Reviewing Agricultural Trade Policies
To Promote Intra-OIC Agricultural Trade
103
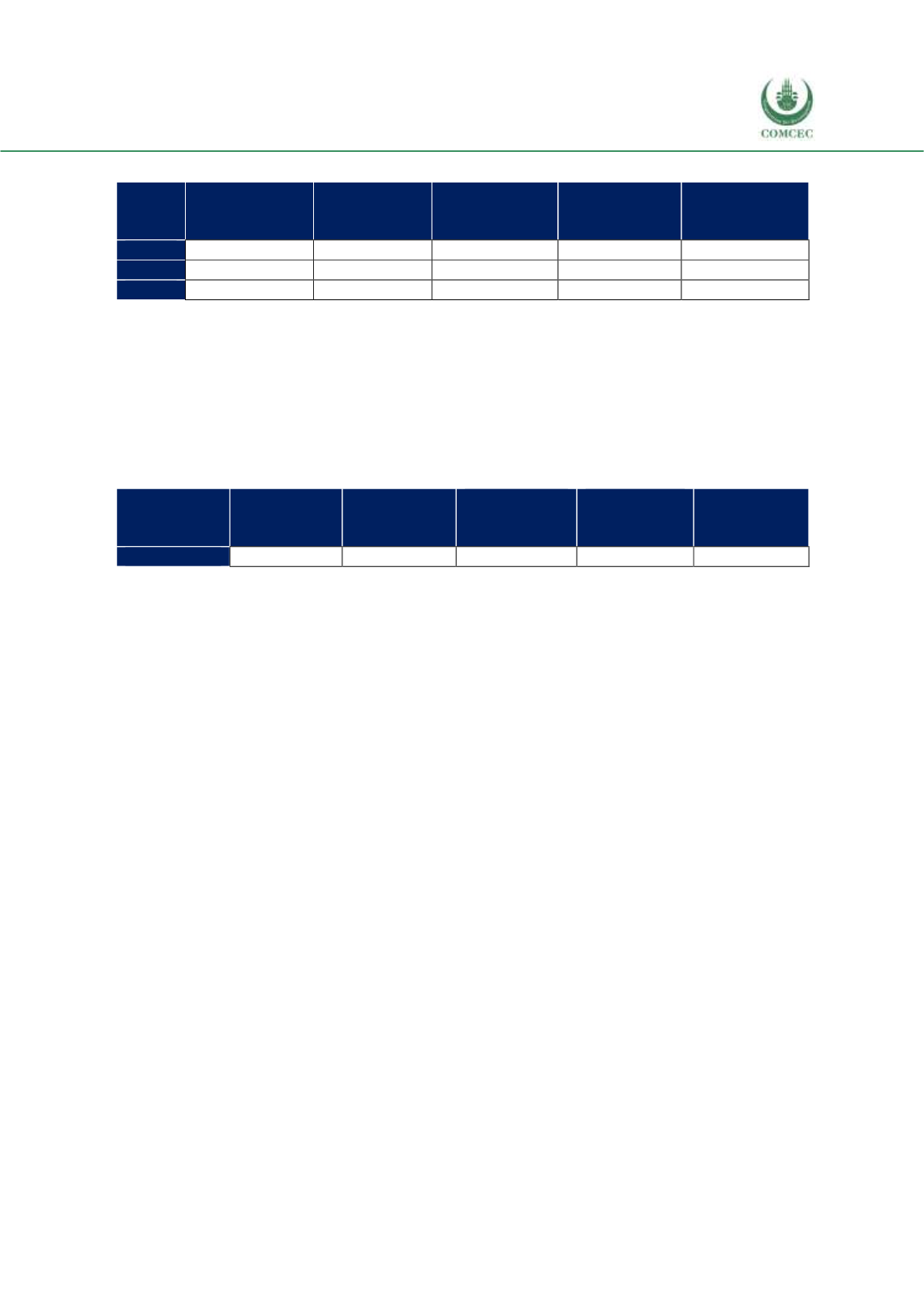
Table 4. 22 Tariffs Set by Morocco for Top 5 Import Products from the OIC Exporters, %
05:
Vegetables,
fruit
41-42-43:
Oils, fats,
waxe
07: Coffee,
tea, cocoa,
spices
08: Feeding
stuff for
animals
11-12:
Beverages,
tobacco
2014
0.8
4.5
6.9
-
22.8
2015
0.3
4.7
7.9
-
23.8
2016
0.7
3.0
6.7
-
23.7
Source: ITC Macmap, CEPII BACI, Eurostat RAMON, UN Comtrade, UN Trade Statistics, and authors’
calculations
Note: Top 5 products are identified considering 3 year average between 2014 and 2016 and ad valorem
equivalent (%) rates are considered for applied tariff rates.
The available data with regards to tariff rates for top five import products from the top 5 OIC
exporters has been presented in Table 4.22. The tariff rate of beverages and tobacco is large and
very slightly increased over the last three years, while the tariff rate for coffee, oils, and
vegetables and fruit decreased during the same period.
Table 4. 23 Tariffs Set by OIC Countries for Morocco’s Top 5 Export Products, %
03: Fish
02: Dairy
05:
Vegetables,
fruit
08: Feeding
stuff for
animals
06: Sugars
2016
21.2
3.9
8.2
2.6
81.7
Source: ITC Macmap, CEPII BACI, Eurostat RAMON, UN Comtrade, UN Trade Statistics, and authors’
calculations
Note: Top 5 products are identified considering 3 year average between 2014 and 2016 and ad valorem
equivalent (%) rates are considered for applied tariff rates.
The tariff rates for Morocco’s top five export products is shown in Table 4.23. The 2016 tariff
rates demonstrate that tariff rates for sugars are the highest, followed by fish, vegetables and
fruit, dairy, and feeding stuff for animals.
NTMs
Tables 4.24 and 4.25 summarize the role of NTMs in Morocco’s agricultural trade. In the former
table, NTM types and product shares and counts affected from NTMs are shown. Food products
and vegetable are the main product categories that are being affected from the existence of
NTMs.
On the other hand, Tables 4.25 indicates that SPS and TBT measures are particularly dominant
for Animals and Vegetable as expected.
Trade agreements and cooperation
Morocco is among the OIC countries that have submitted their updated list of concessions for
the Trade Preferential System within the OIC (TPS-OIC).
Morocco has FTAs with a large number of OIC and non-OIC countries. The major non-OIC
countries and regions in this regard are the USA (since 2006) and the EU (since 2000). The OIC
member countries with whom Morocco has an FTA currently “in force” are Libya, Jordan,
Kuwait, Lebanon, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Oman, United Arab Emirates, Tunisia, Sudan, Qatar,
Bahrain, Yemen and Egypt under the Pan-Arab Free Trade Area (PAFTA) since 2000, Egypt,
Jordan and Tunisia under the Agadir Agreement since 2007, and, finally, Turkey since 2006.
Other than the Agadir Agreement, these FTAs have been notified under the GATT Art. XXIV.
Morocco has a PSA, i.e., the Global System of Trade Preferences among Developing Countries
(GSTP), along with 41 countries across the globe since 1989. The OIC members of GSTP other