
Improving Public Debt Management
In the OIC Member Countries
146
of sovereign
sukuk
is expected to create a benchmark for the issuance of corporate
sukuk
and is
planned to increase flexibility to the funding of strategic projects supporting the
industrialization of the country (NBK 2016). This statement, however, has not been followed
by implementation action up till now.
Domestic debt market
Kazakhstan’s general government debt is largely domestic debt, whose share remained
relatively constant between 2006 and 2015 at around 74% (see Figure 430). Domestic
general government debt of Kazakhstan can be categorized into longterm treasury liabilities
(59%), longterm treasury balanced liabilities (33%) and mediumterm treasury liabilities
(8%). The United Pension Fund (almost $20 billion) has been used up to more than 45% to
purchase bonds issued by the MoF.
Foreign borrowing
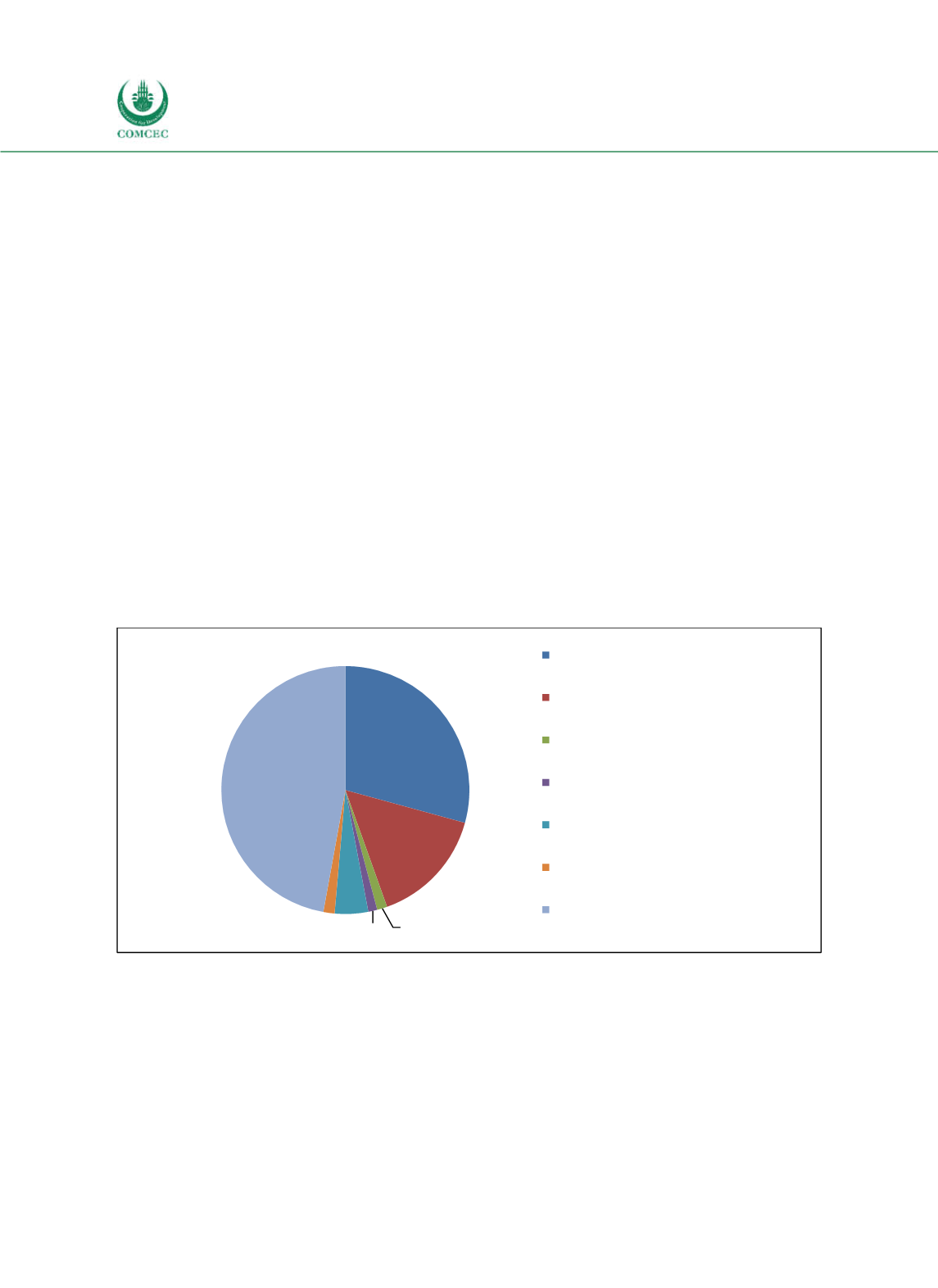
The largest share of external debt (47%) consists of international bonds issued at the
Eurobond market (see Figure 432). With a share of 29%, the International Bank for
Reconstruction and Development represents the secondlargest part of external debt. Other
creditors are the Asian Development Bank (15%), the Japan International Cooperation Agency
(5%), the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (1%) and the Islamic
Development Bank (1%). The share of external debt owed to foreign commercial banks equals
2%.
Figure 4-32: Kazakhstan – Creditor Structure of External Public Debt (2016)
Sources: NBK (2016), calculations by the Ifo Institute.
External debt, which is dominated by longterm debt (99% in 2016), is predominantly
denominated in U.S. Dollar, whose share increased between 2008 and 2014 from around 42%
to 96%. The reason for the high U.S. Dollar share is a policy to lend predominantly from
International financial Institutions which is cost efficient and risk reducing. Over the same
period, the share of Pound Sterling in external debt decreased from 53% to around 3%. The
remainder represents SDRs and other currencies, including but not limited to Euro (Figure 430).
29%
15%
1% 1% 5% 2%
47%
International Bank for Reconstruction and
Development
Asian Development Bank
European Bank for Reconstruction and
Development
Islamic Development Bank
Japan International Cooperation Agency
Foreign commercial banks
Eurobonds
















