
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
172
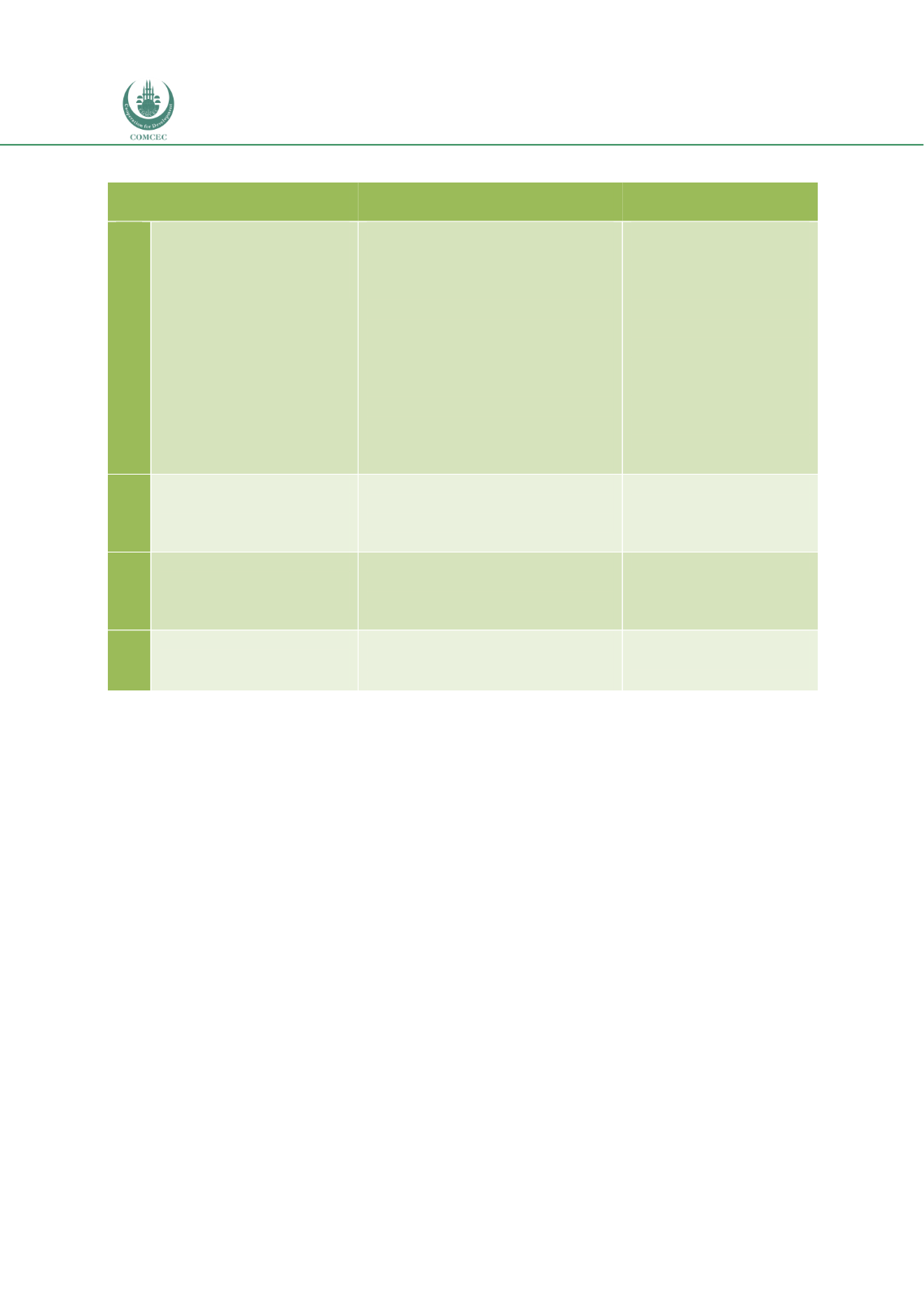
Table 5. 2: Policy Recommendations for Legal and Regulatory Regimes
No.
Recommendations
Specific Steps
Implemented by
2.1
Introduce Appropriate
Laws/Regulations
governing Infrastructure
Laws/regulations related to
private sector participation
(PPP)
Laws/regulations related to
specific infrastructure sectors
Provide a sound legal and
regulatory framework for
encouraging investments in
infrastructure projects
Develop a standardized
Shariah-compliant contract
format that can be used in
different PPP projects
Government and
relevant ministries
Government and
relevant ministries
Governments in
collaboration with
IDB
2.2
Enhance the Public
Procurement
Framework
Enact laws/regulations that
provide clarity with regards to
procurement in PPP
Government and
relevant ministries
2.3
Provide Supportive Tax
Regimes
Adapt/change tax laws to
create a level playing field
between Islamic finance and
conventional finance
Ministry of Finance
2.4
Enact Islamic Financial
Laws
Islamic banking law
Takaful law
Islamic capital markets law
Government
(Ministry of Law/
Legal Affairs)
5.3.
Government and Government Linked Companies
Although the government develops infrastructure projects though procurement, in many
countries government-linked companies (GLCs) or state-owned enterprises (SOEs) are
established to deliver various infrastructure services. Since many of these companies also have
private share-holders, the key objectives of creating GLCs is to improve efficiency and
productivity and encourage innovation. The country case studies show that there are three
types of GLCs when it comes to the infrastructure sector. First, GLCs that provide the
infrastructure services such as utility or telecommunications. Second, government-linked
investment companies (GLICs) that invest in infrastructure projects. Finally, GLCs that provide
support services such as guarantees to promote investments in infrastructure projects. The
role of Islamic finance in supporting infrastructure projects initiated by the government and
GLCs is discussed below.
5.3.1.
Government Budget Support
The country case studies show that governments are still the key players in the provision of
infrastructure in most countries. Many governments have issued sukuk to raise funds for
financing either their budgets in general or infrastructure projects in particular. For example,
in Saudi Arabia, the government raised USD 19.2 billion domestically and USD 12.5 billion from
international investors in 2017 by issuing bonds and sukuk to cover budgetary deficits. Since
the allocations of budgets are also used for infrastructure projects, part of the funds raised has
















