Malnutrition in the OIC Member
Countries: A Trap for Poverty
COMCEC
3.4. Bangladesh
Bangladesh is located in South Asia and came into existence as the result of the split between
Western and Eastern Pakistan in 1971. Bangladesh has an estimated population of 156 million,
the ninth largest in the world. Despite this large population, Bangladesh is a very homogenous
country: 90% of the population is Muslim, 99% speak the Bangla official language and 98% is
ethnically Bengali (CIA 2016).
The country has witnessed impressive economic growth and poverty reduction: the
proportion of people living in extreme poverty has been halved since the 1970s and the
country grew at an average of
6
% over the last two decades. Since 2015, Bangladesh has
become a lower middle income country. This economic record has translated into nutritional
progress: stunting rates went down from 55% in 1997 to 36% in 2014.
Nevertheless, stunting remains very high (the 24th worst rate in the world), and almost
reaches 50% in regions of Syhet and Chittagong. The standards of living remain low despite
the growth record and the economy is hampered by poor infrastructures, insufficient power
supply, a high reliance on garment exports, and political instability. As a result, 41.3% of
people in Bangladesh live in multidimensional poverty and 22.4% are vulnerable to it (76th
out of 112 countries) and Bangladesh ranks 142nd out of 188 countries (corresponding to low
levels of development).
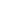
State of Malnutrition in Bangladesh
Figure 31: Malnutrition in Bangladesh at a Glance
Source: BDHS (2014)
104