
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
149
Table 4.5.
3
: Islamic Banks Asset Structure and Financing of the Infrastructure Sector in
Sudan (Q1 2018)
(SDG million)
Total Islamic Banking Assets
Asset Composition
SDG
(Million)
% of
total
Total Shariah-compliant
financing (excluding
interbank financing)
119,122.0
40.5%
Sukūk holdings
20,467.0
7.0%
Other Sharī`ah-
compliant securities
0
0.0%
Interbank financing
0
0.0%
All other assets
154,315.0
52.5%
Total assets
293,904.0
100%
Infrastructure Financing by Islamic Banks
Financing going to
infrastructure
SDG
(million)
% of
total
Electricity, gas, steam and
air-conditioning supply
1,788.0
0.61%
Water supply; sewerage
and waste management
0
0.00%
Transportation and
storage
8,765.0
2.98%
Information and
communication
0
0.00%
Education
0
0.00%
Human health and social
work activities
0
0.00%
Total infrastructure
10,553.0 3.59%
Source: IFSB Prudential and Structural Islamic Financial Indicators
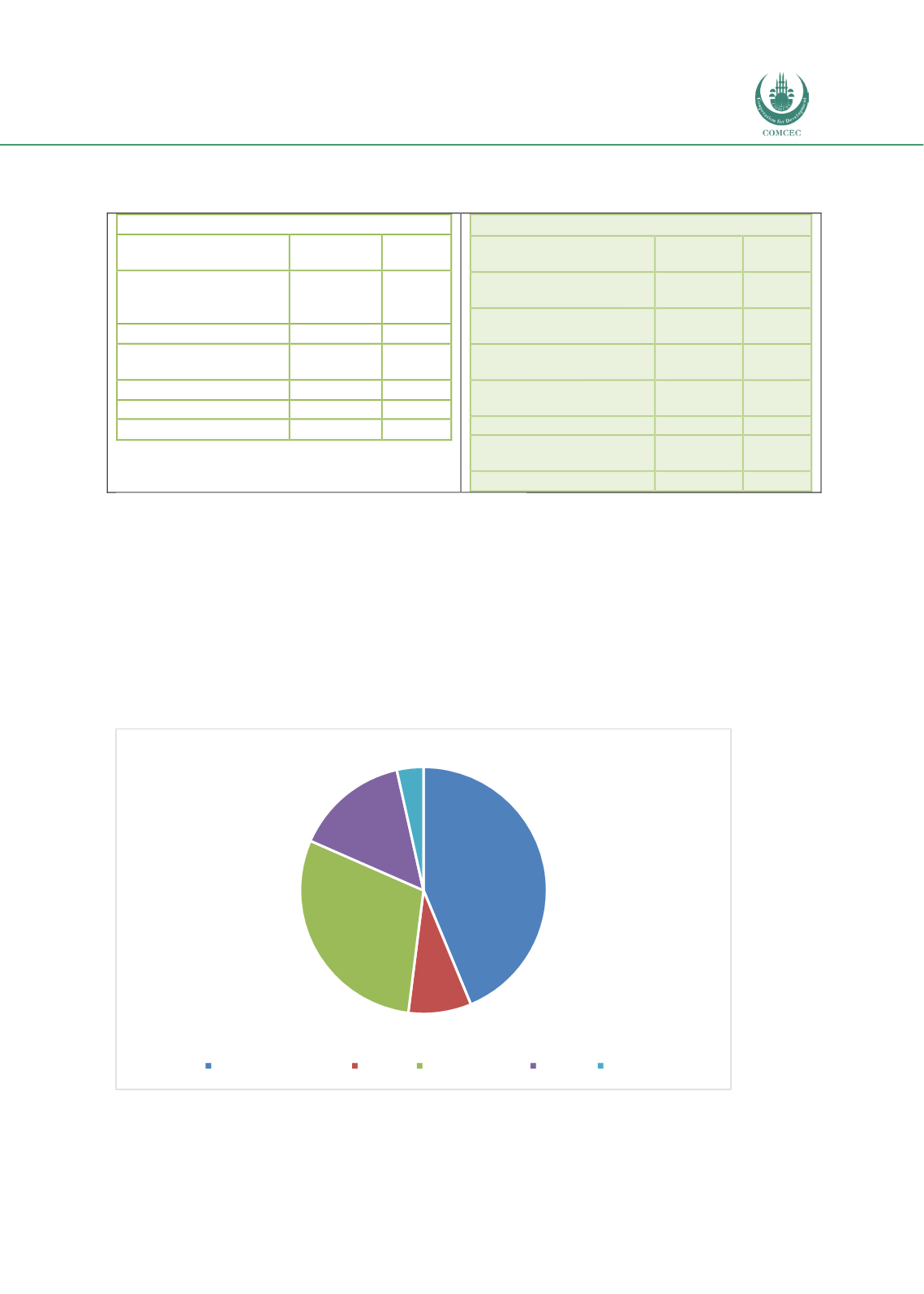
Chart 4.5.5 shows the distribution of assets for the insurance sector in Sudan. Lands and real
estate investments represent 43.7% out of the total insurance sector investment portfolio in
2017 while stocks, Sukuk, and bank deposits represent 14.9%, 8.2%, and 29.6% respectively in
the same year. This means that 96.4% of the insurance investment portfolio is invested in
liquid assets. Although this kind of investment diversification is healthier for the insurance
sector and strengthens its consolidated balance sheet, freezing this huge fund in liquid assets
rather than employing it in reshaping the distribution of general insurance to serve the real
economic sector lessens the contribution of the insurance sector to the national economy.
Chart 4.5. 5: Distribution of Insurance Sector Investments in Sudan (2017) (%)
Source: Insurance Supervisory Authority (ISA), Annual Report 2017
43.7%
8.2%
29.6%
14.9%
3.5%
Lands & Real estate Sukuk Bank Deposits
Stocks
Others
















