COMCEC Trade Outlook 2016
7
Oil price collapse was a combination of both demand side and supply side factors including the
surge in crude oil production in countries outside the OPEC
5
, especially in the United States,
increased oil supply due to continued OPEC production, Iran’s return to oil market, the weakness
of demand and improved energy efficiency in vehicles. (IMF 2016) found that abundant supply
accounts almost all the decline in oil prices. According to (Arazki et al 2015) increased financial
flows to oil in recent years may have also an impact on increased volatility of oil prices.
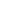
Figure 5: Evolution of Oil and Non-Fuel Commodity Price Indices (2005=100)
Source: IMF
High increases in oil prices reflected themselves in
the rising share of commodities in global trade. Thus,
the share of mineral fuels in global exports rose from
9.8 per cent in 2001 to 16.3 per cent in 2014, moving
up to the first place. However due to fall in oil prices,
share of mineral fuels in global exports declined to
11.4 per cent in 2015. On the other hand, the share of
electrical, electronic equipment in world exports
moved to first place in 2015 from second place in 2001. Figure 6 below, shows the composition
of world exports in 2015 compared to 2001.
5
According to (WB 2016) OPEC production increased further, reaching a three year high, with much of the
increase coming from Saudi Arabia and Iraq.
htttp://pubdocs.worldbank.org/en/898911452202217524/Global-Economic-Prospects-January-2016-Global-Outlook.pdf
“The share of commodities
in the world trade increased
due to soaring commodity
prices”