Increasing the Resilience of the Food Systems
In Islamic States in Face of Future Food Crises
20
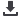
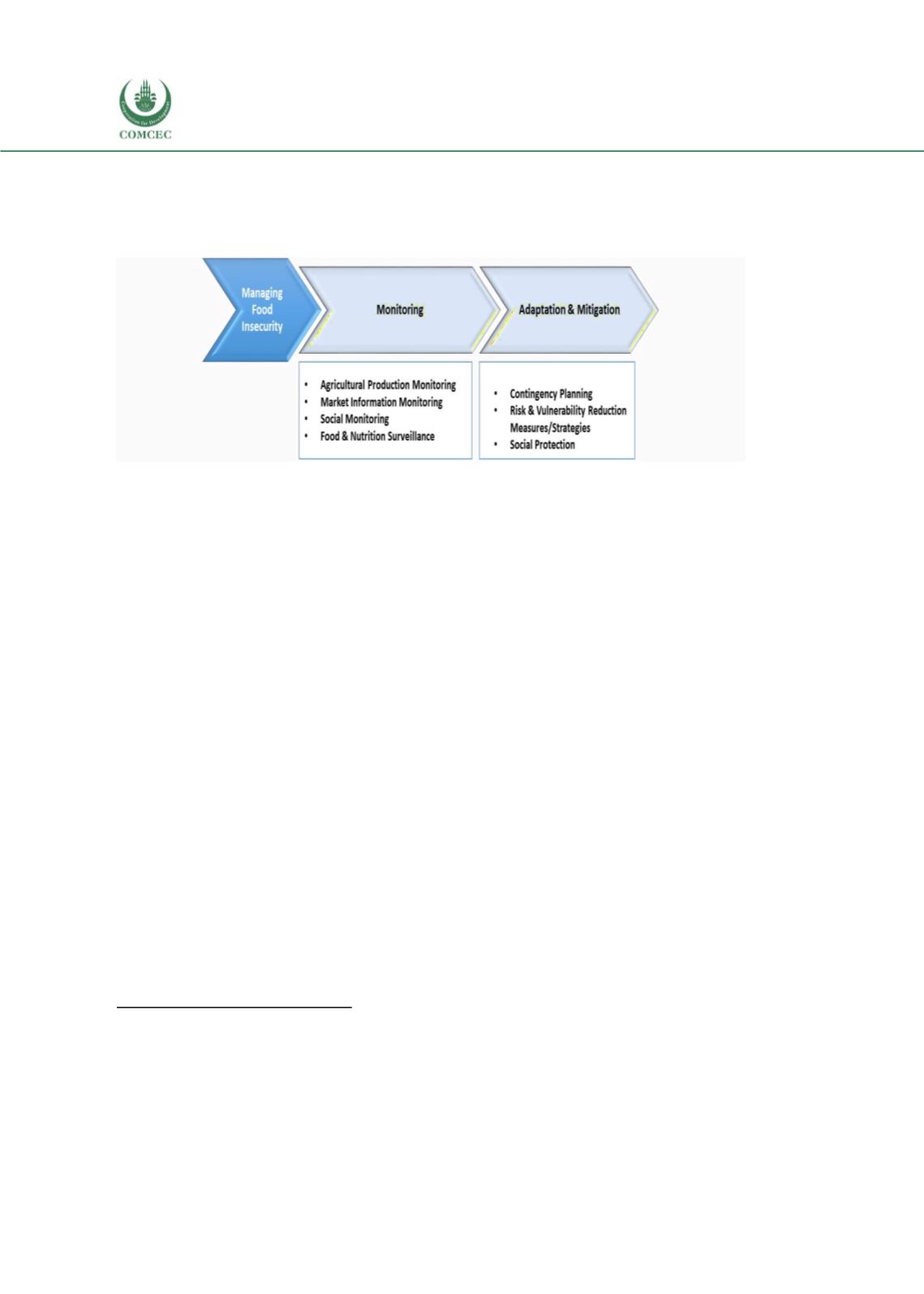
Managing Food Insecurity
A)
Monitoring
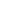
Figure 7: Managing Food Insecurity
Source: DinarStandard Analysis
Monitoring food security is instrumental in managing food insecurity and crises, as monitoring
instruments raisethe alarmin cases of potential riskand provideinformation on the nature of the
crisis and its potential impact. This helps decision makers avoid devastating effects and ensures
relief and emergency aid reaches vulnerable populations. Food security monitoring systems
include agricultural production, market information, and social, food and nutrition surveillance
systems. Agricultural production monitoring systems in many instances also track livestock
farming products. Market information systems trackdomestic tradeand internationaltrade. Social
monitoring or monitoring of vulnerable groups focuses on keeping track of poverty.
49
Food and
nutritional surveillance systems or monitoring supply the necessary information on the
consumption patterns and nutritional conditions of a population , enabling decision makers to
develop national plans for better management of food insecurity.
50
A multitude of international
organizations have developed global early warning systems for food insecurity and famine.
Examples of these include the FAO’s Global Early Warning-Early Action (EWEA) report and the
Famine Early Warning Systems Network (FEWSNET).
B)
Adaptation and Mitigation
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) defines adaptation as “adjustments in
human and natural systems, in response toactual or expected climate stimuli or theireffects, which
moderate harmor exploit beneficialopportunities.” It alsodefinesmitigation as “an anthropogenic
intervention to reduce the sources or enhance the sinks of greenhouse gases.” Thus, mitigation is
concerned with tackling the causes of climate change and adaptation focuses on the
consequences.
51
However, in the contextof this report’s framework, bothmitigation and adaptation
49
FAO. (2000). Handbook for Defining and Setting up a Food Security Information and EarlyWarning System (FSIEWS).
Retrieved
fromhttp://www.fao.org/3/x8622e/x8622e00.htm50
Al Jawaldeh, A., Osman, D., Tawfik, A., & World Health Organization, Regional Office for the EasternMediterranean.
(2013)
.
Food and nutrition surveillance systems: technical guide for the development of a food and nutrition surveillance
system for countries in the EasternMediterranean Region. Retrieved
fromhttps://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/11999551
IPCC. (2012).Glossary of terms. In: Managing the Risksof Extreme Events and Disasters toAdvance Climate Change
Adaptation
[Field, C.B., V. Barros, T.F. Stocker, D. Qin, D.J. Dokken, K.L. Ebi, M.D. Mastrandrea, K.J. Mach, G.-K. Plattner, S.K. Allen,