Reducing Postharvest Losses
In the OIC Member Countries
87
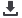
Postharvest
stages
continued
Causes of postharvest
loss
Actor who could reduce loss
(and grain origin)
Loss reduction
options
Farmer
produced
and
home-
stored
local
grain
Govt.
procured,
stored &
milled
local
grain
Govt.
procured
imported
grain
Private
trader
procured
imported
grain
Millers
Consumer
Marketing
Lack of access to transport
X
-
Farmer organisation
to
share
transport,
market info, increase
access to credit and
negotiation positions
-
Support development
of
quality
sensitive
markets, enforce grain
standards efficiently and
equitably
-
More
efficient
payment systems (e.g.
mobile money)
-
More efficient less
complex grain import
systems
-
As
private
sector
procurement
of
domestic
grain
increases,
warehouse
receipt systems may
have a role
Weak incentive for farmers
to produce and sell high
quality grain
X
X
Slow or unreliable payment
processes
X
Spillage and loss during re-
bagging
X
Uncertainty around changes
to import standards
X
X
Too many agencies involved
in grain import, uneven
enforcement of standards,
delays
X
X
Traders
purchase
grain
volumetrically (
ardab
) and
then sell it /kg
X
X
Storage
Poor storage hygiene and
cleaning
of
store
and
container
X
X
X
X
X
-
Awareness
of
and
training on improved
grain
storage
for
farmers, extensionists,
teachers,
traders/importers and
store managers
-
Awareness raising on
scale and value of PH
losses, importance of
clean dry grain at start
of storage
-
Thorough
cleaning
and
maintenance
of
stores
-
Effective protection of
grain to be stored >3
months (e.g. use of
hermetics,
recommended pesticide
application for farmers;
fumigation,
rodent
mgmt. & hygiene of large
stores)
-
Experiential learning
opps. for farmers and
extensionists on grain
storage options
-
Regular monitoring of
and attention to stored
produce
-
Build capacity of large-
scale store managers to
operate without political
interference
Poor inspection of grain at
purchase
X
X
X
Insect infestation
X
X
X
X
X
Attack by rodents
X
X
X
X
X
High
moisture
content
resulting in mould growth
and
increased
risk
of
aflatoxin contamination
X
X
X
X
X
Ineffective grain protection
X
X
X
X
X
Poor monitoring of stored
products and pest levels
X
X
X
X
X
Theft
X
X
X
X
X
Poor store construction/
maintenance lead to damp,
leaks, pests
X
X
X
X
Poor record keeping
X
X
X
X
Insufficiently trained staff
X
X
X
X
Corruption by staff
X
X
X
Political interference in stock
management
X
X
X
X
Milling
Poor hygiene at mill leading
to contamination
X
X
X
-
Increased attention to
mill hygiene, product
separation,
rodent
proofing
and
preventative
maintenance
-
Monitor
equipment
efficiency
Poor
maintenance
of
equipment leading to low
out-turn
X
X
X
Power
outages
affecting
operations
X
X
Political
interference
in
X
X