Reviewing Agricultural Trade Policies
To Promote Intra-OIC Agricultural Trade
105
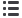
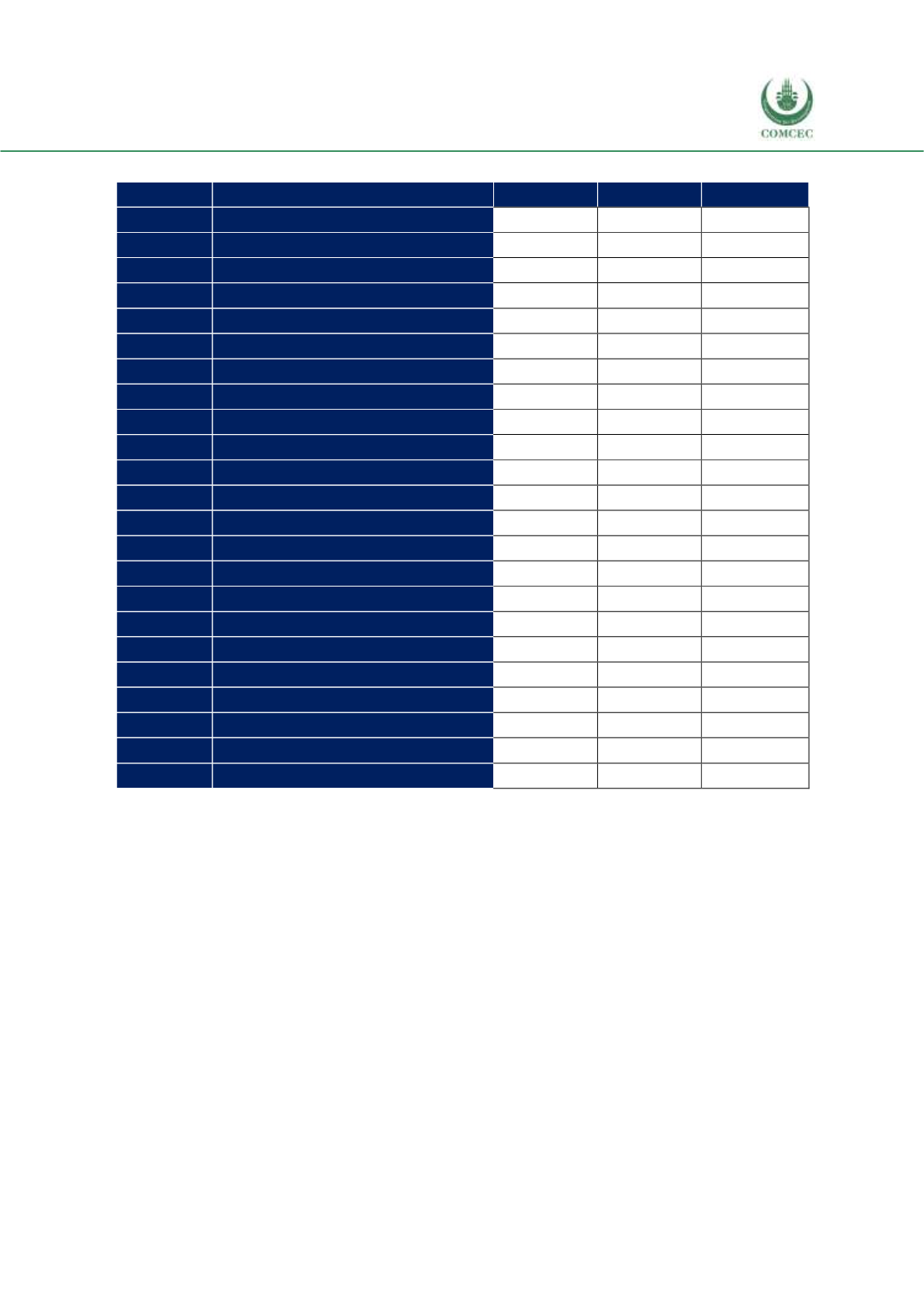
Table 4. 25 NTM Coverage and Frequency Ratios in Agricultural Products, Morocco
Code
Sector
CR
FR
Count
A
Animal
100.0
100.0
204
B
Animal
97.6
94.6
193
F
Animal
0.8
1.5
3
P
Animal
100.0
100.0
151
A
Vegetable
100.0
100.0
317
B
Vegetable
97.3
93.4
296
C
Vegetable
82.7
86.8
275
F
Vegetable
82.7
86.8
275
G
Vegetable
55.2
12.3
39
P
Vegetable
98.4
95.7
225
A
Food Products
65.9
92.4
183
B
Food Products
67.9
90.9
180
C
Food Products
11.0
35.9
71
F
Food Products
24.2
49.5
98
P
Food Products
87.3
76.6
121
A
Hides and Skins
100.0
100.0
59
B
Hides and Skins
13.2
1.7
1
P
Hides and Skins
100.0
100.0
48
A
Wood
36.1
40.4
91
B
Wood
5.2
4.4
10
C
Wood
36.1
40.4
91
F
Wood
36.1
40.4
91
P
Wood
27.9
40.1
65
Source: WITS
Note: A: Sanitary and phytosanitary measures, B: Technical barriers to trade, C: Pre-shipment inspection
and other formalities, F: Charges, taxes and other para-tariff measures, G: Finance Measures, P: Export
related measures
Agricultural trade policies
Agriculture is seen as a crucial aspect of life in Morocco with important political and social
dimensions. The two main purposes of agricultural trade policies are the following: First,
ensuring a minimum level of production in agricultural products is a critical objective regarding
food security, sufficiency and sustainability. Second, protecting the revenue in rural areas and
especially in arid areas and alleviating rural poverty are seen as essential aspects of policy
making.
Trade liberalization of the past decades through tariff reductions is an important leg of
agricultural trade policy in Morocco. But it should also be added that Morocco’s trade regime
remains protective in certain strategic products such as cereals, red meat, and livestock. In some
cereals, quotas are exercised in certain product lines with sufficiently low tariff rates. In red
meat, on the other hand, the main purpose behind prohibitively large tariff rates is to alleviate
poverty risks in arid areas. Morocco has largely adopted the US and EU standards in SPS