
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
59
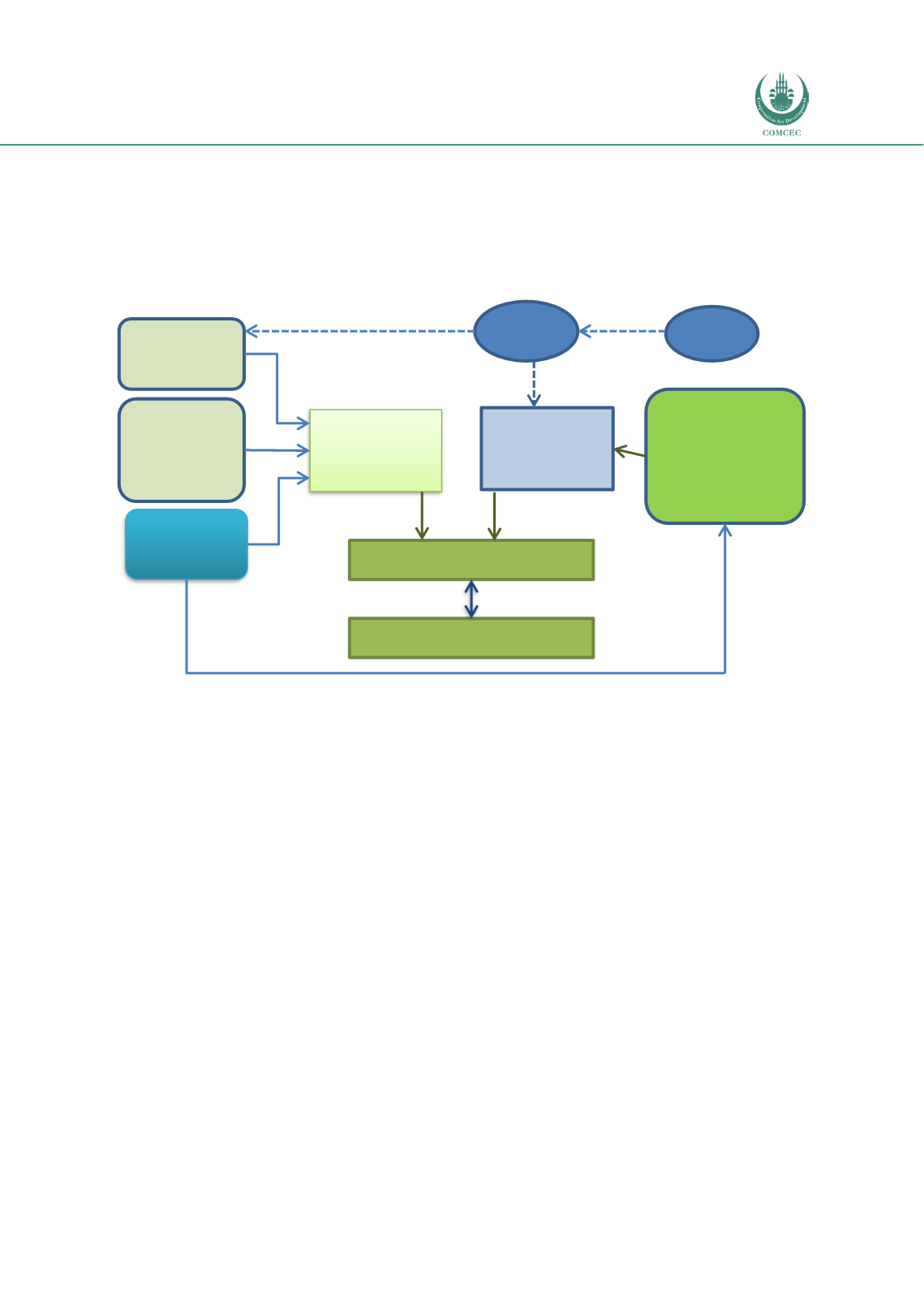
The takaful components came in the form of guarantees for USD 427 million provided by MIGA
to all investors (USD 5 million to DP World and $422 million to the financiers) against risks of
breach of contract, restrictions on currency transfers, expropriation, and civil disturbance and
war. Islamic Corporation for the Insurance of Investment and Export Credit (ICIEC) in turn
provided reinsurance for USD50 million to MIGA.
Chart 3.12: Doraleh Container Terminal Financing Structure
Source: World Bank et. al. (2017) and MIGA (2008)
3.6.
Islamic Capital Markets/
Sukuk
and Infrastructure Financing
Instead of getting direct financing from financial institutions, another option for raising funds
for infrastructure is to use the capital markets by issuing sukuk. AAOIFI identifies various
types of
sukuk
that can be classified broadly as being based on assets, debt, equity, and
services. Asset based
sukuk
include certificates issued against an asset (
ijarah
sukuk
)
or the
usufructs of an asset (
sukuk manfah
). While
ijarah
sukuk
are issued against an existing tangible
asset, leased asset, and/or promise of leasing an asset in the future,
manfah
sukuk
are issued
by owners of the usufruct of existing or future assets. Investors in these
sukuk
become owners
of the assets in the former and usufructs in the latter. Debt-based
sukuks
arise from sale
transactions that create debt. Funds raised by
murabahah sukuk
are used to purchase assets or
goods that are then sold at a mark-up to the obligor. Similarly,
istisna sukuk
are used to raise
funds that are used in the construction of real estate. The investors become the owners of the
real estate upon completion and lease it to the obligor against periodic rental payments.
Equity-based
sukuks
can take the form of mudarabah or musharakah whereby partnership is
formed between the investors and the obligor. Investors of
mudarabah sukuk
participate in a
project by contributing funds and then appointing the Project Company as a manager. The
profit of the project is shared by the investors and obligor at an agreed upon ratio.
Musharakah
sukuk
is similar to mudarabah sukuk with the difference that investors have a say in the
management of the project. Under the agency-based
sukuks
such as
wakala
, the investors
DP World
Djibouti FZCO
Government
of Djibouti
Islamic Financiers
•
Dubai Islamic
Bank
•
Standard
Chartered
BankWestLB AG
Port
Autonome
International
de Djibouti
Financiers
Investment agent
Doraleh
Container
Terminal S.A.
(Project
Company)
DCT Musharakah JV
Doraleh Container Terminal Project
Owns
Concession
Owns
Owns
Contributes
MIGA
ICIEC
Equity
Guarantee
Musharakah
financing
Guarantee
Reinsurance
Direct Agreement
















