COMCEC Trade Outlook 2016
28
4.
TRADE ENVIRONMENT IN THE OIC MEMBER STATES
In this section, the trading environment in the OIC Member States will be brought into focus with
more in-depth analysis of the current state of affairs in terms of trade liberalization, facilitation,
promotion and financing.
Trade Liberalization:
Trade liberalization aims at eliminating the tariffs and other trade barriers hindering the flow
of goods and services among the countries. Recent studies such as OECD (2011), Pavcnik (2009)
and IMF (2001) have found that trade liberalization increases trade, supports production, job
creation and poverty alleviation, prevents illegal trade and contributes to economic growth. The
existing literature has found strong correlation between openness to trade and economic
growth. For example, Panagariya (2005) concludes that it’s unlikely to find an example of a
developing country that has grown rapidly while maintaining high trade barriers.
Trade liberalization has been on top of the agenda of the international economic relations since
the Second World War. General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) was initiated in 1947
for multilateral trade negotiations to liberalize trade. Since then, the number of countries joining
the GATT has increased dramatically. In 1994, World Trade Organization (WTO) was
established to continue these negotiations. The WTO negotiations aim at eliminating the tariffs,
non-tariff barriers and other barriers to international trade in goods and services among its
members.
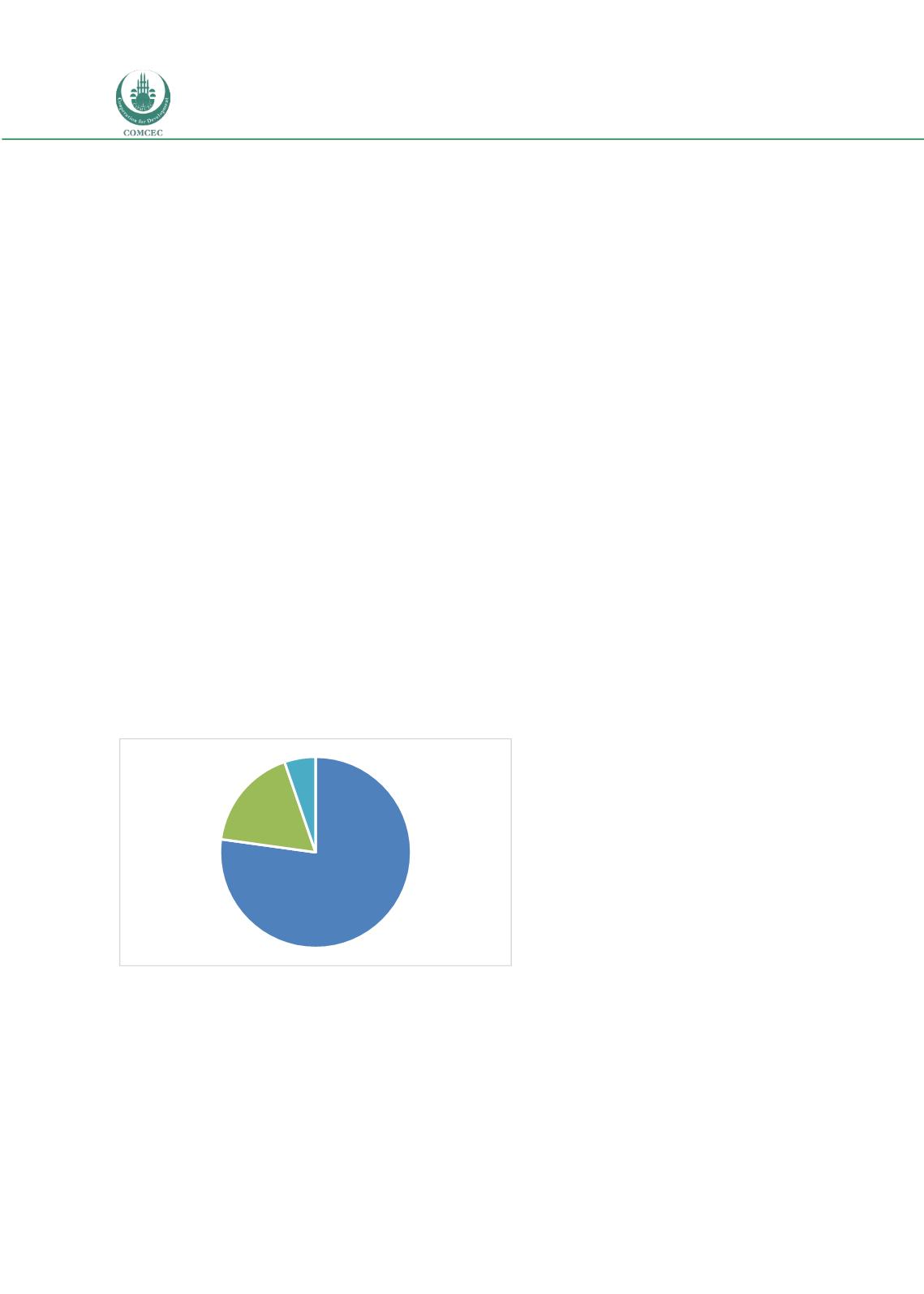
Most of the OIC Member States have also showed interest in joining the WTO. As of August 2016,
44 OIC Member States have acceded to theWTO and 11 Member States have the observer status.
Afghanistan is the last OIC Member State that joined the WTO in July 29th, 2016.
Figure 31: WTO Membership Status of OIC Countries
Source: WTO
Regional Trade Agreements (RTAs) is another approach for trade liberalization. Two or more
countries initiate trade arrangements to liberalize trade among themselves. Members of RTAs
get the advantage of exporting to the other parties to the RTAs than the others. The European
Union which was first initiated in 1950s made a domino effect on the expansion of the RTAs
worldwide. Today, many countries, including the developed ones are party to one or more RTAs.
Members;
44
Observers;
10
Others; 3