
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
170
the Ministry of Finance covers different stages of government procurement processes to
enhance transparency and mitigate corrupt practices. The Government Tenders and
Procurement Law was enacted in Saudi Arabia by Royal Decree No.M/58 in 2006 to regulate
procedures of tenders and procurements carried out by the government authorities and
ensure they are not influenced by personal interests in order to protect public funds.
As discussed in Chapter 2, World Bank (2018f) identifies three main stages of the institutional
setup of PPP project cycle as preparation, implementation and management of contract. While
in the preparation stage the potential infrastructure projects that can be procured for
development as PPPs are identified, in the second stage the assessment and execution of
procurement is executed. In the final stage, PPP is managed by monitoring and evaluating the
activities and processes vis-à-vis the contract. The status of the procurement regime in the
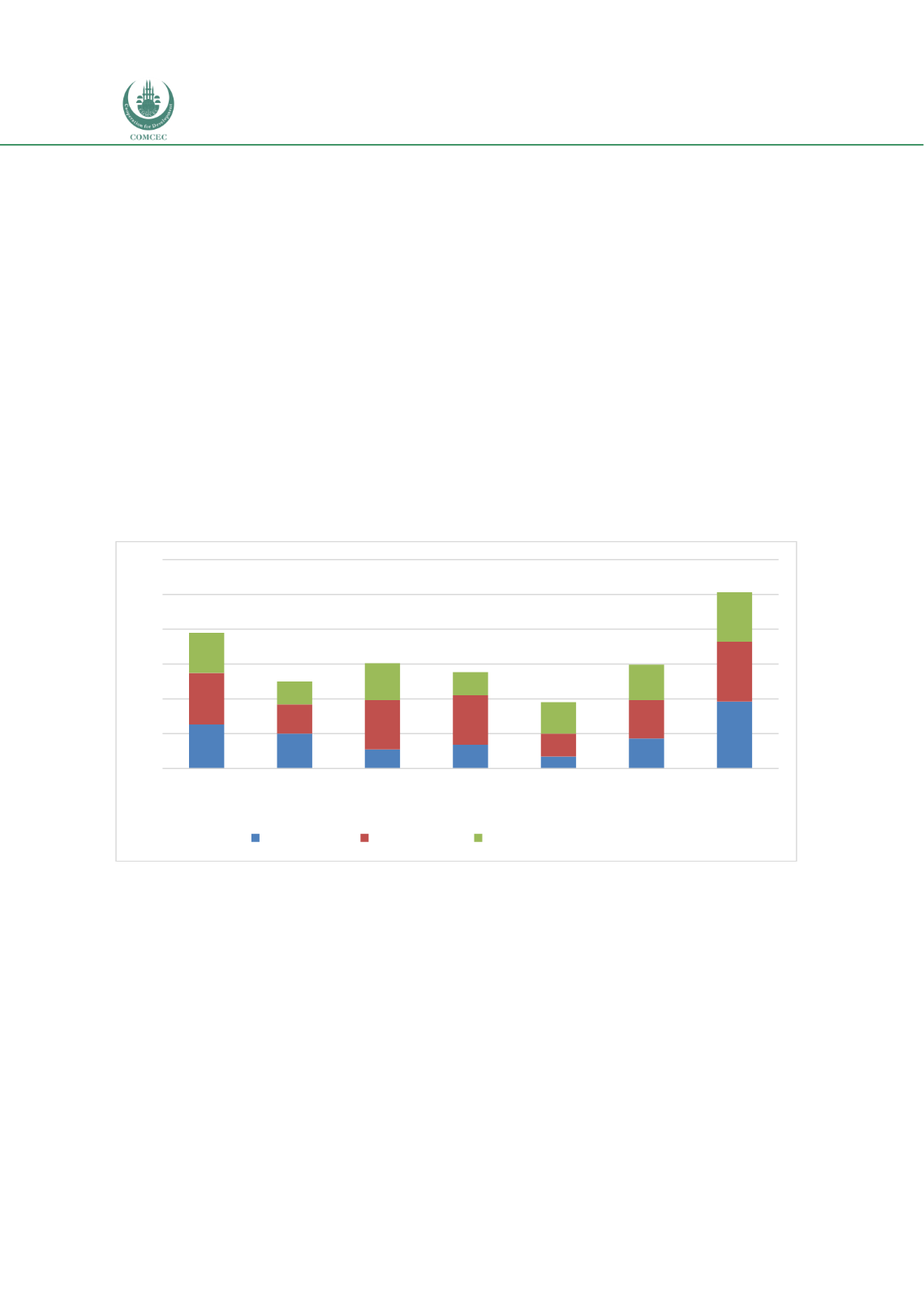
countries examined is shown in Chart 5.2. The procurement regime in the UK scores the
highest, followed by Indonesia. The procurement regimes for other OIC countries in the sample
are relatively underdeveloped. While Indonesia has a better procurement regime and Nigeria’s
procurement regime is similar to the OIC average, the remaining countries (Malaysia, Saudi
Arabia and Sudan) have a lower status of procurement compared to the OIC average
Chart 5. 2: Relative Status of PPP Procurement Regimes (0-100 Highest)
Source: World Bank (2018f)
5.2.4.
Legal Environment for Islamic Finance
A supportive legal and regulatory environment for Islamic finance is necessary for its growth
and contribution to the development of the infrastructure sector. In this regard, there is a need
to have supportive Islamic financial laws covering banks, takaful and capital markets. Islamic
finance laws can be issued as stand-alone laws incorporated into existing financial laws. While
Sudan’s whole financial sector is Islamic, in other countries there is a need to enact new laws
or adjust existing financial laws to accommodate Islamic financial practices.
The Malaysian government has enacted various laws that are supportive of Islamic finance.
While IFSA 2013 provides a robust, legal framework for the Islamic banking and takaful
sectors, the Capital Markets and Services Act 2007 has provisions for Islamic securities such as
63
50
27
34
17
43
96
74
42
71
71
33
55
86
58
33
53
33
45
51
71
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
Indonesia Malaysia
Nigeria Saudi Arabia Sudan OIC Members
(40)
United
Kingdom
Preparation
Procurement
Contract management of PPPs
















