Increasing the Resilience of the Food Systems
In Islamic States in Face of Future Food Crises
22
in 136 countries benefited from social assistance programs.
58
Social protection also has the
potential to increase agricultural productivity by helping farmers access agricultural inputs
through subsidies, facilitating credit, and providing weather-related insurance cover.
59
Boosting FoodSecurity
A)
Resilience
Resilience is defined by FAO as "the ability to prevent disasters and crises as well as to
anticipate, absorb, accommodateor recover from them in a timely, efficient and sustainable
manner. This includes protecting, restoring and improving livelihoods systems in the face
of threats that impact agriculture, nutrition, food security and food safety."
60
Within the
context of the report’s framework, the resilience section will focus on long-term
strategies—such as enhancing productivity, diversifying livelihoods, and building human
capital—rather than short-term or immediate responses to crises discussed in the
Adaptation and Mitigation section.
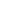
Figure 8: Boosting Food Security
Source: DinarStandard Analysis
Enhancing productivity is a cornerstone of income building and asset diversification.
Strategies to enhance productivity include water management systems, adoption of new
technologies, and, microfinance schemes to support training, start-up capital and initial
assets. Diversifying livelihoods involves diversifying income sources and protecting the
income, assets and systems created in the face of shocks by building a durable, diverse
livelihood base—including assets, resources, and infrastructure. Strategies to enhance
livelihoods include improving infrastructure and supporting rural processing and local
transport service industries. Building human capital enables people to efficiently use any
available or potential resources. It involvesenhancing human skills and knowledge through
investments in education in general and nutrition education in particular. Building human
capital also involves strategies to fight malnutrition and promote diet diversity.
61
58
FAO. (2016). Social Protection in Protracted Crises, Humanitarian and Fragile Contexts. Retrieved from
http://www.fao.org/emergencies/resources/documents/resources-detail/en/c/415688/59
UNDP. (2011). Exploring the Role of Social Protection in Enhancing Food Security in Africa. Retrieved from
https://www.undp.org/content/dam/rba/docs/Issue%20Briefs/Exploring%20the%20Role%20of%20Social%20Protection%20in%20Enhancing%20Food%20Security%20in%20Africa.pdf
60
FAOWebsite.
http://www.fao.org61
Webb, Patrick. and Beatrice Rogers. (2003). Addressing the ‘In’ in Food Insecurity. USAIDOccasional Paper No. 1. Feb
2003. Retrieved
fromhttp://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US201700009692