Islamic Fund Management
49
infrastructure sector, which may have complementing effects to securities in the
construction, cement and steel sectors.
In the structuring of Shariah-based investment funds, the asset manager will choose the
various screening methodologies available in the market. For example, depending on the
geographical location of the investors, the Dow Jones, the MSCI or the FTSE Shariah screening
standards can be adopted to meet the requirements of global investors.
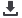
Figure 3.4 shows the
basic structure of an Islamic equity fund.
Figure 3.4: Basic Structure of an Islamic Equity Fund
Source: RAM
2.
Fixed-Income Funds
Debt funds invest in fixed-income securities such as bonds and treasury bills. A debt fund is
less volatile and provides a steady but low income relative to an equity fund. The basic
structure will be similar to an equity-based fund, except the type of investments will be fixed-
income securities or sukuk, as shown i
n Figure 3.5 .Types of fixed-income funds include:
a)
Liquid funds
: These funds invest in highly liquid money market instruments and
provide easy liquidity. They invest in securities with a residual maturity of not more
than 91 days. Investors can park their money in these for a short period of, say, a few
days to several months. Compared to other funds, these fluctuate very little.
b)
Ultra short-term funds
: Most ultra short-term funds invest in securities with a residual
maturity of not more than one year. These funds are suitable for investors who are