
National and Global Islamic Financial Architecture:
Prolems and Possible Solutions for the OIC Member Countries
195
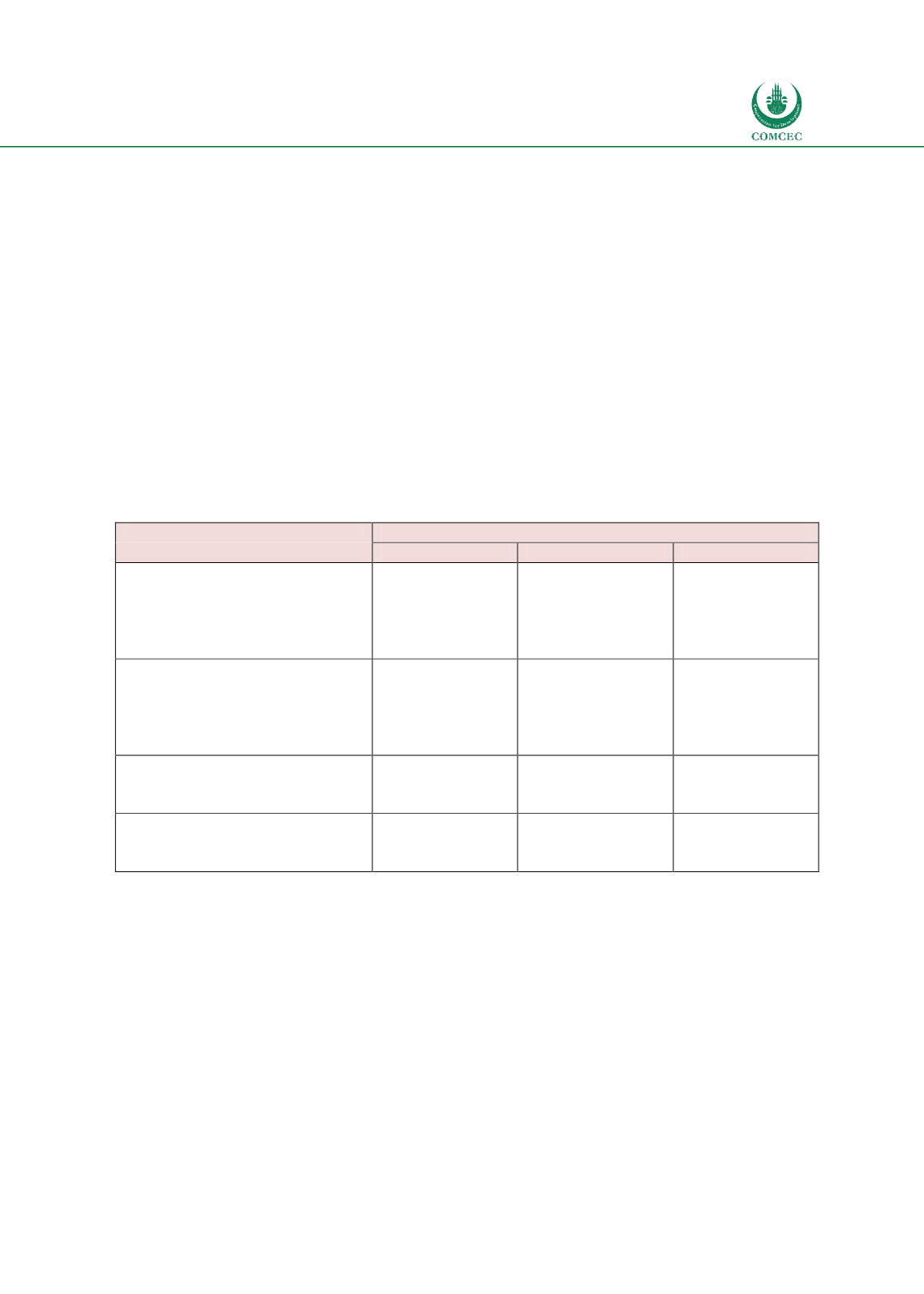
institutions, have a national Shariah board and also have issued Shariah standards/parameters
for Islamic financial transactions. A second group of countries have legal/regulatory
requirements for Shariah governance and a central Shariah authority for certain financial
sectors. Bangladesh, Nigeria, Oman and Sudan fall under this category of countries. Note that
while in most countries the central Shariah board is introduced by the regulators, in Indonesia
it is established by the Ministry of Religious Affairs and in Bangladesh the Islamic banks have
taken this initiative with the encouragement of regulators.
A third group of countries have weaker Shariah governance regimes with only laws and/or
regulations mentioning some sort of Shariah governance but no specific guidelines on their
form or structures. UAE falls in this category. In the last group of countries (such as Saudi
Arabia, Senegal and Turkey) there are no legal/regulatory initiatives for Shariah governance.
Note that there are some sector wise disparities in the Shariah governance regimes for
different sectors. For example, in Bangladesh the banking sector has a central Shariah board,
but the takaful and capital market segments do not have one. Similarly, there is the regulatory
framework for Shariah governance for the takaful sector in Egypt for which there are no
corresponding requirements for the banking and capital market segments in the country.
Table
6.6: Status of Shariah Governance Regimes
Institutional Setup
Financial Sectors
Banking
Takaful
Capital Markets
Legal/Regulatory
requirements
for Shariah governance
Bangladesh,
Indonesia,
Malaysia, Nigeria,
Oman, Pakistan,
Sudan, UAE
Egypt,
Indonesia,
Malaysia, Nigeria,
Oman,
Pakistan,
Sudan, UAE
Egypt, Indonesia,
Malaysia, Nigeria,
Oman, Pakistan,
Sudan
Existence of national Shariah
Supervisory/Advisory Board
Bangladesh,
Indonesia,
Malaysia, Nigeria,
Oman, Pakistan,
Sudan
Indonesia,
Malaysia, Nigeria,
Oman,
Pakistan,
Sudan
Indonesia,
Malaysia, Oman,
Pakistan, Sudan
Shariah standards/parameters
Indonesia,
Malaysia,
Pakistan
Indonesia,
Malaysia, Pakistan
Indonesia,
Malaysia,
Pakistan, UAE
No Shariah related issues in laws
and regulations
Egypt,
Saudi
Arabia, Senegal,
Turkey
Bangladesh, Saudi
Arabia,
Senegal,
Turkey
Bangladesh, Saudi
Arabia, Senegal,
Turkey
6.1.4.
Liquidity Infrastructure
The liquidity infrastructure for Islamic finance would include appropriate Shariah complaint
liquidity instruments and money markets in the private domain and the lender of last resort
facility provided by the central bank. The case studies show variation in the liquidity
infrastructure. A sound liquidity infrastructure for Islamic finance can be found in Indonesia,
Malaysia, Pakistan and Sudan where all three elements of liquidity infrastructure identified
above are present.
















