Reducing Postharvest Losses
In the OIC Member Countries
86
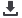
Table 44: Causes of postharvest loss in Egyptian cereal supply chains, supply chain actors
involved, and loss reduction options
Postharvest
stage
Causes of postharvest loss
Actor who could reduce loss
(and grain
origin)
Loss reduction
options
Farmer
produced
and home-
stored
local grain
Govt.
procured,
stored &
milled
local grain
Govt.
procured
imported
grain
Private
trader
procured
imported
grain
Pre-harvest
factors
affecting
PH
Varietal choice, as some are less
drought
tolerant
and
more
susceptible to storage pests
X
-
Cereal
breeding
for
drought tolerance and PH
characteristics
(e.g.
storage
pest
susceptibility)
-
Awareness of timely
planting, soil management
Timing of planting, and soil-water
management
X
Harvesting
Late harvesting, grain shattering,
insect infestation in field
X
-
Awareness of optimal
harvest
timing,
field
infestation risk
-
Better
advanced
planning for PH activities
Poor
harvesting/
labour
management – some grain left in
field
X
Field
drying
Theft by birds, livestock, wild-
animals, humans
X
-
Stooking and/or quick
removal of mature crop
from field
-
Use of clean sheets/
containers to protect crop
Contamination by fungi, insects,
foreign matter if on ground
X
Transport
from field
Spillage through use of unsuitable
containers/ carelessness
X
-
Better
advanced
planning & monitoring of
PH activities.
-
Awareness on cross-
contamination risks
Theft by humans
X
Contamination through use of old
sacks/ dirty containers
X
Further
drying
Rain during drying
X
-
Supervise grain drying
so it can be quickly
covered, tether or fence
livestock
-
Awareness on risks of
drying on ground and
need for safe moisture
content, use sheets/tarps
or raised crib, thin layer
Inadequate
drying
practices/
knowledge
X
Theft/ damage by domestic or wild
animals
X
Contamination by fungi, insects,
foreign matter if on ground
X
Threshing/
shelling
Rough threshing/ shelling leading
to damaged/ broken grains
X
-
Erect
sides
around
threshing/shelling
platforms
and
sheets
underneath,
gentler
beating
to
prevent
breakage,
timely
harvesting before crop
over
matures,
maintenance/ knowledge
of threshing machine to
minimise breakage
Scattering and loss of grains
X
Contamination with foreign matter
(e.g. small stones, dust)
X
Sorting
No price premium for high quality,
so no incentive for sorting
X
X
-
Awareness:
removing
broken grains reduce pest
damage.
Support
development of quality
sensitive markets
Transport
to market
or
govt.
store
Contamination through use of dirty
containers and vehicles
X
X
X
X
-
Awareness re loss risks
of over-filling and use of
dirty/contaminated
containers
-
Awareness on need to
cover food grain during
transport
-
Improved roads and
barge routes to reduce
delays,
theft
and
deterioration.
Anti-
corruption actions
Theft/ corruption by humans
X
X
X
X
Over-filling sacks resulting in them
splitting
X
X
Uncovered transport leading to
contamination and damage
X
X
X
X
Poor road quality, and insufficient
barge routes increase costs
X
X
X
X
Unauthorised payments required
X
X
X
X