
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
134
A key institution that is involved in the infrastructure sector is the Public Investment Fund
(PIF), the sovereign wealth fund of the country that has invested through many infrastructure-
related companies. Infrastructure-related companies owned by PIF include power, water
utility and sewerage (Marafiq, NWC, Saudi Electric Company), Telecommunications (Saudi
Telecomm Company) and transportation (Saudi Railway SAR). While the bulk of the
government-linked companies get their equity capital from the government, they can raise
further funds through capital markets by issuing sukuk.
4.4.5.2. Islamic Banks
The role of Islamic banks in financing the infrastructure sector can be seen by examining the
composition of the asset side of banks. Table 4.4.3 shows the asset contribution and
composition of the Saudi Arabian Islamic banking sector for the Q1 2018 period. Of the total
assets of SAR 596.744 billion (USD 159.131 billion), the total Shariah-compliant financing
(excluding interbank financing) is SAR 397,266.7 million constituting 66.6% of the total assets.
The Islamic banks held sukuk worth SAR 51.401 billion which is 8.6% of the total assets. The
table shows that, of the Shariah-compliant financing, only SAR 22.332 billion (USD 5.955
billion), equivalent to 3.74% of the total assets, was used in the infrastructure sector. Among
the infrastructure sectors that were financed, electricity, gas, steam and air-conditioning
supply received the highest financing of SAR 11.97 billion followed by SAR 10.31 billion for
transportation and storage and SAR 48.5 million for the health and social work sector.
However, Islamic banks did not provide any financing for the water supply, sewerage and
waste management, information and communication, and education sectors.
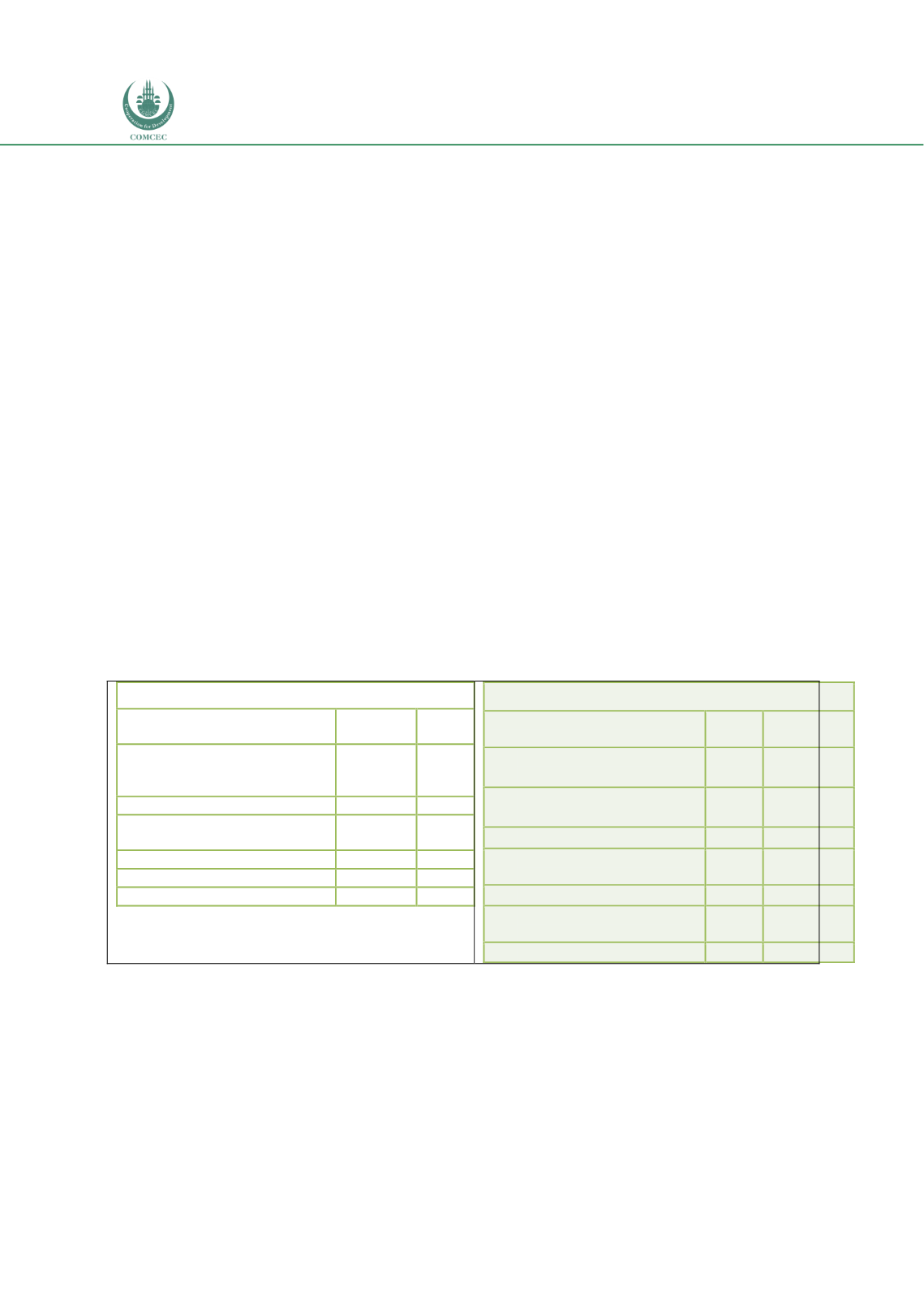
Table 4.4. 3: Islamic Banks Assets Structural Composition and Financing of Infrastructure
Sector (Q1 2018)
Total Islamic Banking Assets
Asset Composition
SR
(million)
% of
total
Total
Shariah-compliant
financing (excluding interbank
financing)
397,266.7
66.6%
Sukūk holdings
51,401.4
8.6%
Other
Sharī`ah-compliant
securities
4,935.4
0.8%
Interbank financing
38,531.6
6.5%
All other assets
104,609.2
17.5%
Total assets
596,744.3
100%
Infrastructure Financing by Islamic Banks
Financing going to infrastructure
SR
(million)
% of
total
Electricity, gas, steam and air-
conditioning supply
11,973.1 2.01%
Water supply, sewerage and
waste management
0.0
0.00%
Transportation and storage
10,311.3 1.73%
Information
and
communication
0.0
0.00%
Education
0.0
0.00%
Human health and social work
activities
48.5
0.01%
Total Infrastructure
22,332.9
3.74%
Source: (IFSB, 2018),
https://www.ifsb.org/psifi_03.php4.4.5.3. Capital Markets
As shown in Chart 4.4.9, the sukuk sector in Saudi Arabia is relatively small compared to the
Islamic banking sector. The total number and value of debt and sukuk instruments during
2016 and 2017 that are listed in the CMA are shown in Chart 4.4.9. While in 2016 a total of 31
instruments were offered worth SAR 21.35 billion, in 2017 28 instruments worth SAR 86.25
billion were listed with the CMA. As noted before, the bulk of the domestic sukuk was issued by
the government to finance budget deficits.
















