
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
148
4.5.5.2.
Islamic Financial Institutions
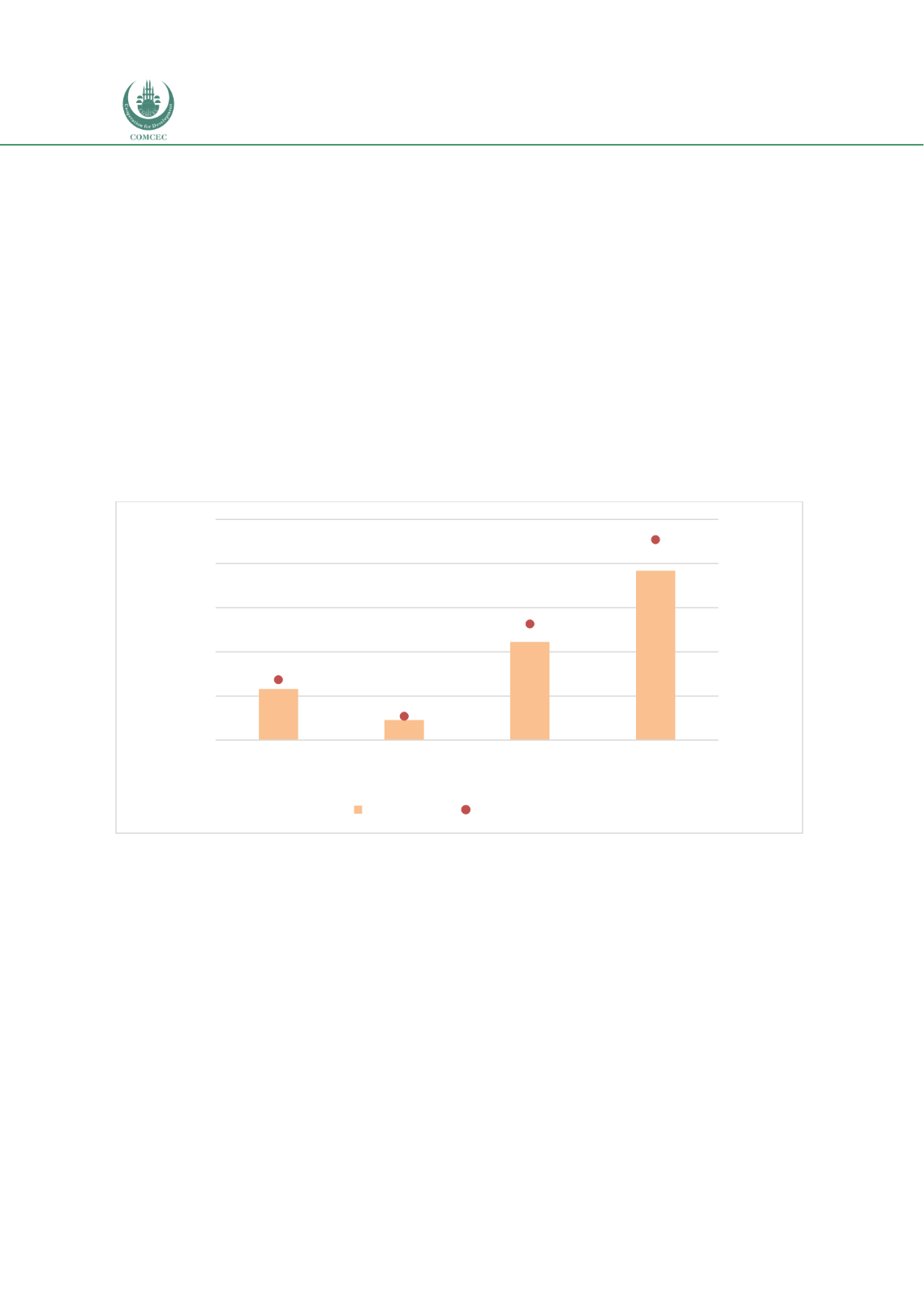
Chart 4.5.4 shows the banks’ direct and indirect financing for the infrastructure sector in
Sudan. Out of a total assets of SDG 211.246 billion, an investment of SDG 5.795 billion (2.7% of
the total) was made in the transportation and storage sector and an SDG 2.279 (1.1% of the
total) investment was made in the mining and energy sector. The banks held government
sukuk and GICs worth SDG 11.126 billion, constituting 5.3% of total banking assets. The issuer
of government sukuk and GICs, the Sudan Financial Services Company (SFSC), claims that the
funds raised are invested in infrastructure and development project financing such as health
projects, hostel construction, river transportation, railways, and other infrastructure projects
in Sudan's regional States (SFSC, 2018). Thus, the bulk of the banks’ infrastructure funding is
done indirectly through sukuk and GICs, which represent 58% of the total bank infrastructure
financing. It should be noted that while the direct financing by banks in the infrastructure
sector is illiquid, the indirect financing through sukuk and GICs makes the investments liquid
since these instruments can be sold on the stock exchange.
Chart 4.5. 4: Bank Infrastructure Financing: Sudan (2017) (SDG million)
Source: CBOS Annual Reports (2017)
The direct investments in the infrastructure sector by Sudanese banks in Q1 2018 are shown
in Table 4.5.3. The results in the table confirm those reported in Chart 4.5.4, showing that only
3.59% of the total assets are invested in the infrastructure sector.
5,785.3
2,279.9
11,126.1
19,191.3
2.7%
1.1%
5.3%
9.1%
0%
1%
2%
3%
4%
5%
6%
7%
8%
9%
10%
0
5,000
10,000
15,000
20,000
25,000
Transportation &
Storage
Mining & Energy
Sukuk & GICs Total Infrastructure
Financing
% of total assets
SDG (Million)
SDG (million)
% of total assets
















