Increasing Broadband Internet Penetration
In the OIC Member Countries
101
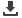
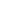
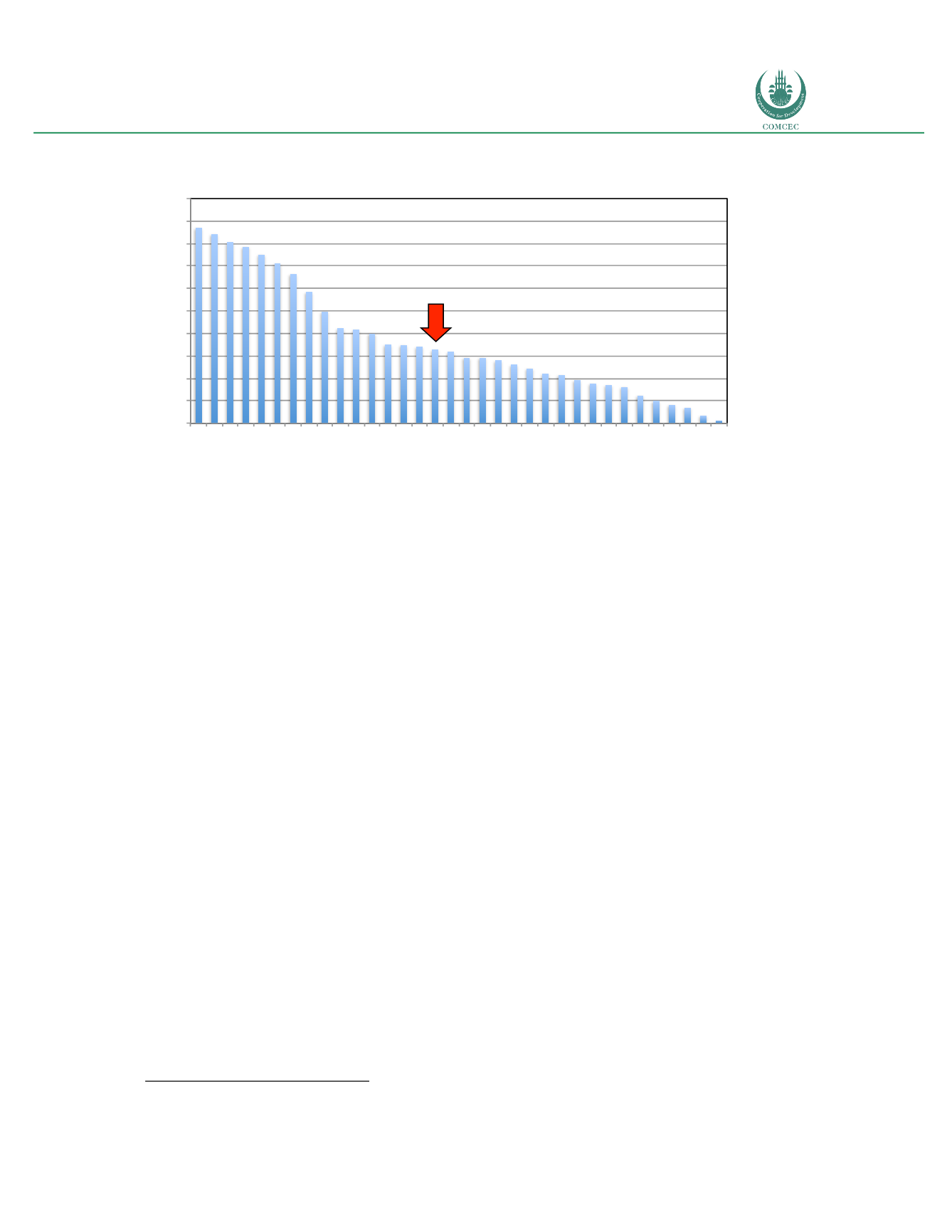
Figure 29: Sub-Saharan Africa: Telecommunications Affordability Index (2014)
Source: Telecom Advisory Services analysis
The intermediate position of Cote d’Ivoire among its regional peers would indicate that the
pricing of telecommunications services represents a barrier to adoption. In general terms, two
policies can serve as levers to improve the affordability of broadband (see Katz and Taylor,
2014): (1) reduce taxes born by consumers on the purchase of broadband; and (2) increase the
level of competitive intensity to stimulate price competition. Along these lines, with the
objective of reducing the consumer broadband acquisition cost, the government has enacted in
2016 an exemption of import duties and VAT for customer terminal equipment (including
smartphones, tablets, modems and routers). Under this program, the price of a low-end
smartphone starts at CFA 20,000 (US$ 33). This policy will remain in place until 2018. This
measure is expected to greatly facilitate broadband adoption. As a demonstration of the
policy’s positive effect, with 10 months into the program, subscriptions for Orange have
jumped from 80,000 sold in 2015 to an estimated 200,000 in 2016.
41
Another program aimed at dealing with the affordability barrier, now under development,
entails lowering the price of broadband connections. A benchmarking study conducted by the
regulatory authority indicated that the price of broadband service in Cote d’Ivoire is higher
than that of Senegal, a country considered as having similar socio-economic characteristics.
The results of the study are expected to be reported to the operators by the end of 2016, and
an affordability price point will be set up, specifying the cost of broadband service. In response
to this, the operators are expected to provide policy alternatives and suggestions, which would
in turn be used to design the program.
41
Source: field trip interviews.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
South Africa
Swaziland
Namibia
Gabon
Botswana
Eq. Guiea
Ghana
Nigeria
Angola
Zambia
Guinea
Kenya
Mozambique
Tanzania
Cameroon
Cote d'Ivoire
Lesotho
Mauritania
Uganda
Liberia
Sierra leone
Congo
Burkinfa Faso
Rwanda
Madagascar
Gambia
Zimbabwe
Mali
Togo
Congo DemocraVc Rep.
Chad
Niger
Benin 13.03
Malawi