Preferential Trade Agreements and Trade Liberalization Efforts in the OIC Member States
With Special Emphasis on the TPS-OIC
75
The dates of ratifications or entry into force of agreements can be treated as broadly indicating
the time when the agreements might have started being implemented. The distribution
10
The analysis refers to an RTA defined geographically. Where there is more than one
overlapping agreement (e.g. separately concerning goods and services) between a given
groups of countries, this is counted as one. For instance, South Asian Free Trade Agreement
(SAFTA) and SAARC Agreement on Trade in Services (SATIS) is counted as one of these dates
over time is similar to the signature dates. A certain number of agreements has not yet been
ratified or entered into force (or this information was not available in the consulted sources).
Of the analysed agreements, 101 are believed to have been actually implemented in that
certain trade liberalisation steps have actually taken place. However, it should be noted that
this category is broadly defined and may imply very different levels of progress in the
liberalisation of trade relations between participating countries. This is due to the large
heterogeneity of the agreements themselves and their level of ambition and length of the
implementation period originally foreseen and/or actually followed. On average an OIC
member country is currently party to four RTAs with the number of such agreements ranging
from 1 in the case of Yemen, Tajikistan, Chad or Gabon to 21 in the case of Turkey.
11
Six
countries (Turkey, Malaysia, Jordan, Pakistan, Egypt, and Indonesia) have more than 10
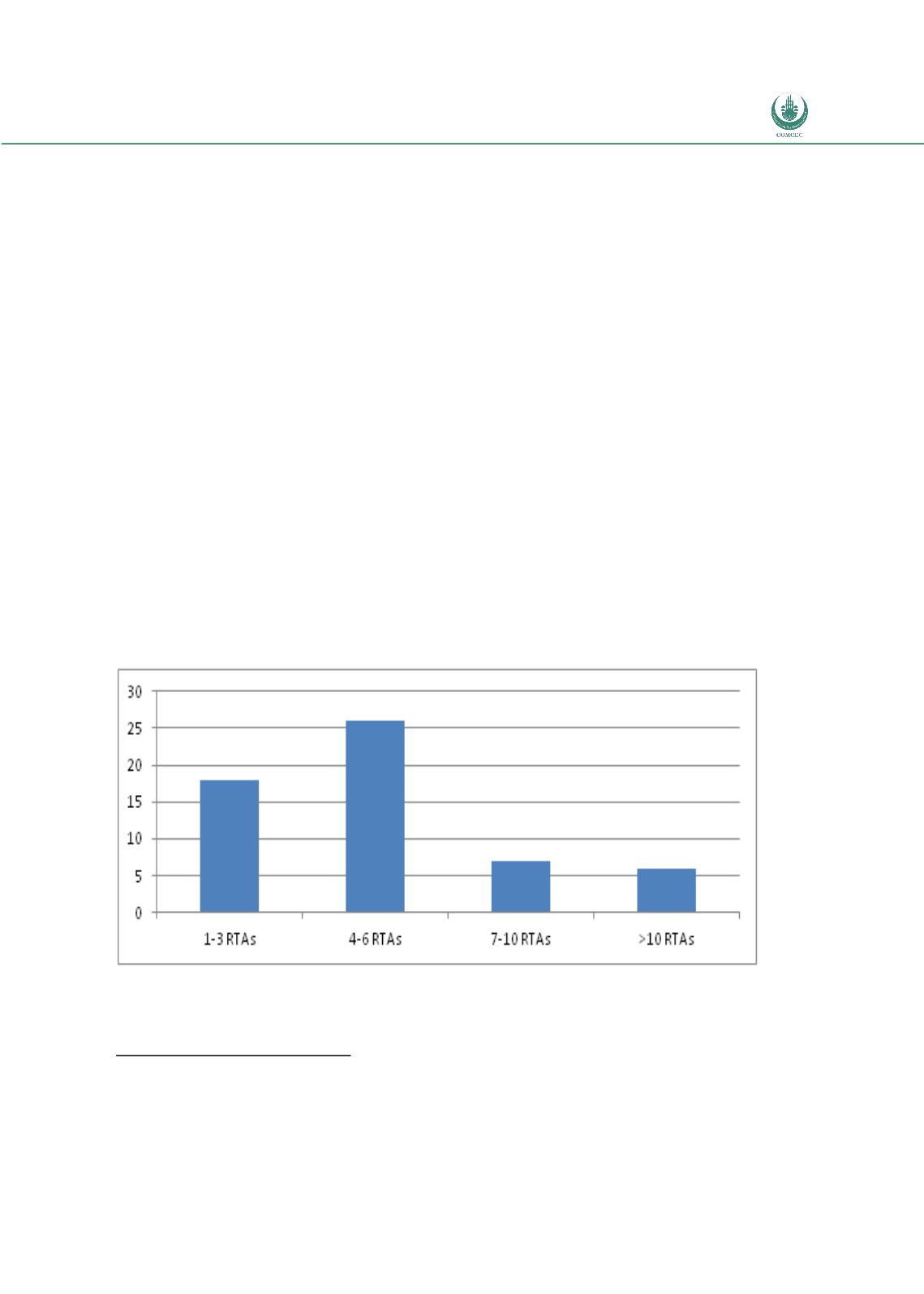
agreements in place. Figure 5 provides a distribution of the number of agreements that OIC
members participate in. It shows that 26 OIC countries have between four and six
implemented RTAs and 18 counties have between one and three RTAs.
Figure 5:
Distribution of the Number of OIC Countries by RTA Membership
Source: WTO
10
The analysis refers to an RTA defined geographically. Where there is more than one overlapping agreement
(e.g. separately concerning goods and services) between a given group of countries, this is counted as one. For
instance, South Asian Free Trade Agreement (SAFTA) and SAARC Agreement on Trade in Services (SATIS) is
counted as one.
11
Four is both the median and mode value for the number of agreements per OIC member.