COMCEC Transport and Communications
Outlook 2019
44
5.
PRIVATIZATION IN TRANSPORT
Network industries necessitating big infrastructure investments such as transportation,
telecommunication, energy, and water and sewerage have been traditionally state-owned and
-operated for two major reasons. Firstly, huge initial investments created a barrier to entry for
private investors. Secondly, because of the economic and social importance of such industries,
governments preferred to keep them under state ownership. However, poor performances of
state ownership and operations, such as low operating efficiency, labour redundancy, politically
motivated tariff setting, and underinvestment, initiated a tendency to appeal to private finance
and management.
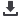
Where the real benefit of a PPP project lies?
To make a comparison between the traditional public procurement and public procurement
through PPP models, we can divide the total value of a project into three: (1) the cost of services
provided, (2) the cost of capital, and (3) the risks assumed by the government (Figure 24).
Figure 24: The comparison of traditional public procurement with PPP procurement
Source: Moriarty (2006)
Regarding cost of capital, state procurement is generally more advantageous than PPP-type
procurement because cost of borrowing of a private entity is generally higher than that of public
sector, given generally high risks inherently involved in PPP projects. On the other hand,
advantages of PPP-type procurement arise by regarding cost of services provided and risks
Risks assumed
by the
government
Procurement
through PPP
Value for
money
Value
($, €, £)
Cost of capital
Cost of services
provided
Traditional
procurement
method