Improving Transnational Transport Corridors
In the OIC Member Countries: Concepts and Cases
109
cross the border just to work, returning to their homes abroad in the evenings. The available
data indicates that this migration plays a significant role in reducing poverty in the less
wealthy countries. This is most apparent in the Kyrgyz Republic, where remittances reduce the
national poverty rate by some 6-7 percentage points (UNDP, 2015). The following table shows
the social profile of the corridor countries.
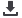
Table 28: Social factors of countries on CAREC corridor 3
Source: World Bank.
4.4.6.
Safety, security and the legal liability
Road infrastructure accounts for the most investment in CAREC transport corridors. However,
this means that little attention has been paid to addressing
road safety
. Similarly, road safety
records remain poor, and crash rates are more than four times those in countries that have
adopted good road safety practices
42
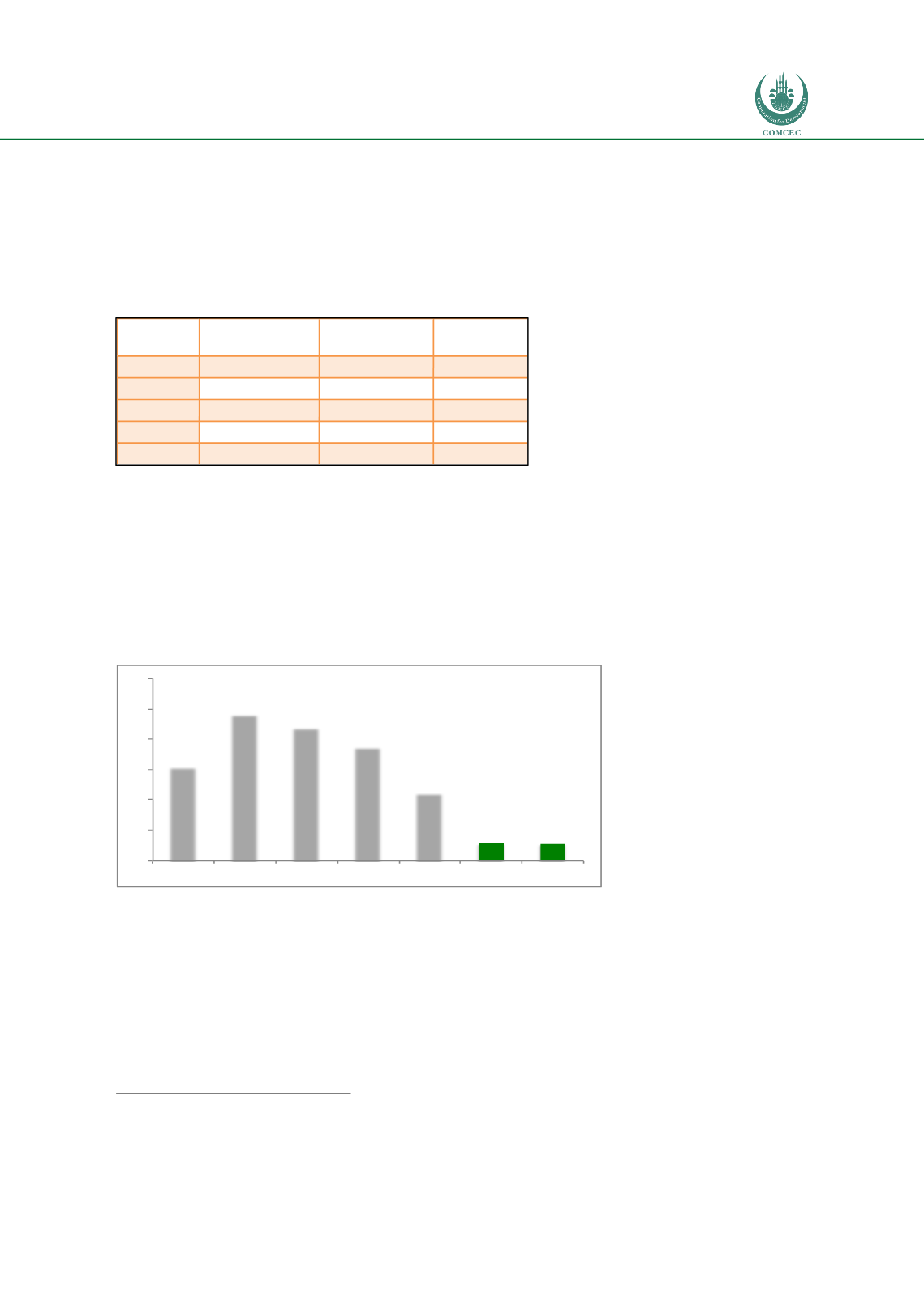
. This is also shown in the figure here below.
Figure 39: Fatalities per 100,000 populations on corridor 3 countries
in 2015
Source: Global Status Report on Road Safety 2015, WHO.
On corridor 3, a high incidence of road traffic accidents is mostly caused by poor road
condition. On the trunk road connecting Bishkek to Osh there were 4,248 road crashes in 2009
and 4,813 in 2013, resulting in 1,022 deaths (CAREC, 2015). A road rehabilitation project on
this section is ongoing (see Appendix 4, project code IP9). Improved capacity and safety level is
one of the expected outcomes.
42
World Health Organization. 2013.
Global Road Safety Report 2013
. Geneva.
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
AFG KAZ
KGZ
TAJ
UZB
UK Sweden
Country
Population
(Million)
Unemployment
(%)
Poverty
Index (%)
AFG
32.5
8.5
N/A
KAZ
17.5
5.2
2.7
KYRG
6
7.7
32.1
TAJ
8.5
10.8
31.3
UZB
31.3
8.9
14.1