Reducing Postharvest Losses
In the OIC Member Countries
88
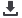
operations
-
Investment in diesel or
alternative energy run
machines
Utilisation
Poor quality products (e.g.
bread) lead to high wastage
X
-
Awareness raising on
food safety issues
-
Increase autonomy of
food
choices
and
availability
Poor stacking and closing
of containers leading to
spillages,
dampness,
rancidity, infestation etc.
X
4.1.4.
Measures and Strategies Implemented for Postharvest Loss Reduction in
Uganda
Many of the causes of postharvest cereal losses in Egypt can be addressed through raising
greater awareness of the level of losses and situations where they occur, the causes of the
losses, well-known options and actions for addressing and reducing these losses and changes
to the enabling environment. Postharvest innovation systems are complex and dynamic,
bringing many different activities, actors, sectors and goals together
(Figure). Using an
innovation systems perspective can help to examine technological and institutional change as a
complex process of interactions among diverse actors engaged in generating, exchanging, and
using knowledge, and the social and economic institutions that condition their actions and
interactions (Spielman
et al
., 2008; Larsen
et al
., 2009). The innovation systems concept
extends beyond the creation of knowledge to encompass factors affecting demand for and use
of new and existing knowledge (Hall
et al
., 2004).