COMCEC Trade Outlook 2019
6
downward trend is expected to continue in 2019, with trade projected to grow by just 2.6 per
cent
4.
Heightened trade tensions cannot be the only cause of the trade slowdown in 2018 but they
undoubtedly played a significant role as slower trade growth coincided with announced or
anticipated trade actions, such as tariff raising, by governments.
Trade and output were also influenced by temporary
shocks, such as the federal government shutdown in the
United States and production problems in the automotive
sector in Germany towards the end of the year. These
incidents were likely to have transitory effects, causing
consumers and businesses to postpone purchases and
production decisions rather than cancelling them
outright
5.
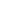
Figure 4: Tariffs and Non-tariff Measures
Source: Reprinted from” Evolution of the International Trading System and Its Trends from a Development
Perspective” UNCTAD, Trade and Development Board, TD/B/64/5, Sixty-fourth session, 3 July 2017. Retrieved
from
http://unctad.org/meetings/en/SessionalDocuments/tdb64d5_en.pdf.
There have been some emerging patterns shaping the global trading environment recently.
First
trend
is the proliferation of non-tariff barriers. The Figure above which is taken from UNCTAD
(2017) provides data for 1995-2015 period and illustrates that while tariffs have declined
considerably in the 2000s, little progress was achieved in terms of further declines in tariffs
since the global crisis.
The number of non-tariff measures continue to rise especially in the aftermath of the crisis.
Slower pace of trade liberalization and increased protectionist measures are considered among
factors which constrain world trade. According toWTO
6
, WTOmembers introducedmore trade-
4 https://www.wto.org/english/res_e/booksp_e/anrep_e/anrep19_chap1_e.pdf5
World Trade Statistical Review 2019
, https://www.wto.org/english/res_e/statis_e/wts2019_e/wts2019chapter03_e.pdf“
Heightened trade
tensions cannot be the
only cause of the trade
slowdown
in
2018”