Increasing the Resilience of the Food Systems
In Islamic States in Face of Future Food Crises
16
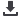
Figure 6: Assessing Food Security
Source: DinarStandard Analysis
Various indicators have been proposed by academics and development agencies to measure the
four food security pillars.For measurementof availability,these indicators includeaverage protein
supply, averagevalue of food production, and share of dietary energy supply derivedfrom cereals,
roots and tubers. For access, the indicators include road and rail line density, gross domestic
product (in purchasing power parity), domestic food price index, share of food expenditure of the
poor, and prevalenceof undernourishmentand food inadequacy. Forutilization, indicators include
access to improvedwater sources and sanitation facilities;percentage of childrenunderfive years
of age affected bywasting, stunting, anemia or being underweight; prevalence of vitamin A or iodine
deficiency in the population; and percentage of pregnant women affected by anemia. For stability,
the indicators include cereal import dependency ratio; value of total imports over value of
merchandise imports; domestic food price volatility; per capita food production and supply
variability; and political stability and the absence of conflict.
38
Two of the most widely used global indexes in the area of food security and nourishment are the
Global Food SecurityIndex (GFSI) andthe Global Hunger Index (GHI). The GHIuses four indicators
tomeasure three areas relatedtohunger: child undernutrition, childmortality andinadequate food
supply. The GFSI measures 28 indicators in four main areas affecting food insecurity, covering a
large extent of the elements of the four food security pillars. The four indicators measured by the
GHI include the percentage of children under five years of age affected bywasting ; the percentage
of children under five years of age affected by stunting; the percentage of the population suffering
from undernourishment; and the under-five mortality rate. The four areas measured by the GFSI
are: availability, affordability (which reflects elements from the access pillar), quality and safety
(which reflects elements from the utilization pillar), and natural resources and resilience (which
reflects elements from the stability pillar). The indicators used in the GFSI, whichwill be used for
38
FAO, IFAD andWFP. (2015). The State of Food Insecurity in theWorld 2015. Meeting the 2015 international hunger
targets: taking stock of uneven progress. Retrieved
fromhttp://www.fao.org/3/a-i4646e.pdf