Islamic Fund Management
56
Fund Structure
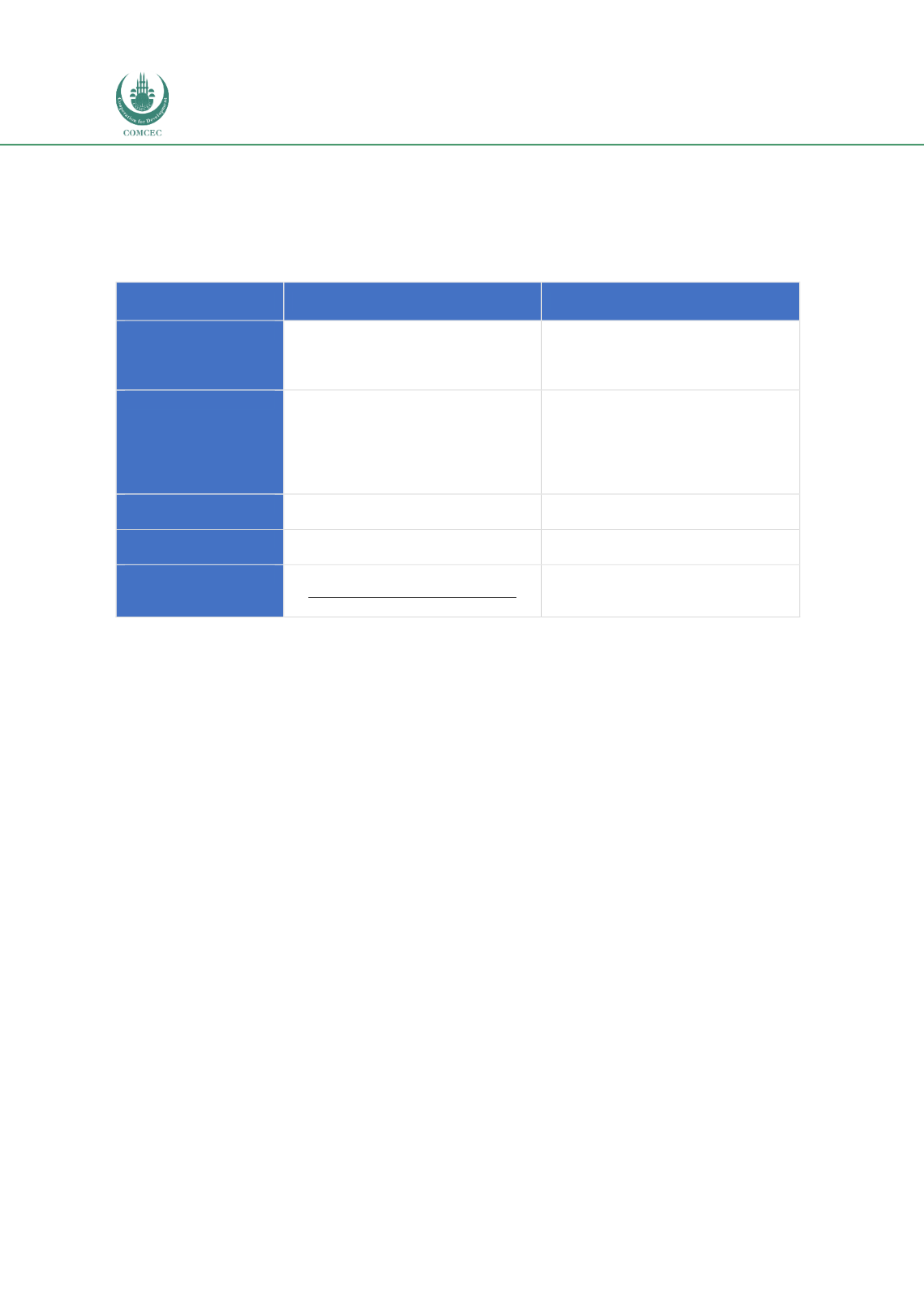
Funds can be structured as open-ended or close-ended. Most of the funds in circulation have
open-ended structures. The key distinctions between the two are explained i
n Table 3.5.Table 3.5: Comparison between Open-Ended and Close-Ended Funds
Type
Open-Ended Fund
Close-Ended Fund
Feature
A fund which can issue and redeem
units at any time (e.g. most mutual
funds, ETFs).
A company (investment company)
which issues shares for subscription
(e.g. REITs). Redemption period is
specified.
Characteristic
Refers to a fund operated by the fund
manager that makes an offer to the
public and invests the proceeds in a
group of assets, in accordance with
the fund’s objectives.
Refers to a fund with a fixed number
of outstanding units. Similar to a
stock, units can be redeemed/sold by
investors on the stock exchange. Once
listed, the fund manager will not
create new units.
No. of Units
No restriction on the number of units
the fund will issue.
Limited number of units.
Tradability
Buying and selling through unit trust
companies.
Appoint broker to buy and sell the
units on the stock exchange.
Price – NAV
Computed daily:
(Fund’s Total Assets – Liabilities)
No. of Outstanding Units
Based on market demand―higher or
lower than the NAV per share.
Source: SC
Investment Objectives
As highlighted earlier in
Figure 3.9 ,investment objectives are generally based on the
following themes:
Equity Funds:
The aim of growth funds, which include income funds, is to achieve
capital appreciation over the medium to long term. Such funds have comparatively high
risks.
Fixed-Income Funds:
Funds that invest in medium to long-term debt instruments
issued by private companies, financial institutions, governments and other entities in
various sectors.
Balanced Funds:
These funds provide both growth and regular income as they invest in
both debt and equity. The NAVs of these schemes are less volatile than those of pure
equity funds.
Money Market Funds:
Invest in short-term (maturing within one year) fixed-income
securities. These instruments are highly liquid and provide investment safety. Money
market funds are therefore the safest investment option relative to other types of
mutual funds.