
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
50
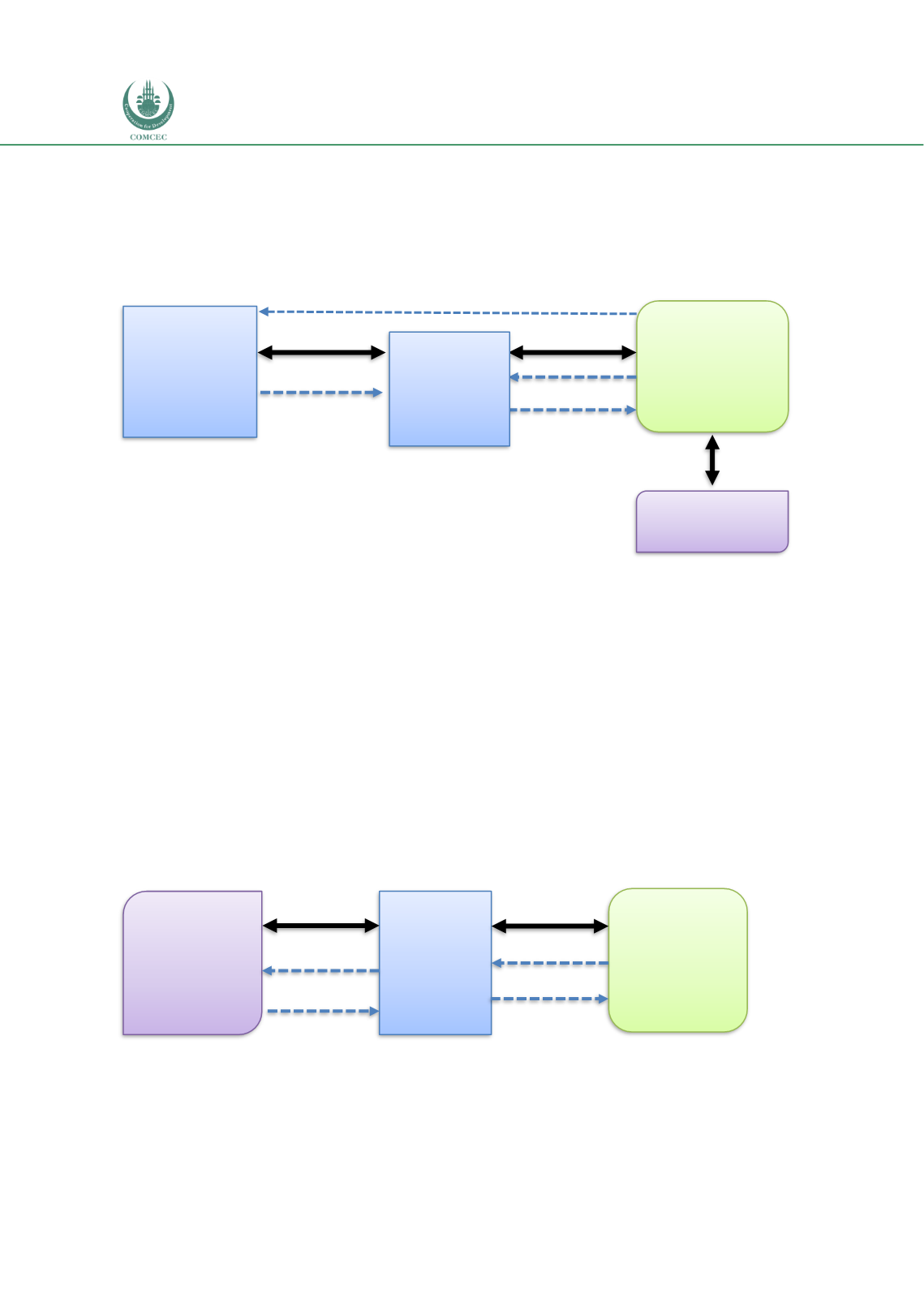
the operation phase. Under the diminishing musharakah framework, the periodic payments to
the Funding Company include imbursements of the principal that result in the gradual transfer
of project assets to the Project Company. The structure of the
musharakah
-based
infrastructure financing is shown in Chart 3.4.
Chart 3.4: Musharakah Structure for Infrastructure Finance
Source: Adapted from Ahmed (2009a) and Khaleq et al (2012).
Murabahah
Under the
murabahah
structure, the Funding Company buys assets/inputs from a vendor and
sells it to the Project Company at a mark-up. For the murabahah to be valid, the Funding
Company must own and possess the asset before entering into the sale contract with the
Project Company. The price of the asset/inputs can be paid in the future in instalments. Since a
debt is created, the Funding Company can ask for guarantees and collateral for protection
against defaults. Being a debt instrument, the amount due cannot be increased in case of
delinquency and the bills of trade resulting from a
murabahah
transaction cannot be traded at
a discount. Due to these reasons,
murabahah
will usually be used for financing specific assets
that have short-term tenor. The
murabahah
structure for infrastructure financing is shown in
Chart 3.5.
Chart 3.5: Murabahah Contract for Infrastructure Finance
Source: Adapted from Ahmed (2009a) and Khaleq et al (2012)
Funding
Company
Project
Company
EPC Company
Musharaka
h
Musharakah
4
3
2
1
1-Contribution to
Musharakah
Company
2-Construction of project assets
3-Funding company leases its share to Project Company
4-Payments of rent and principal (
musharakah
assets)
Musharakah
Company
1
Funding
Company
Project
Company
Suppliers
Sale
Purchase
4
3
2
1
1-Payment for asset/input
3-Delivery of asset/input
2-Delivery of asset/input
4-Payment for asset/input in installments
















