
Facilitating Trade:
Improving Customs Risk Management Systems
In the OIC Member States
51
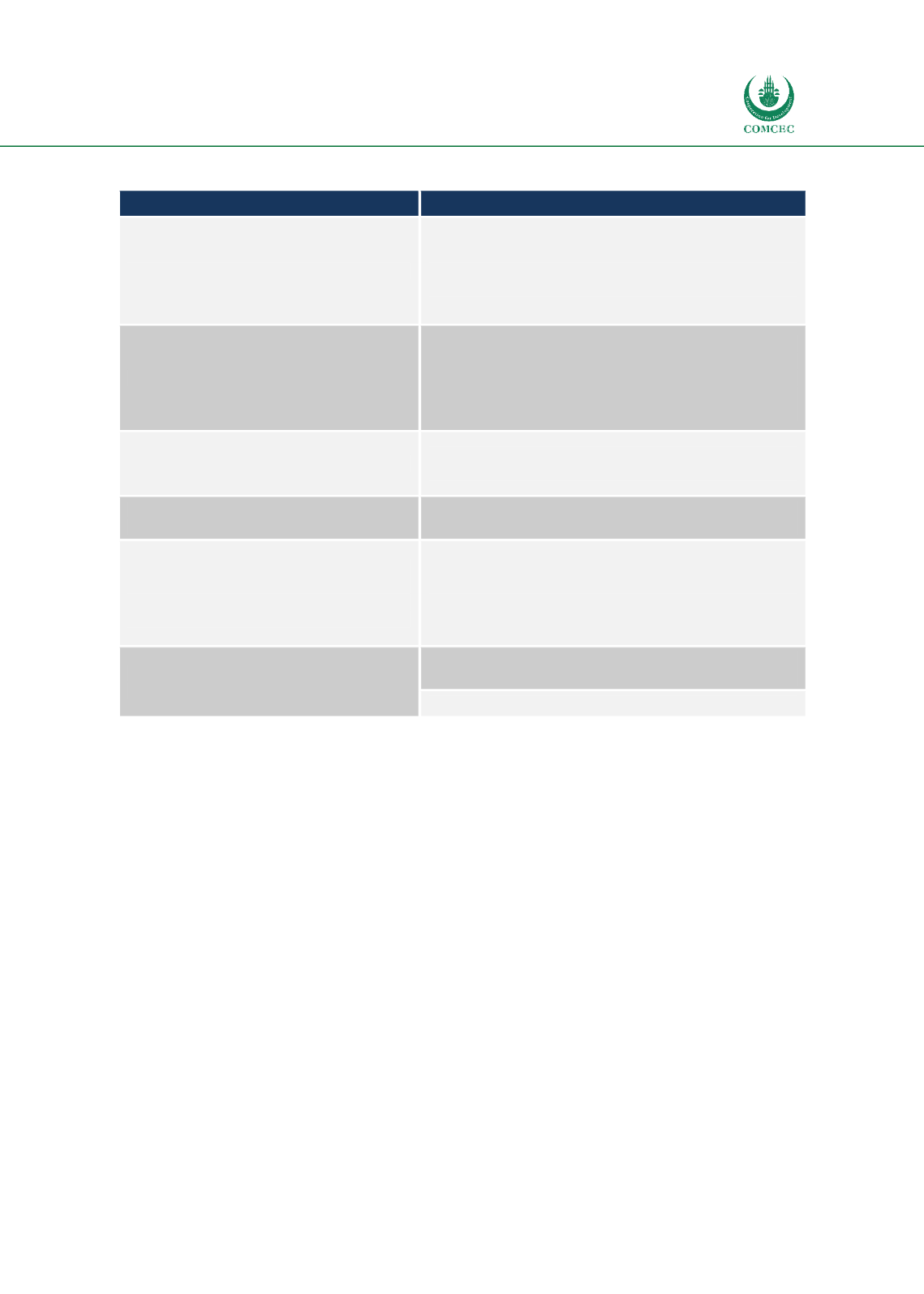
Table 7: Kosovo CRM previous and current approach
Previous approach
Risk-based approach
100% physical inspection of shipments
26434 CD 11% green channel with 5% random selectivity,
154268 CD 67% yellow channel, 36730 CD 16% red
channel, 4883 CD 2% blue channel, 8457 CD 4% orange
channel, average effectiveness 3.66 % (2015 offences,
criminal reports)
No CRM selectivity
463 risk profiles and 9 selectivity lists activated in the AW.
Risk profiles kept being analysed and consequently
modified (42), de-activated (35) or added (18) -
approximately 1200 profiles were applied in the CDPS’s
from 2005 till 2017
No CRM/Intelligence Unit established
Intelligence and Risk Analysis Sector established and
incorporated within the Department for Law Enforcement
No reporting/analysis services, no feedback
from control
Implementation of DWH and Business Intelligence
platform
Use unsecured, different and technologically
obsolete text and data processing system for
management of Law Enforcement
information (CRM and Intelligence)
Implementation/Integration of Law Enforcement IT
System
Single Customs National Domain data
repository
Exchange of customs data in real time with neighbouring
countries (SEED)
Risk Assessment on pre-arrival information
Source: Author’s compilation
3.2.1.6
Border Clearance Performances
KC is sustainably improving the border clearance performance also through the successful
operation of its Monitoring Office introduced at the end of 2013. There are 27 experienced
officers in the HQ unit dealing with verification of import declarations supported by AW
selectivity features including valuation issues and SAD (CD) validation rules. All Customs
procedures, including international transit, use pre-arrival information for early controls with
the AW Selectivity module. Excise declarations are currently processed on paper.
Undervaluation of imports presents a significant risk to the KC. KC has developed an AW
Valuation module for managing lists of specific goods with an additional HS sub-classification of
four extra digits. The sub-classification helps distinguish customs values of specific goods, i.e.
brands, models, used or new, and so on. Currently, there are few thousand codes maintained for
that purpose in the KC. The Monitoring Office also checks declarations and clearance activities
to minimize undervaluation risk.
Post Clearance Audit selects trade operators based on risk analysis. Depending on the level of
risk, the PCA decides to undertake desk audit and/or visit the company, and at the same time,
they are opening a case in the LES. The first activity is always a preparatory task (desk audit)
assigned to each member of the team including the team leader.
If the outcome of the
preparatory tasks identifies additional risks, the Head of the PCA can extend the scope of the
controls to include these other/additional risks. Depending on the findings, the audit officers
















