14
COMCEC Agriculture Outlook 2019
2.
Sectoral Indicators
Sectoral indicators providemore specific information on the structure of a sector. In agriculture
land use, crop productions and yields, labor productivity, water use and fertilizer use are
considered as the main sectoral indicators.
2.1 Land Use
The world’s cultivated area has grown by 12 percent over the last 50 years. The global irrigated
area has doubled over the same period, accounting for most of the net increase in cultivated
land. Meanwhile, agricultural production has grown between 2.5 and 3 times, thanks to
significant increase in the yield of major crops. However, global achievements in production in
some regions have been associated with the degradation of land resources, and the deterioration
of related ecosystem goods and services, such as decreasing biomass and carbon storage as well
as damaging soil health and biodiversity.
According to FAO’s 2016 data, agriculture uses 4.87 billion hectares, representing 37.4 percent
of the world’s land surface. Agriculture is a major user of land. Hence, in order to make
agriculture sustainable, it is important to maintain the quantity and quality of soil resources.
Agriculture must be at the center of any discussion on natural resourcemanagement and global
environmental objectives. The responsible management of natural resources requires
ensuring adequate food and water for all while at the same time achieving sustainable rural
development and livelihoods for the current and future generations.
Land resources and the way they are used are central to the challengeof improving food security
across the world. Demographic pressures, climate change, and the increased competition for a
land are likely to increase vulnerability to food insecurity, particularly in Africa and Asia. The
challenge of providing sufficient food for everyone worldwide has never been greater.
For improving nutrition and alleviating food insecurity and undernourishment, future
agricultural productionwill have to rise faster than population growth. This will have to occur
largely on existing agricultural land. Improvements will thus have to come from su stainable
intensification that makes effective use of land without harming and spoiling this precious
resource. As estimated by FAO, almost 5 to 7million hectares of agricultural land are lost each
year due to land degradation and urbanization.
Taking intoaccount the issuesmentioned above, for the OIC member countries sustainable land
management is vital, asmost of them are faced with food insecurity and have higher population
growth than theworld average.
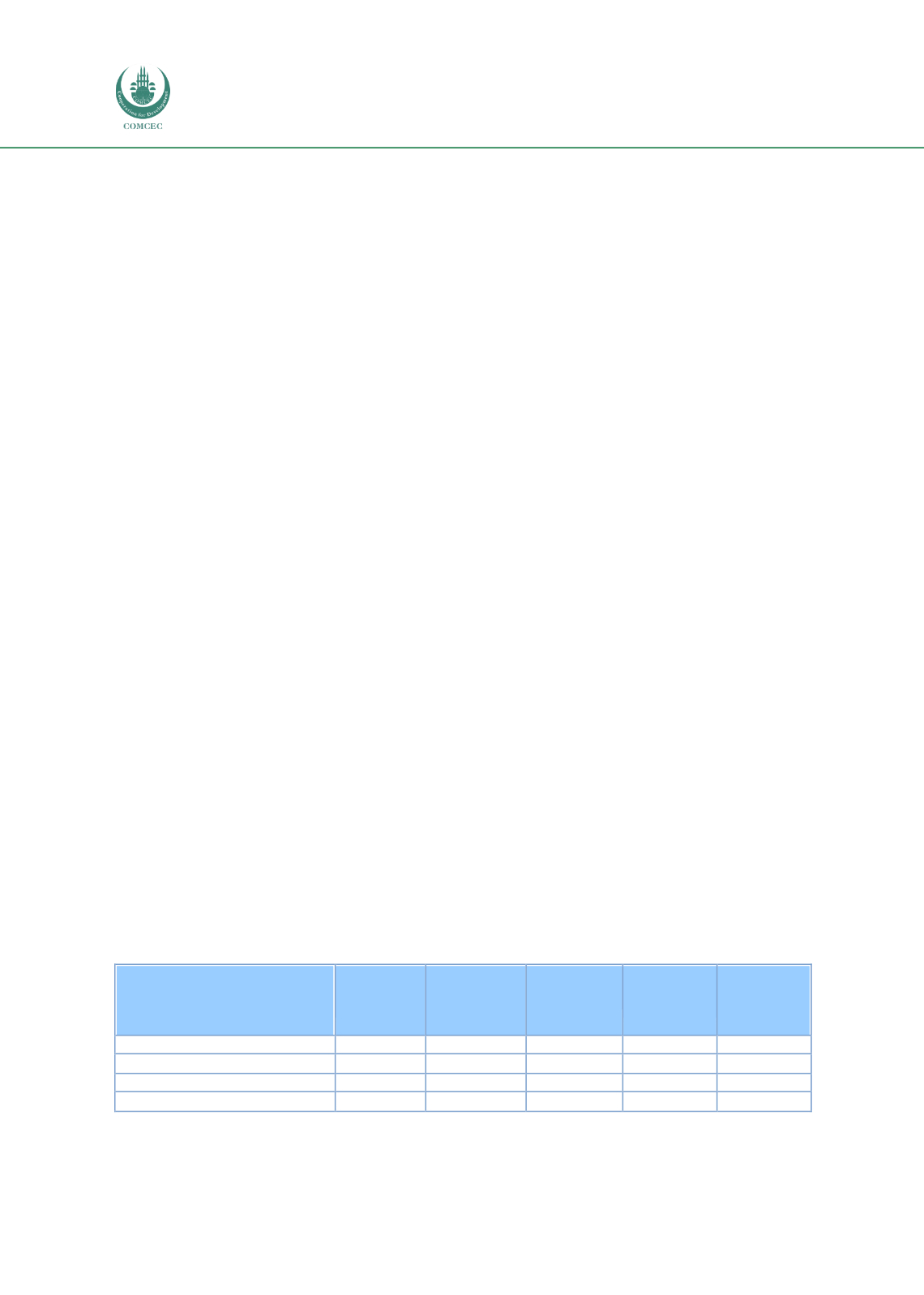
Table 5 Land Use in the OIC and its Share in the World, 2016
Total Land
Area
Agricultural
Area
Arable land
Permanent
Crops
Permanent
Meadows
and
Pastures
OIC (millionha)
2,940
1,370
310
64
996
Share in Total Agr. Area (%)
100
22.6
4.7
72.7
World (million ha)
13,009
4,870
1,424
166
3,277
Share of OIC in the World (%)
22.60
28.1
21.8
38.6
30.4
Source: FAOSTAT