
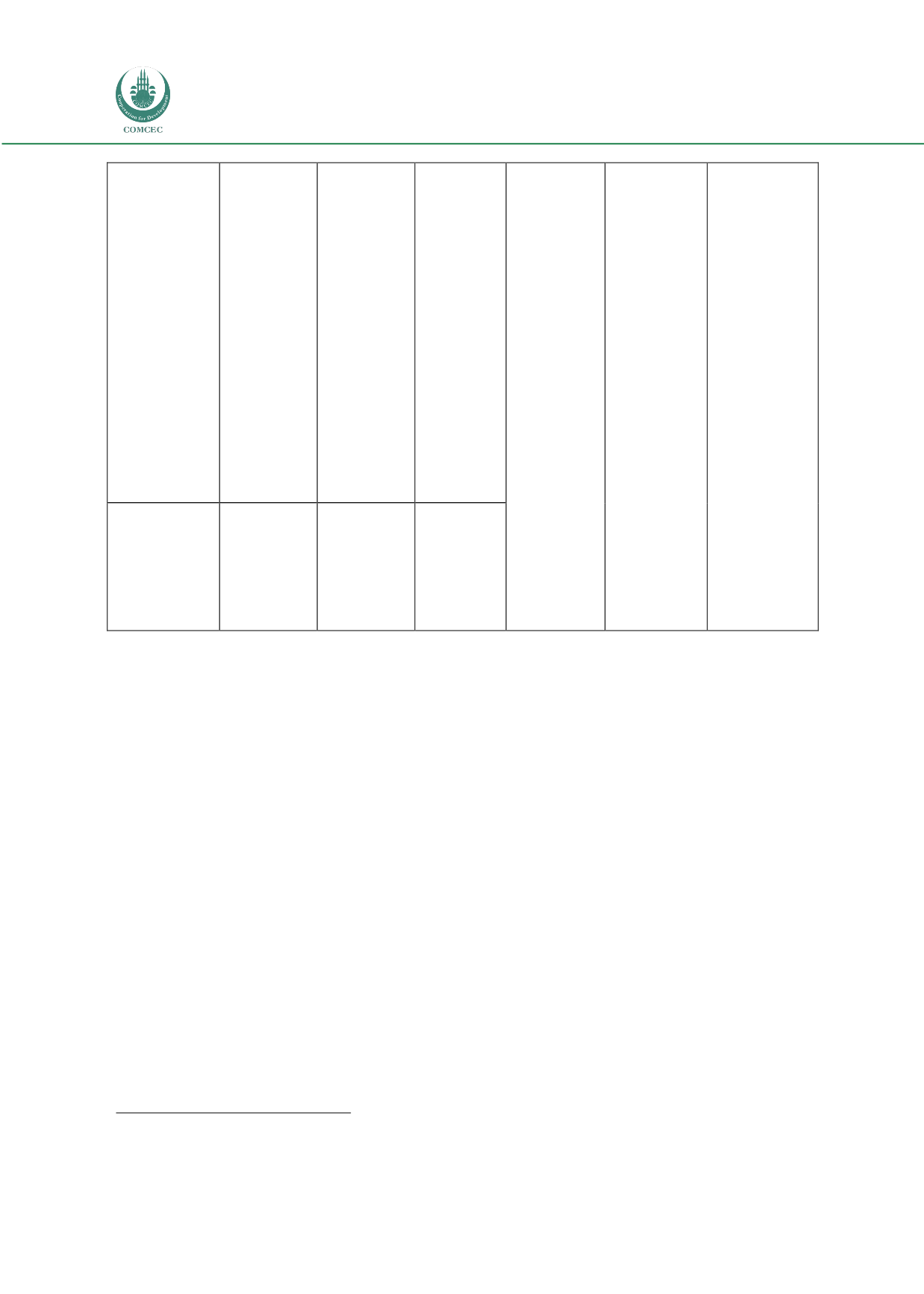
Risk Management in
Islamic Financial Instruments
30
Musharakah
Term Finance
Sukuk (MTFS)
Medium
term
redeemable
musharakah
certificate
based on
diminishing
musharalah
- tradable as
well as
redeemable
Musharakah
has high
default risk
(see Khan
and Ahmed
2001),
however,
MTFS could
be based on
the strength
of the entire
balance
sheet
Similar to
the case of
the floating
rate. This is
however,
unique in
the sense
that the
rate is not
indexed
with a
benchmark
like LIBOR,
hence least
exposed to
this risk
contracts
these risks
can be
overcome.
Salam Sukuk
Securitized
salam, fixed-
rate and
non-
tradable
Salam has
unique
credit risk
(see Khan
and Ahmed
2001)
Very high
Auto fixed
rate
Source: International Conference on Islamic Banking: Risk Management, Regulation, and Supervision (2003)
From the inherent discrepancies concerning asset-based vs. asset-backed sukuk to the
objectives of the Shari’ah and the paradoxes existent in the current sukuk market, there are an
amalgam of different risks important to interested investors and researchers.
2.6 TAKAFUL MARKET RISKS
In our discussion of the risks associated with Islamic insurance mechanisms,
takaful,
it is
important for the reader to understand the transactional sequences as well as the different
entities involved in the two main
takaful
structures,
wakalah
and
mudarabah
-based models,
which are outlined in the following charts, as well as modified versions of those models on the
pages following. The nature and fast expansion of the takaful industry has left glaring
risk/Shari’ah gaps in the eyes of Islamic scholars, many of whom do not believe Islamic
insurance, particularly life insurance, is a viable Islamic financial structure. Experts have cited
many issues with both the
mudaraba
and
wakalah
models, namely issues pertaining to
corporate governance. It should be made plain that, when people contribute money, they
typically expect some sort of immediate or future remuneration. Thus, Hassan and Lewis posit
the question, “Is it really co-operative in nature,” since the number of operators using the co-
operative model is limited.
19
Only a fraction of those who purchase these policies are also
conscious that the premium is for mutual help, and though most
takaful
operators are actual
19
Hassan, Kabir, and Maryn K. Lewis. "Governance Issues in Islamic Insurance." FMA International, 2011. Web.

















