
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
130
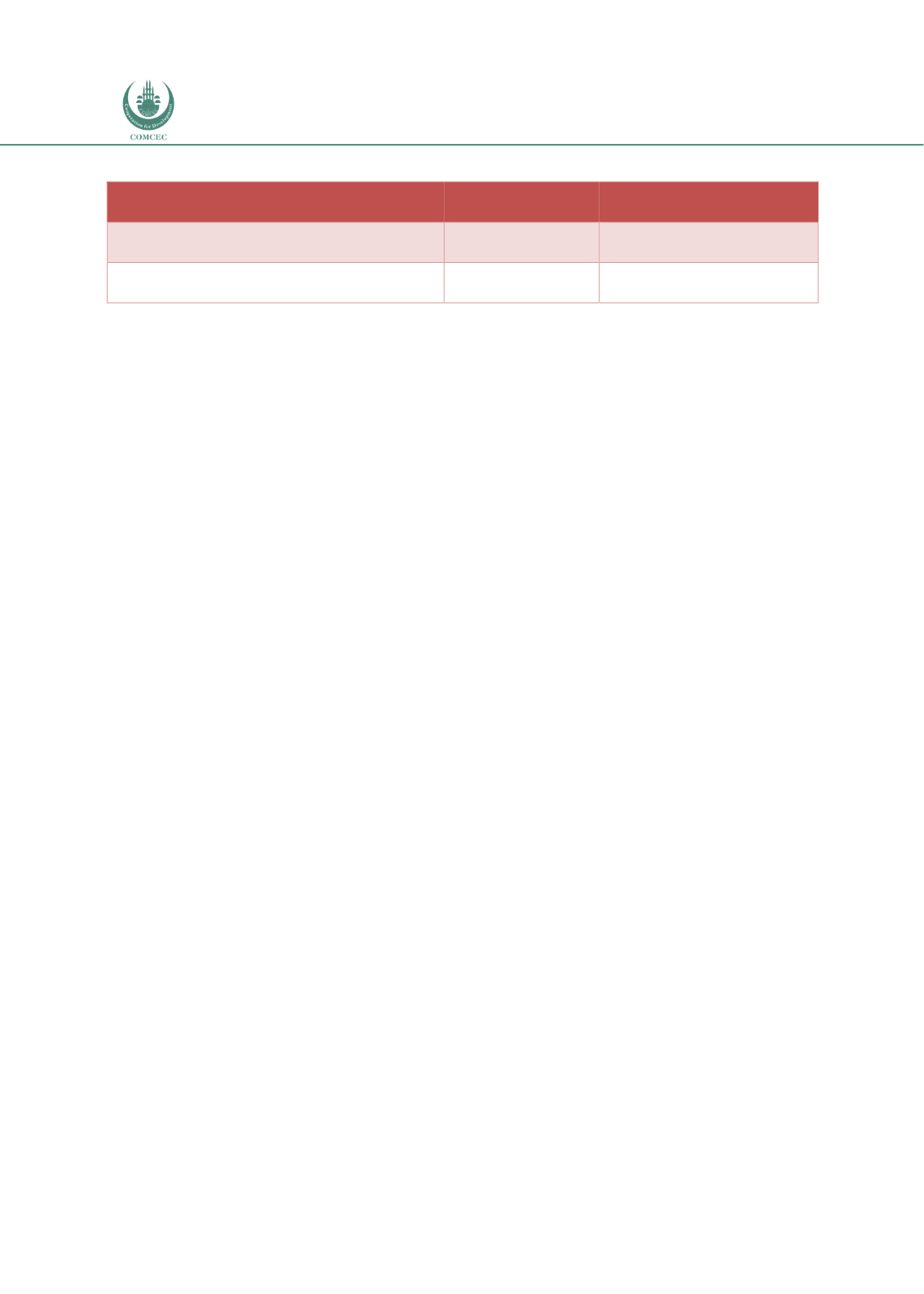
Table 4.4. 2: Targets of Vision 2030 in Introducing PPP Projects
2016
2020 Target
Total no. of PPP investments
0
14
Total value of PPP investments
0
SAR 24-38 billion
Source: Saudi Vision 2030: Privatization Program (Delivery Plan 2020)
.
Initiatives of the Public Investment Fund Program (2018-2020) as part of Vision 2030 include
developing infrastructure projects and undertaking certain giga-projects. The former includes
investments in air transport infrastructure hubs (Developing King Khalid International Airport
City in Riyadh and King Abdulaziz International Airport City in Jeddah), social infrastructure
(establishing a Housing Community Development Company), and infrastructure to facilitate
pilgrimage (developing the Hajj and Umrah facilities and capacity in Makkah and Madinah).
4.4.4.
The Legal and Regulatory Framework for Infrastructure Investments
While Sharia is the main source of law in Saudi Arabia, many economic and financial activities
are governed by legislations in the form of royal decrees, royal orders, ministerial resolutions,
circulars, and resolutions by the Council of Ministers
(Jaballah et al., 2018). Since the
government of Saudi Arabia was the main player in the development of infrastructure in the
past, the country did not have any laws related to PPP until very recently. As indicated, key
features of Vision 2030 include diversifying the economy to non-oil sectors and enhancing the
role of the private sector in the economy, including the infrastructure sector. In order to
achieve these targets, the National Centre for Privatization & PPP (NCP) initiated the
Privatization Program that has three strategic pillars.
A key strategic pillar to promote private sector involvement in infrastructure is to develop the
general legislative frameworks for Private Sector Participation (PSP). The first step in this
regard was the issuance of Resolution No. 665 on 8/11/1438H by the Council of Ministers
which approved the Rules of Conduct of the Supervisory Committees of PSP-targeted sectors
(GSA 2018) The resolution also instructed the National Centre for Privatization & PPP (NCP) to
come up with a draft law that encompasses all rules governing PSP. Accordingly, NCP
published a draft of the
Private Sector Participation Law
for public consultation to address the
challenges and legislative gaps that exist in the regulatory environment for private sector
involvement in the economy (Government of Saudi Arabia, 2018). When the PSP Law was
finally approved in accordance with the legislative procedures, it would not prejudice the
existing PSP projects or any decisions made by the Supervisory Committees. This is important
in order to preserve the laws governing the land and not hinder the current infrastructure
development programmes in the Kingdom. The NCP Board of Directors also issued the
Privatization Projects Manual
through resolution No. (2/5/2018) dated 03/08/1439H and
The
Rules Governing the Work of the Supervisory Committees, their Teams and Advisors
through
resolution No. (3/5/2018) dated 03/08/1439H.
There are laws and regulations that govern the specific infrastructure sectors in Saudi Arabia.
The Electricity & Cogeneration Regulatory Authority (ECRA) (ECRA 2005) was established
through Royal Decree No. M/56 dated 20th Shawwal 1426 / 22/11/2005 with the law aiming
at promoting consumer-oriented electricity services and also protecting consumer rights as
















