
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
62
Case Study: Composite Mudarabah-Ijarah Sukuk
16
A composite
mudarabah-ijarah sukuk
was issued in Malaysia by Projek Lintasen Shah Alam
Bhd. (PLSA) to raise RM 745 million to finance the 14.7km Lebuhraya Kemuning-Shah Alam
highway in 2008. PLSA was responsible for the design, construction, management and
maintenance of the toll road for a 40-year concession period given by the Federal Government
of Malaysia. Structured by RHB Islamic Bank Berhad and RHB Investment Bank Berhad, PLSA
issued two
sukuks
to finance the project, one based on
mudarabah
and the other on
ijarah
. The
total value of the
mudarabah
sukuk
was RM 415 million (USD 118 million) with a tenor of a
maximum of 29 years. It was used to raise funds for the project and pay for the existing bridge-
financing facilities. The
mudarabah
sukuk was structured as a joint venture in the toll-road
project between PLSA (Project Company) and the investors with the former acting as the
manager (
mudarib
). The funds provided by
sukuk
holders (RM 415 million) was used to
construct the highway and cover working capital needs during the operation stage. With the
sukuk
holders getting a profit share of 90% upon completion of the toll road, the expected rate
of return for the investors was around 7% per annum.
The
ijarah
sukuk
was worth RM 330 million (USD 94 million) with a maturity of 19 years to
raise additional funds from other investors. The
ijarah
sukuk
used the toll road as the
underlying asset which was transferred to
sukuk
holders through an SPV. The
sukuk
holders
then leased the road back to the mudarabah venture for 19 years in return for periodic rental
payments. The investors received the rental payments from the beginning of the construction
period under the principle of the forward lease (
ijarah mausufah fil dhimmah
). Since the rental
payments include the amortised capital component, the toll road will be transferred back to
the Joint Venture at the nominal value of RM1 at the end of the lease period. Having equity-like
features,
mudarabah sukuk
investors had lower priority than
ijarah sukuk
holders in case of
default or bankruptcy. RAM Ratings Services Bhd gave a rating of A3 to the former
sukuk
and
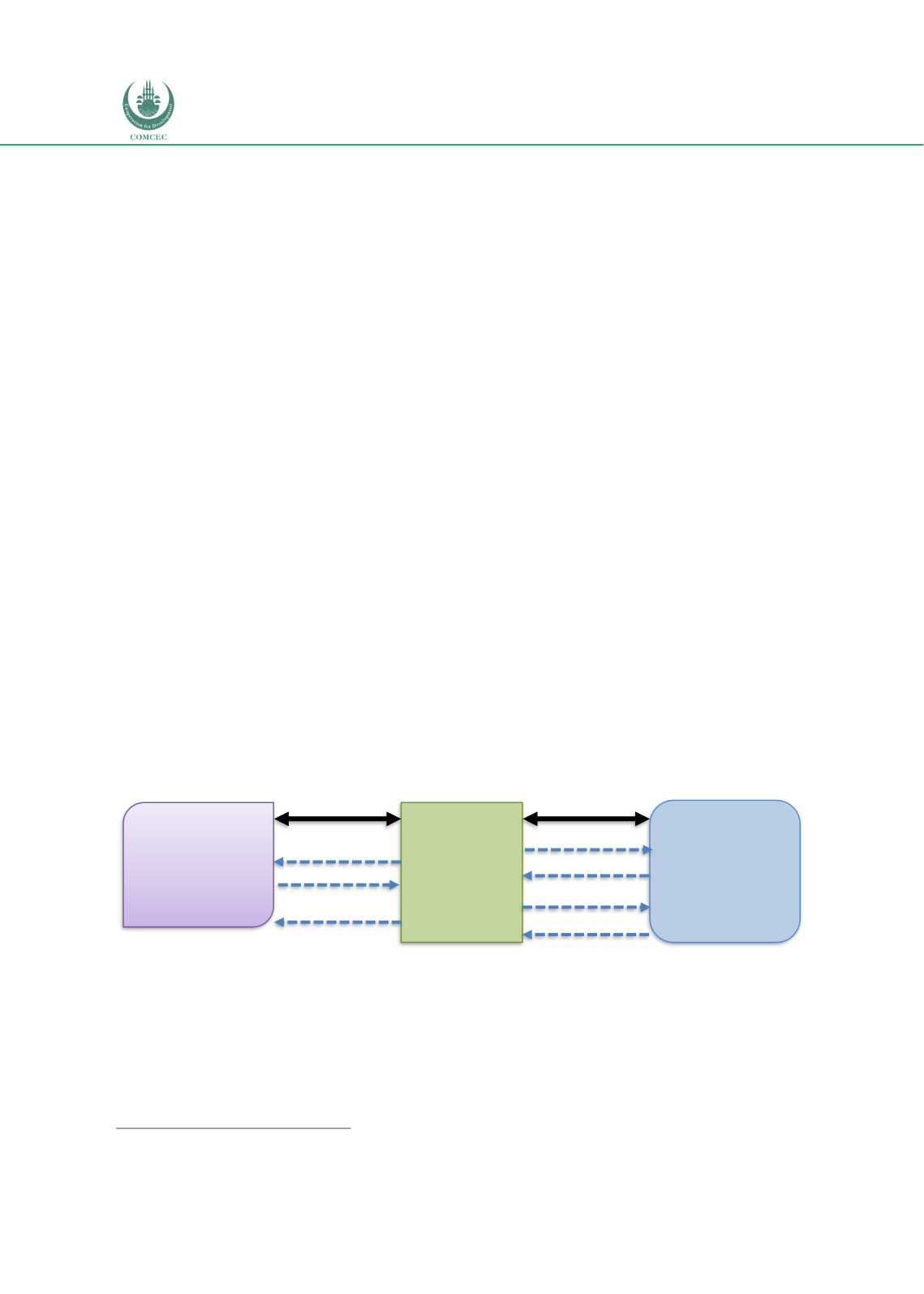
A1 to the latter (RAM 2009). The basic structure of the PLSA composite
sukuks
is shown in
Chart 3.15.
Chart 3.15: Composite Mudarabah-Ijarah Sukuk
Source: Adapted from Ahmed (2009a)
16
The case study has been prepared by the author based on Ahmed (2009a) and RAM (2009)
Project
Company
Sukuk
Ijarah
Investors
Sukuk Mudarabah
Investors
Ijarah
Mudarabah
2
1a
1b
3a
4b
3b
4a
1a and 1b—Issue of mudarabah sukuk & receipt of funds
2—Distribution of periodic profit
3a and 3b—Sale of ijarah assets & receipt of price
4a and 4b—Lease of assets & rental payments
















