
Infrastructure Financing through Islamic
Finance in the Islamic Countries
85
4.1.6.2. Case Studies
Case Study: Cash Waqf Linked Sukuk (CWLS)
CWLS is a recent development of Sukuk initiated by the National Waqf Body (BWI), Ministry of
Finance (MoF), Ministry of Religion (MoR) and Bank Indonesia (BI) in collaboration with the
Productive Waqf Forum (FWP), Islamic banks, and social institutions (Ministry of Finance,
Bank Indonesia, Financial Service Authority, 2018). CWLS was officially launched during the
IMF/World Bank Annual Meeting 2018 in Bali as a unique instrument since it combines the
Islamic social instrument (waqf) with the sukuk market (SBSN) to take part in government
public projects such as government schools, public hospitals, mosques, etc.
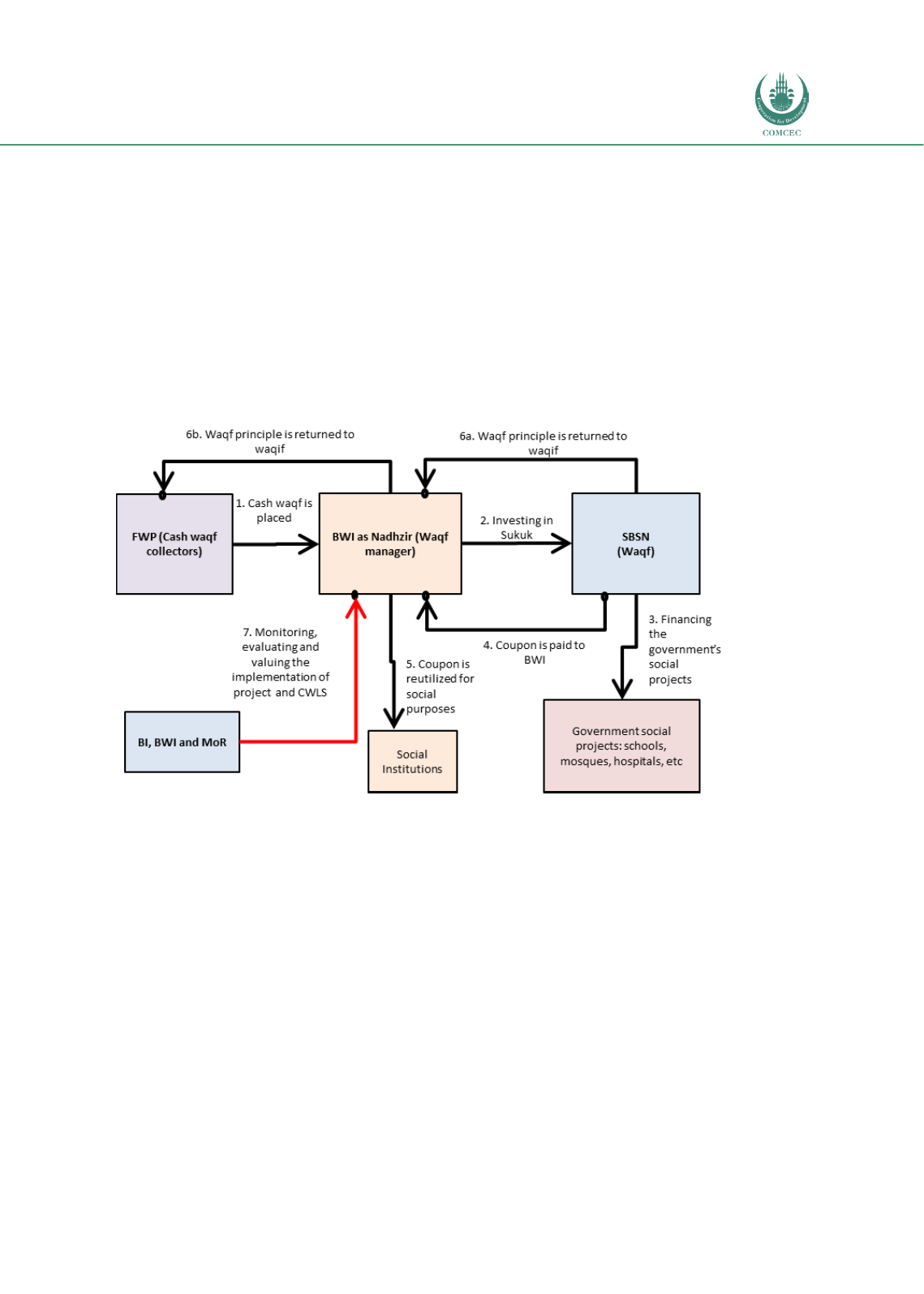
Chart 4.1. 9: The Structure of Cash Waqf Linked Sukuk (CWLS)
Source: Cash Wakaf Linked Sukuk Feasibility Study 2018
Technically, the CWLS model involves the FWP, BWI, Ministry of Finance (MoF), Ministry of
Religion, social institutions and Islamic Banks as in the following:
1.
FWP collects cash waqf (temporary) fromWaqif (social investors) and extends it to the
National Waqf Body (BWI) via Islamic banks.
2.
BWI (as Nadhzir or Waqf manager) places the cash waqf in SBSN (waqf contract) with
a private placement mechanism for a temporary period (5 years).
3.
The government (Ministry of Finance) uses the cash waqf funds to finance government
social projects such as schools, hospitals, etc.
4.
The government (for an appreciation) pays regular coupon to BWI via Islamic banks.
5.
The Coupon (return from waqf investment and treated as another waqf fund) is to be
used by social institutions for other social purposes.
6.
In the maturity date (6a), the MoF returns the principal of SBSN (waqf contract) to
BWI and then it is extended to FWP (6b).
7.
Bank Indonesia, BWI and the Ministry of Religion (MoR) monitor, evaluate and value
the implementation of projects and CWLS.
















