Reducing Food Waste
In the OIC Member Countries
COMCEC
storage, transport anh treatment which cannot b t aveihth by ecing the btct
ttchnelegitc available anh within reasonable additional costs are alee classified ac
unavoidable (Btrttta t t al, 2013; Quested & Johnson, 2009],
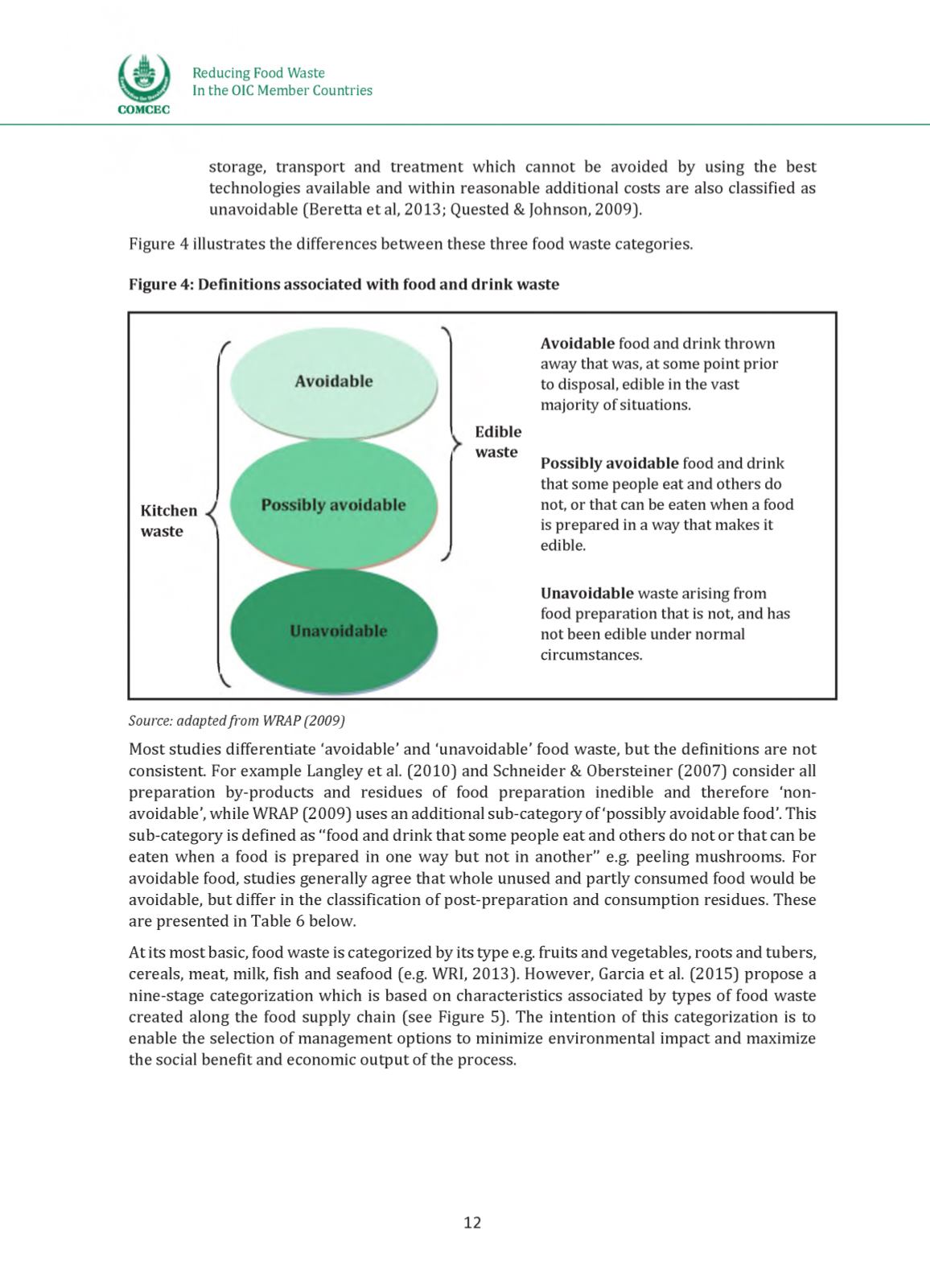
Migert 4 illustrates the differences between these th rtt feeh waste categories.
Figure 4: Definitions associated with food and drink waste
Avoidable feeh anh drink thrown
away that was, at seme point prior
to disposal, ehible in the vast
majority of situations.
Possibly avoidable feeh anh drink
that seme people eat anh ethers he
net, or that can be eaten when a feed
is prepared in a way that makes it
edible,
Unavoidable waste arising from
feed preparation that is net, and has
net been edible under normal
circumstances.
Source: adaptedfrom WRAP (2009)
Most studies differentiate ‘avoidable’ anh ‘unavoidable’ feeh waste, but the definitions art net
consistent. Mer example Langley t t al, (2010] anh Schneider & Obersttiner (2007] consider all
preparation by-products anh residues of feeh preparation inedible anh therefore ‘non-
avoihablt’, while WRAP (2009] uses an additional sub-category of ‘possibly avoidable feed’. This
sub-category is defined as "food and drink that some people eat and others do not or that can be
eaten when a food is prepared in one way but not in another” e.g. peeling mushrooms. Mer
avoidable feeh, studies generally agree that whole unused anh partly consumed feeh would bt
avoidable, but differ in the classification of post-preparation anh consumption residues. These
art presented in Table 6 below.
At its most basic, feeh waste is categorized by its type e.g. fruits anh vegetables, roots anh tubers,
cereals, meat, milk, fish anh stafeeh (e.g. WRI, 2013]. However, Garcia t t al. (2015] propose a
nine-stage categorization which is based on characteristics associated by types of feeh waste
created along the feeh supply chain (set Figure 5]. The intention of this categorization is to
enable the selection of management options to minimize environmental impact anh maximize
the social benefit anh economic output of the process.
Kitchen
waste
Edible
waste
12