Islamic Fund Management
77
Islamic ETFs
Islamic Unit Trusts
Islamic PRS
Islamic Wholesale
Funds
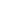
As at end-2017, there
were 5 Islamic ETFs
among the 9 ETFs in
total, with a market
capitalisation of RM468.4
million (or
24.2
%)
compared to RM1.9
billion overall.
As at end-2017, there were
213 Islamic unit trusts
with a collective NAV of
RM77.8 billion (or
18.2
%) compared to the
entire market’s RM427.0
billion.
As at end-2017, there
were 25 Islamic PRS
with an NAV of RM0.72
billion (or
32.3
%)
compared to the
overall market’s
RM2.23 billion.
As at end-2017, there
were 77 Islamic
wholesale funds, with an
NAV of RM37.7 billion
(or
44.5
%) compared
to the entire market’s
RM84.7 billion.
Sources: SC, Bursa Malaysia, Eikon-Thomson Reuters
4.2.2
Evolution of Malaysia’s Islamic Fund Management Industry
Malaysia’s ICM operates within a well-established and facilitative regulatory environment
under the umbrella legislation of the Capital Markets and Services Act 2007 (CMSA). Its capital
market regulatory framework is benchmarked against the International Organisation of
Securities Commissions’ (IOSCO) principles of securities regulation, which are aimed at
ensuring the protection of investors; maintaining fair, efficient and transparent markets; and
reducing systemic risks.
The issuance and offering of all products and services, including Shariah-compliant, are subject
to identical requirements for disclosure, transparency, governance and best practices, as well
as oversight of intermediaries and their agents carrying out regulated activities, to be
conducted within a single supervisory framework. Investors in the ICM, therefore, receive at
least the same level of legal and regulatory protection as those in conventional markets.
The regulatory framework for the ICM is further enhanced by Shariah governance and tax
frameworks. The SC has established a two-tier Shariah governance framework through a
national-level SAC and the requirement of appointing Shariah advisers registered with the SC
at the firms’ level. Various Shariah rulings and scholarly reasonings are compiled and
published in a transparent manner, to provide guidance and assurance to issuers, investors
and intermediaries on the consistency of application of Shariah principles.
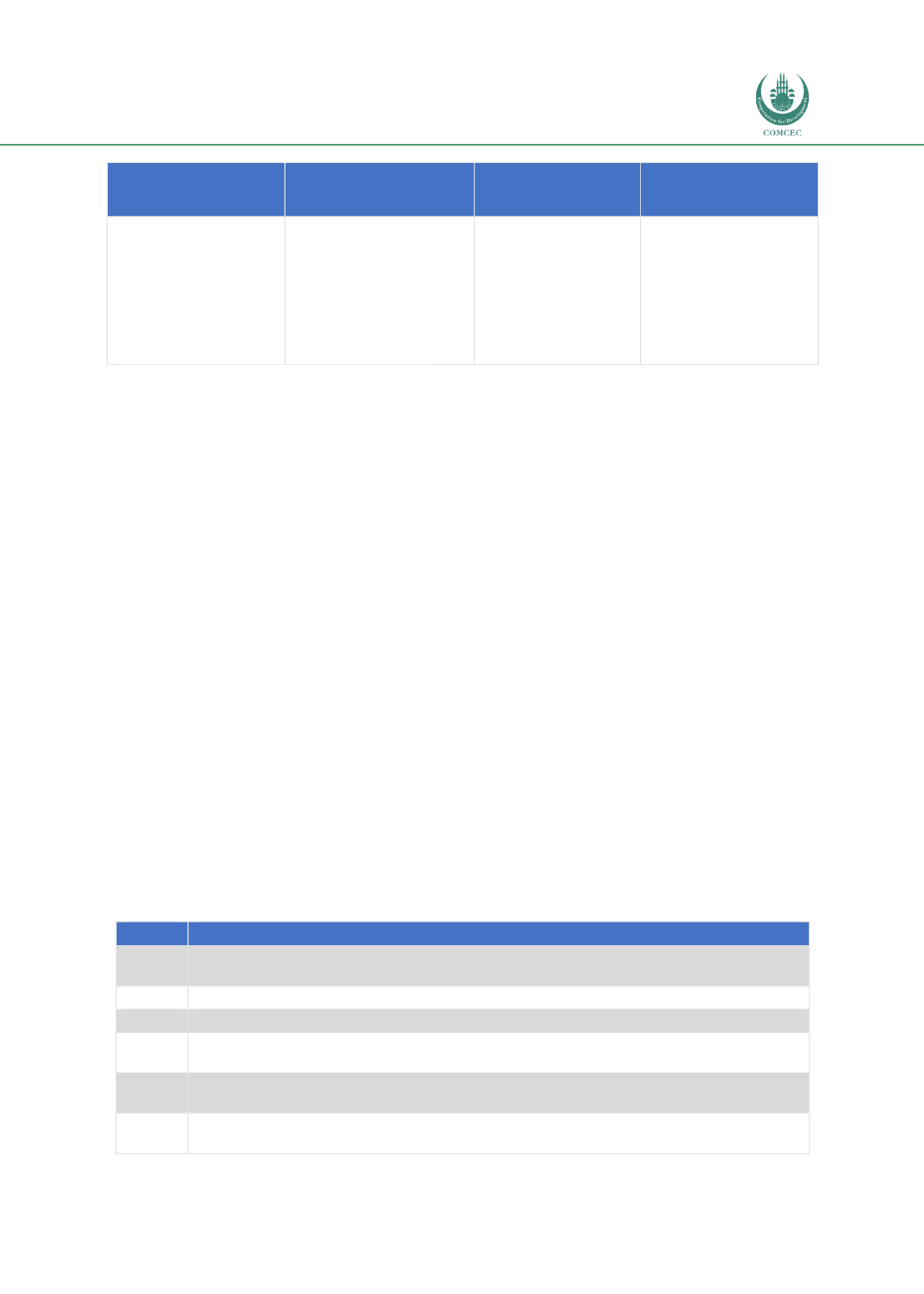
Table 4.4outlines the developmental milestones and release of policies and guidelines that
have had an impact on Malaysia’s Islamic fund management industry.
Table 4.4: Timeline of Key Regulatory Initiatives in Malaysia
Year
Timeline Description
1995
Guidelines on public offerings of securities of closed-end funds.
Release of Shariah screening methodology.
2000
Guidelines on the establishment of foreign fund management companies.
2002
Release of CMP
2005
Guidelines on the compliance function in fund management.
Guidelines on Islamic REITs.
2007
Guidelines on Islamic fund management.
SC signed mutual recognition agreement (MRA) with Dubai Financial Services Authority.
2008
Guidelines on unit trust funds.
Guidelines of CIS.