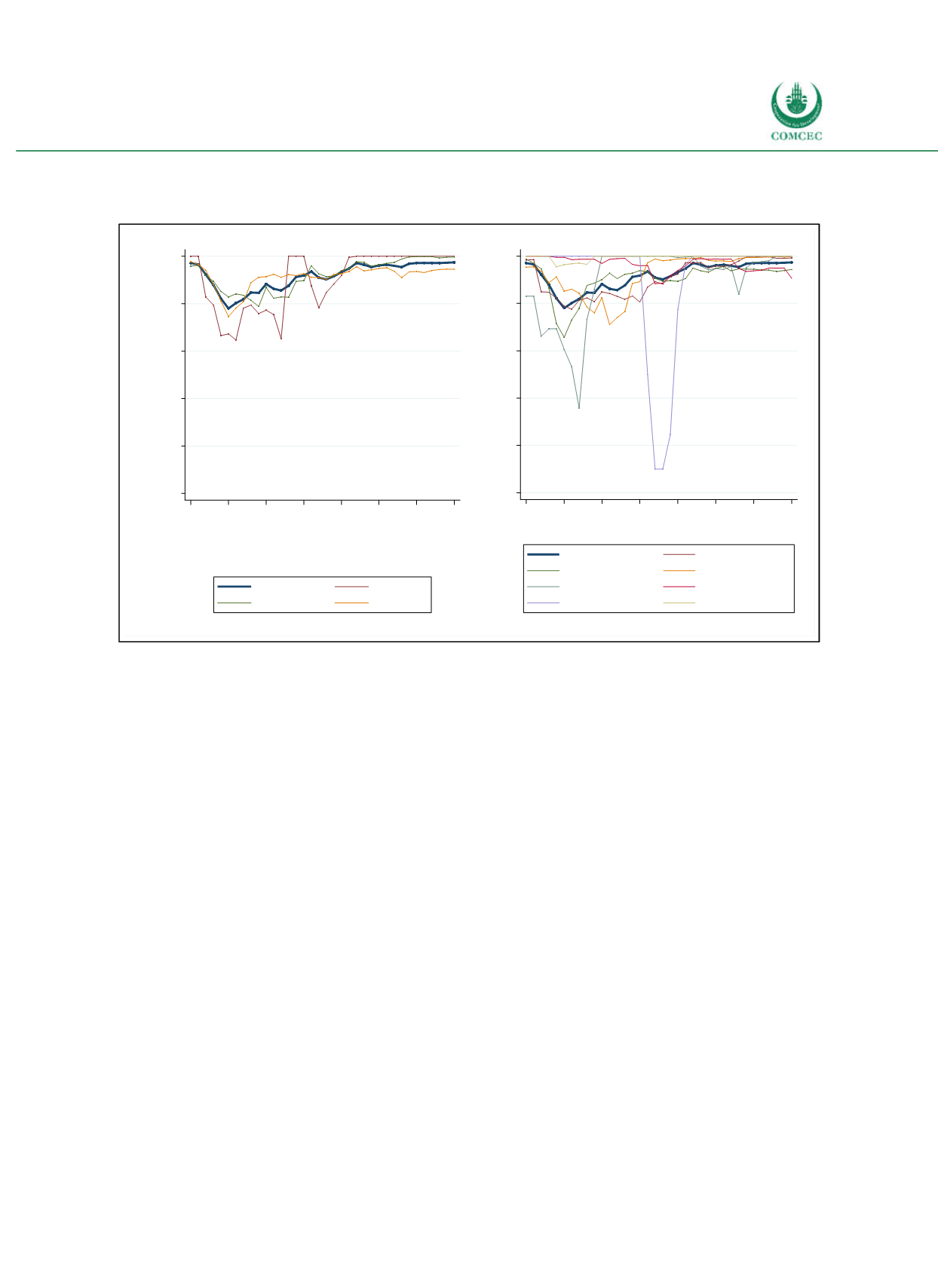
Figure 2-10: Interest Rate Types Worldwide
Share of fixed interest rate credits in total credits (in %)
Sources: BIS Debt Securities Statistics (2016), calculations by the Ifo Institute.
Due to missing data the graphs for Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia & MENA (right panel) cover a shorter time
period only.
Interest rates
Interest rates determine the costs of outstanding debt. Besides the level of debt, interest rates
influence the difference between general and primary public balance. Figure 211 highlights
that financing costs have decreased over time as interest rates follow the global falling trend.
Interestingly, the average interest rate is often lower than the U.S. lending rate to the private
sector. This might be explained be the importance of concessional lending to governments. The
separation between official and private creditors supports this hypothesis: Official creditors
lend at preferential rates. While the difference between private and official creditors was
substantial in the 1980s, it has become less pronounced since then. Lowincome countries face
lower interest rates than middleincome countries, because they have greater access to
concessional lending.
0
20
40
60
80
100
%
1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015
Year
All
Low income
Middle income
High income
0
20
40
60
80
100
%
1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015
Year
All
East Asia, Pacific
Europe, Central Asia
Latin America & Carib.
MENA
North America
South Asia
Sub-Saharan Africa
















