COMCEC Transport and Communications
Outlook 2019
47
1991 and 2018. Energy sector had the largest share (57.1%) in terms of number of PPI projects
and it was followed by transport sector (22.7%).
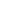
Table 14: Distribution of PPI projects by infrastructure sectors (1991-2018)
Sectors
Number of PPI
projects
Percentage
shares
Energy
5 497
57.1%
Information and communication technology
(ICT)
527
5.5%
Municipal Solid Waste
362
3.8%
Transport
2 142
22.2%
Water and sewerage
1 101
11.4%
Total
9 629
100.0%
Source: Author from the World Bank PPI Database
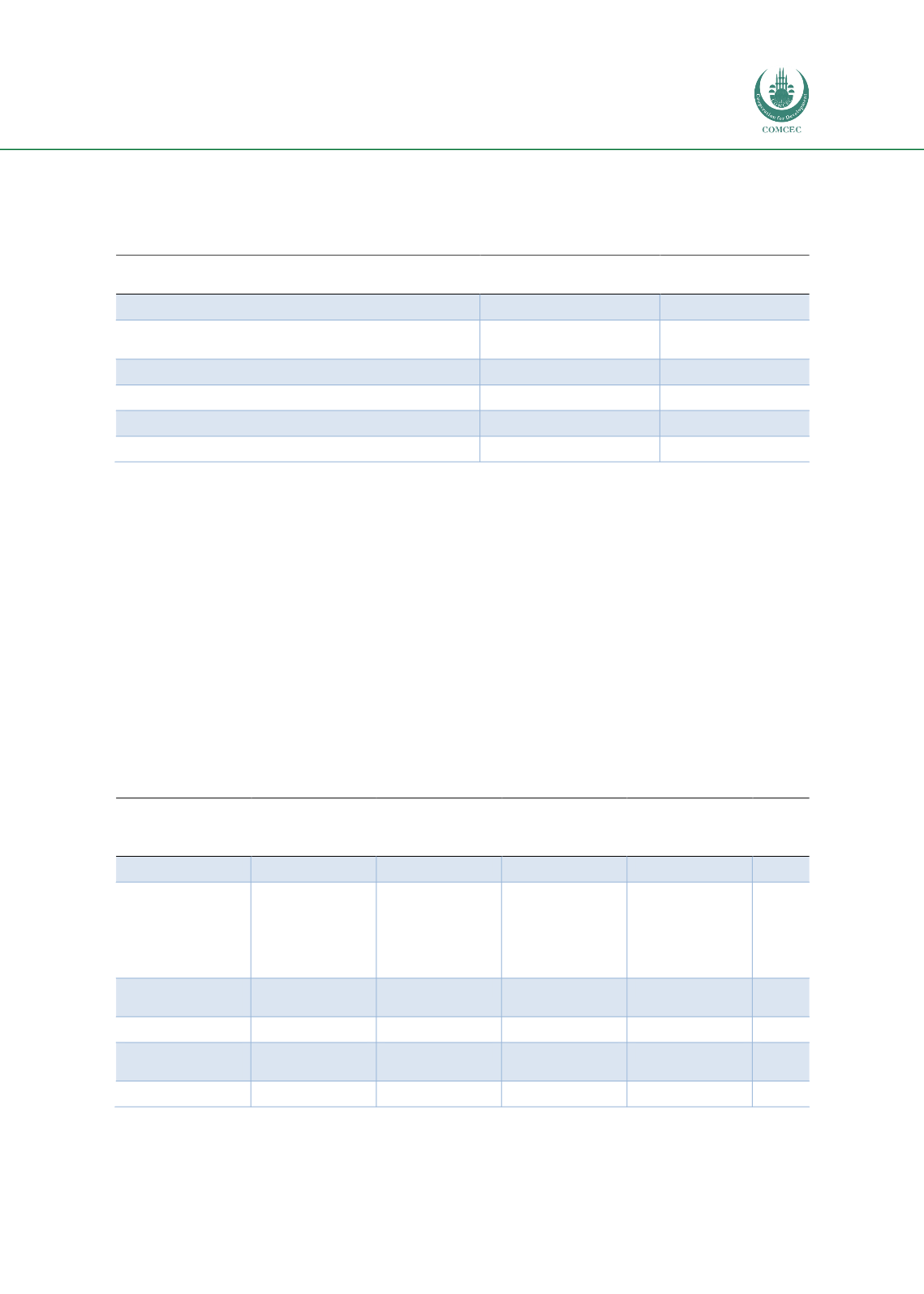
Table 16, which presents the distribution of PPI projects by their PPI-types during the 1991-
2018 period shows that some variations in PPI-type exist depending on the characteristics of
individual sectors. Table 16 shows that greenfield projects have been the most frequently used
PPI type in all sectors but transport, which mostly adopted brownfield. On the other hand, both
energy and ICT sectors applied divestitures more frequently than the other three sectors in both
absolute and percentage terms. In addition, water and sewerage sector used management and
lease contracts more than any other sector did. Among various PPI types, brownfield projects
have been the most common form of PPI investment in the transport sector with a share of
60.3% whereas 32.1% of the transport PPI projects has been implemented through greenfield
schemes. Divestitures andmanagement and lease contracts had relatively lower shares, i.e. 4.0%
and 3.6%, respectively.
Table 15: Distribution of the PPI projects by PPI-types (1991-2018)
Sector
Brownfield
Divestiture
Greenfield
project
Management
and lease
contract
Total
Energy
692
970
3449
65
5497
Information
and
communication
technology
(ICT)
8
188
321
10
527
Municipal Solid
Waste
10
1
274
77
362
Transport
1292
85
687
78
2142
Water and
sewerage
417
33
468
183
1101
Total
2419
1277
5199
413
9629
Source: Author from the World Bank PPI Database