
Risk Management in
Islamic Financial Instruments
29
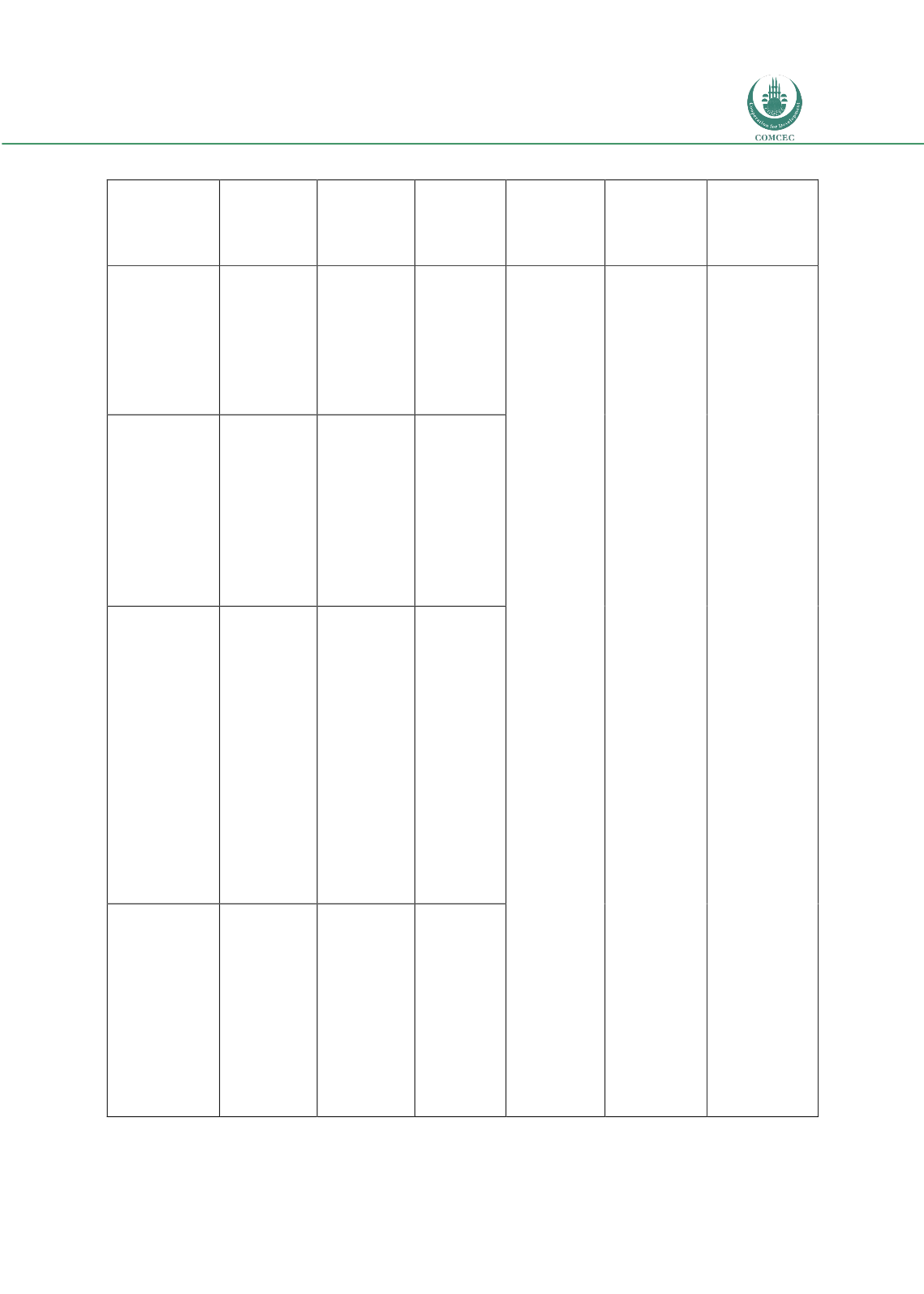
Figure 2.4: Types of sukuks and different risk metrics
Types of
Sukuk
Description
of Sukuk
structure
Credit Risk
Rate of
return
(Interest
rate risk)
FX risk
Price risk
Other risks
Zero coupon
Sukuk
Istisna',
Murabahah
debt
certificates -
non-
tradable
Unique
basis of
credit risks
exist, see,
Khan and
Ahmed
(2001)
Very high
due to fixed
rate.
remains for
the entire
maturity of
the issue
If all other
conditions
are similar,
FX risk will
be the same
for all cases
of Sukuk.
However,
those Sukuk
which are
liquid or
which are
relatively
short term
in nature
will be less
exposed.
The
composition
of assets in
the Pool will
also
contribute
to the FX
risk in
different
ways. Hence
this can be
very useful
tool to
overcome
the FX risk
by
diversifying
the
pool in
different
currencies.
Price risk
relates to the
prices of the
underlying
commodities
and assets in
relation to
the market
prices.
Ijara Sukuk
are most
exposed to
this as the
values of the
underlying
assets may
depreciate
faster as
compared to
market
prices.
Maintenance
of the assets
will play an
important
Part in this
process.
Liquidity of
the
Sukuk will
also play an
important
part in the
risk. Salam is
also exposed
to serious
price risks.
However,
through
parallel
Liquidity risk
is serious as
far as the non-
tradable
Sukuk are
concerned.
Business risk
of
the issuer is
an important
risk
underlying
Sukuk
as compared
to traditional
fixed incomes.
Shari'ah
compliance
risk
is another one
unique in caw
of Sukuk.
Infrastructure
rigidities, i.e..
non-existence
of efficient
institutional
support
increases the
rise of Sukuk
as compared
to traditional
fixed incomes,
see
Swndararajan,
& Luca (2002).
Fixed Rate
Ijara Sukuk
Securitized
Ijara,
certificate
holder owns
part of asset
or usufructs
and earns
fixed rent -
tradable
Default on
rent
payment,
fixed rate
makes
credit risk
more
serious
Very high
due to fixed
rate,
remains for
the entire
maturity of
the issue
Floating Rate
ljara Sukuk
Securitized
ljara,
certificate
holder owns
part of asset
or usufructs
and earns
floating rent
indexed to
market
benchmark
such as
LIBOR -
tradable
Default on
rent
payment,
floating rate
makes
default risk
lesser
serious - see
previous
case
Exists only
within the
time of the
floating
period
normally 6
months
Fixed rate
Hybrid/Pooled
Sukuk
Securitized
pool of
assets; debts
must not be
more than
49%,
floating rate
possibility
exists -
tradable
Credit risk
of debt part
of pool,
default on
rents, fixed
rate makes
credit risk
serious
Very high
due to fixed
rate,
remains for
the entire
maturity of
the issue

















