
National and Global Islamic Financial Architecture:
Prolems and Possible Solutions for the OIC Member Countries
23
Stability
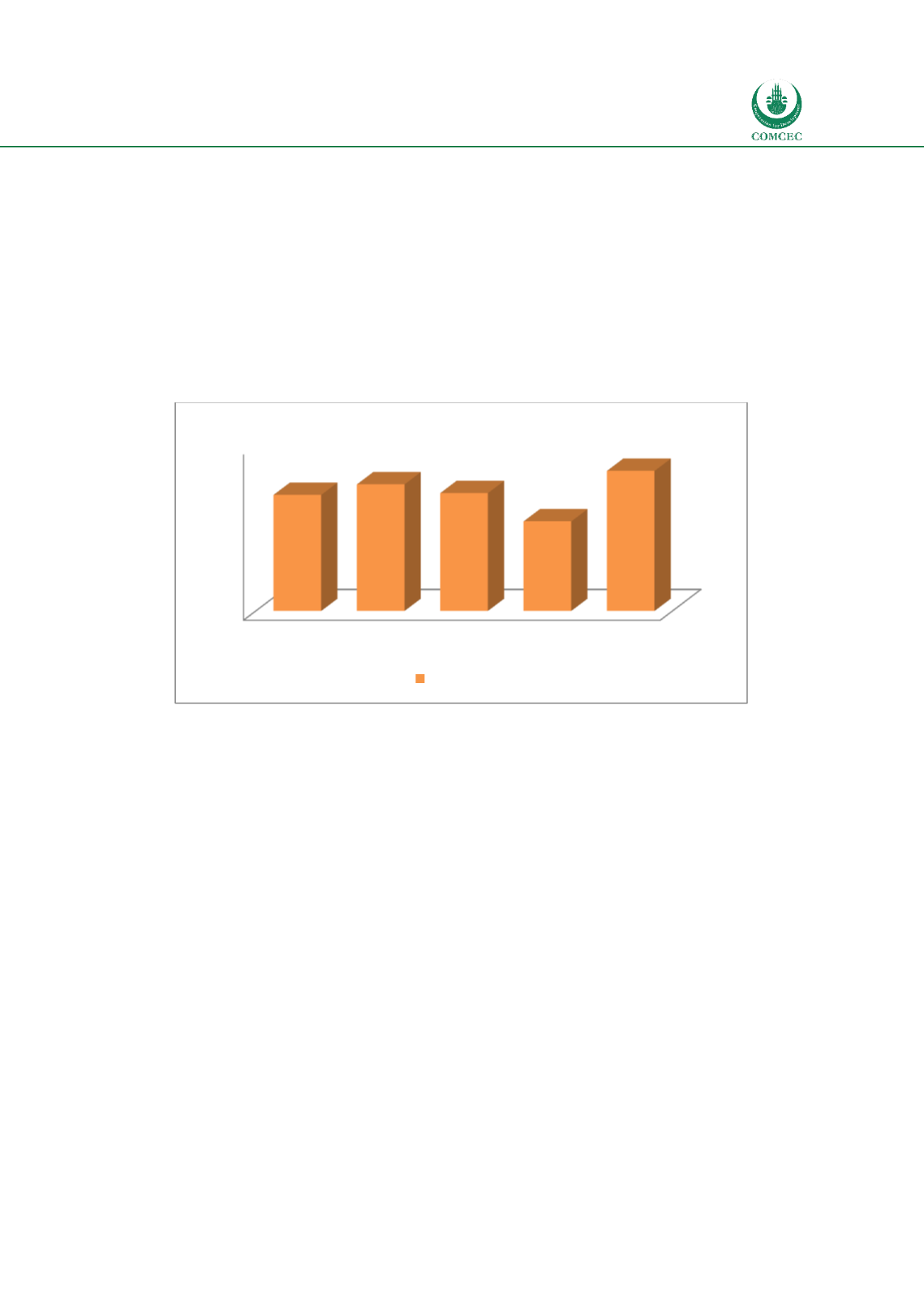
Stability of financial institutions is estimated by Z-score for commercial banks which is
estimated as [ROA + (equity/assets)]/standard deviation of ROA. Z-score shows the relative
strengths of the banking system’s buffers (return and equity) compared to the risks (volatility
of returns) (WB 2016: 160). Chart 2.12 shows that the average Z-score for 54 OIC MCs is 17,
which is the highest compared to all other groupings (average for the world is at 14.1, high
income countries at 15.3, middle income countries at 14.3 and low income countries at 10.9).
Thus, financial institutions in OIC MCs are relatively more stable on the average compared to
their counterparts in the rest of the world.
Chart
2.12: Financial Institutions-Stability
Source: Calculated from World Bank Global Financial Development database
Stability of financial markets is measured by a 360-day standard deviation of the return on the
national stock market index. Chart 2.13 shows that the average stock price volatility of 18 OIC
MCs is 12.2, which is lower than that of world (15.2), high income countries (16.1) and middle
income countries (14.6). Even though the volatility of the stock price is lower for low income
countries (9.4), the information indicates that financial markets in OIC MCs are relatively
stable.
0
5
10
15
20
World
High
Middle
Low OIC
14,1
15,3
14,3
10,9
17,0
Bank Z-score
















