COMCEC Trade Outlook 2018
5
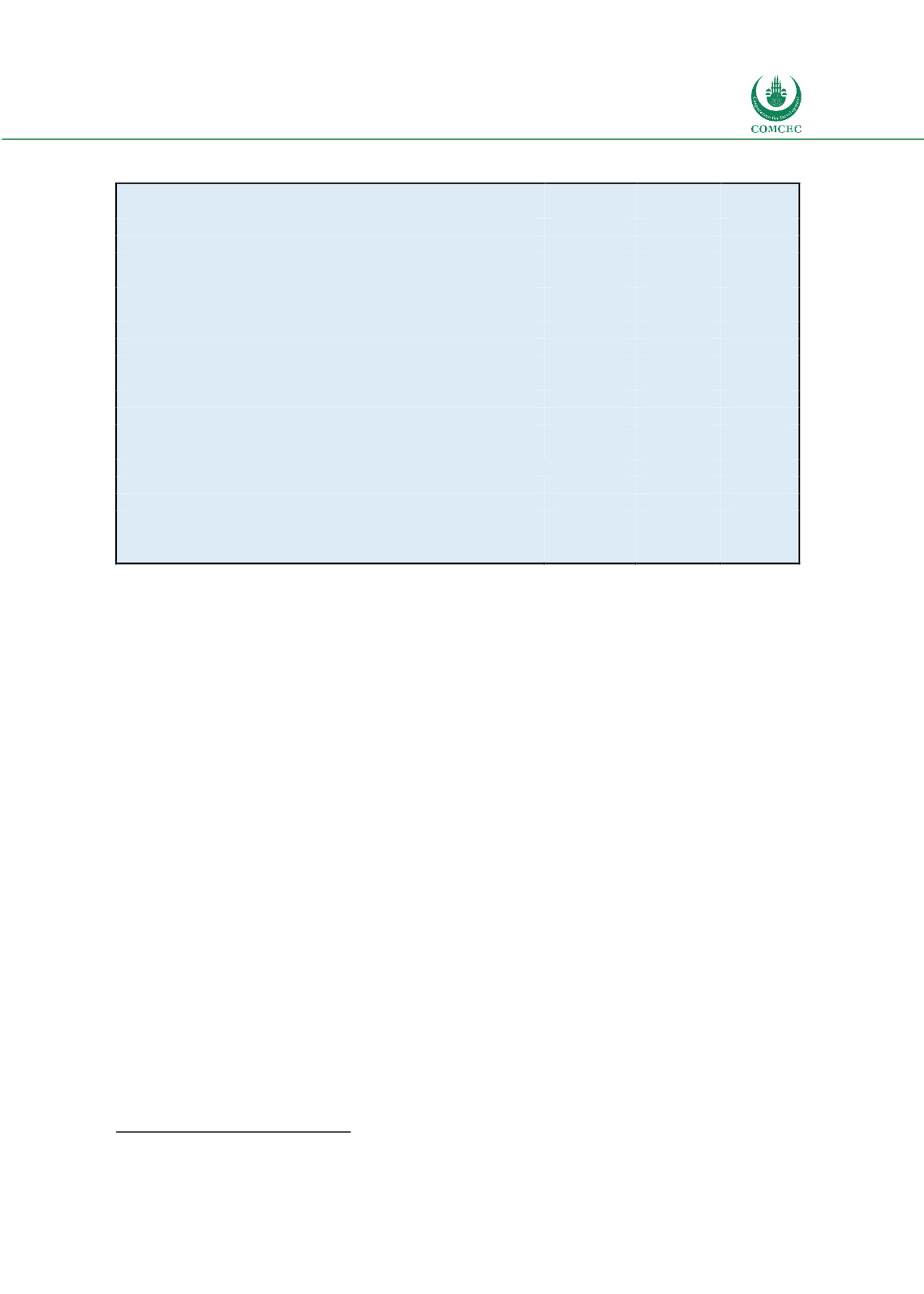
Table 1: Trade Volume and GDP, Annual % change
2015
2016
2017
Volume of world merchandise trade
2.5
1.8
4.7
Exports
Developed Economies
2.3
1.1
3.5
Developing Economies
2.4
2.3
5.7
North America
0.8
0.6
4.2
Europe
2.9
1.1
3.5
Asia
1.5
2.3
6.7
Imports
Developed Economies
4.3
2.0
3.1
Developing Economies
0.6
1.9
7.2
North America
5.4
0.1
4.0
Europe
3.7
3.1
2.5
Asia
4.0
3.5
9.6
World output (real GDP at market exchange rates,2005)
Developed Economies
2.3
1.6
2.3
Developing Economies
3.7
3.6
4.3
North America
2.7
1.5
2.4
Europe
2.3
1.9
2.6
Asia
4.2
4.1
4.5
Source: WTO
1.1. Recent Trends in World Merchandise Trade
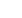
There have been some emerging patterns shaping the
global trading environment recently. First trend is the
proliferation of non-tariff barriers. The Figure below
which is taken from UNCTAD (2017) provides data for
1995-2015 period and illustrates that while tariffs have
declined considerably in the 2000s, little progress was
achieved in terms of further declines in tariffs since the
global crisis. The number of non-tariff measures continue to rise especially in the aftermath of
the crisis. Slower pace of trade liberalization and increased protectionist measures are
considered among factors which constrain world trade.
According to WTO
6
, WTO members
introduced more trade-restrictive measures (tariff increases, stricter customs procedures,
imposition of taxes and export duties) in mid-October 2017 to mid-May 2018 period compared
to the previous review period.
6
https://www.wto.org/english/news_e/news18_e/trdev_25jul18_e.htm“Further rise in trade
restrictive measures
could pose a risk for
global trade