
Risk Management in
Islamic Financial Instruments
111
The Rate of return, which is directly connected to mark-up risk, has severe influence on bank
deposits in IFIs. According to Figure 5.1, 39 percent of the respondents believed that lower
rates of return in IFIs, compared to conventional banks, would force a major portion of the
deposit-holders to withdraw their funds. This phenomenon is also connected to ‘displaced
commercial risk’. We conducted an extended analysis by decomposing these problems into
regional groups. Regulatory and lack of understanding problems are closely connected to
developing MENA countries and South Asian countries.
5.3 RISK REPORTING
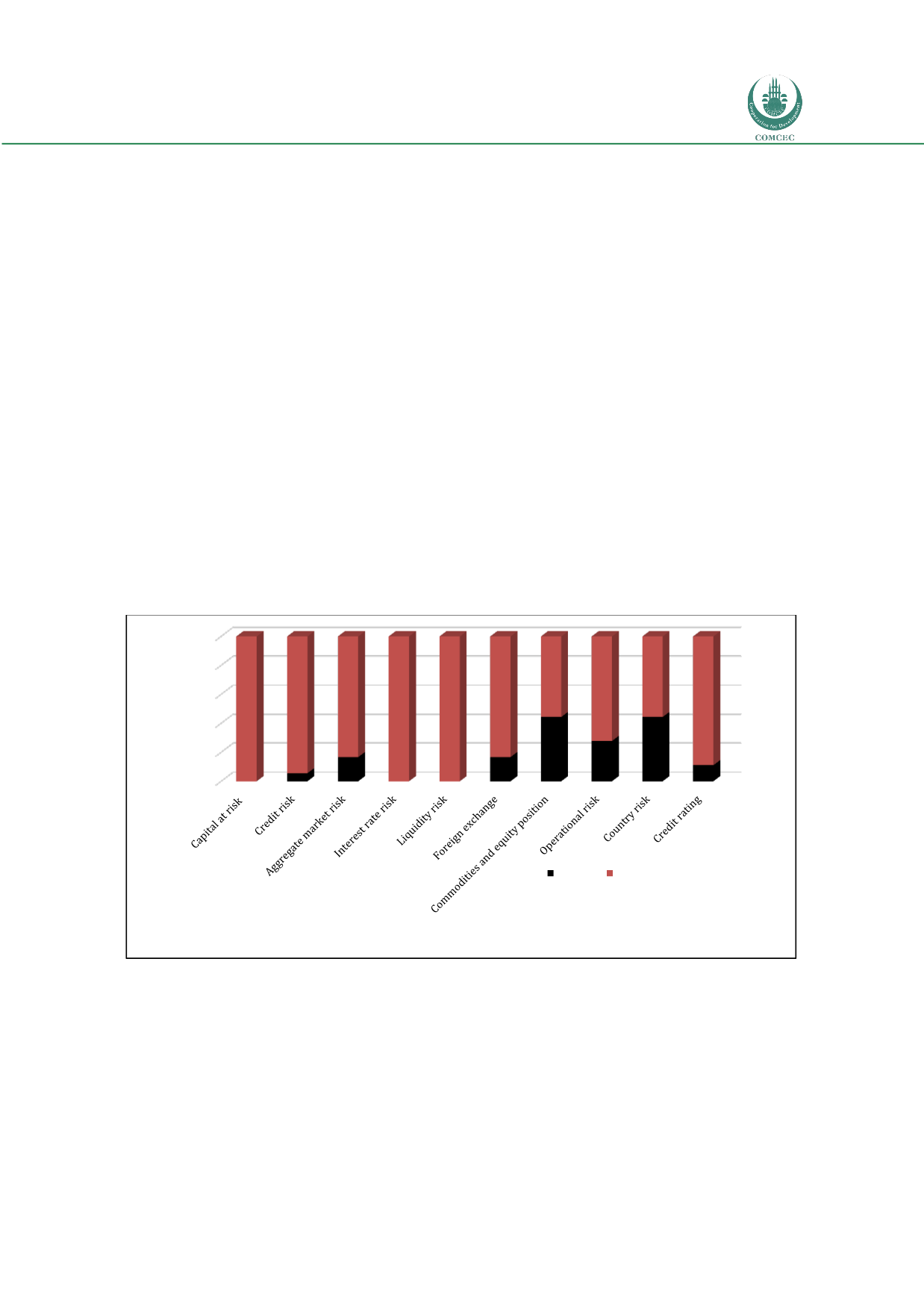
Risk reporting is an essential component of efficient risk management. The IFIs are required to
report partially or in full content, the amount of risk taken in various financial activities. IFIs
produce a number of risk reports. Figure 5.2 provides explanations of the presence of various
risk reports. Not all the reports were equally important, and, thus, were not prepared by all
IFIs. IFIs did not report changes in commodities prices, which might be of concern for the
Salam mode of financing. The country risk report was not needed, as the IFIs were not globally
diversified. However, we must consider the country risk report very important for cross-
border banking activities in the future. Operational risk was not reported fully as well. Hence,
operational risk remains an influential risk among IFIs.
Figure 5.2: Risk Reporting
It is clear why IFIs have operational, credit, liquidity and mark-up risks. In order to fully
understand the risk profile of the banks, the IFIs must report the types and propensity to such
risks in a formal manner. These reports should also be monitored at a periodic basis. While the
risk perceptions and reporting face limitations, IFIs are analyse the existing internal
environment. The start of this environmental scanning is to gather information on the ideal
risk management requirement and policies and procedures that are considered prerequisites
to efficient risk management.
0
20
40
60
80
100
100
94,4
83,3
100
100
83,3
55,6
72,2
55,6
88,9
No (%)
Yes (%)

















