Reducing Postharvest Losses
In the OIC Member Countries
61
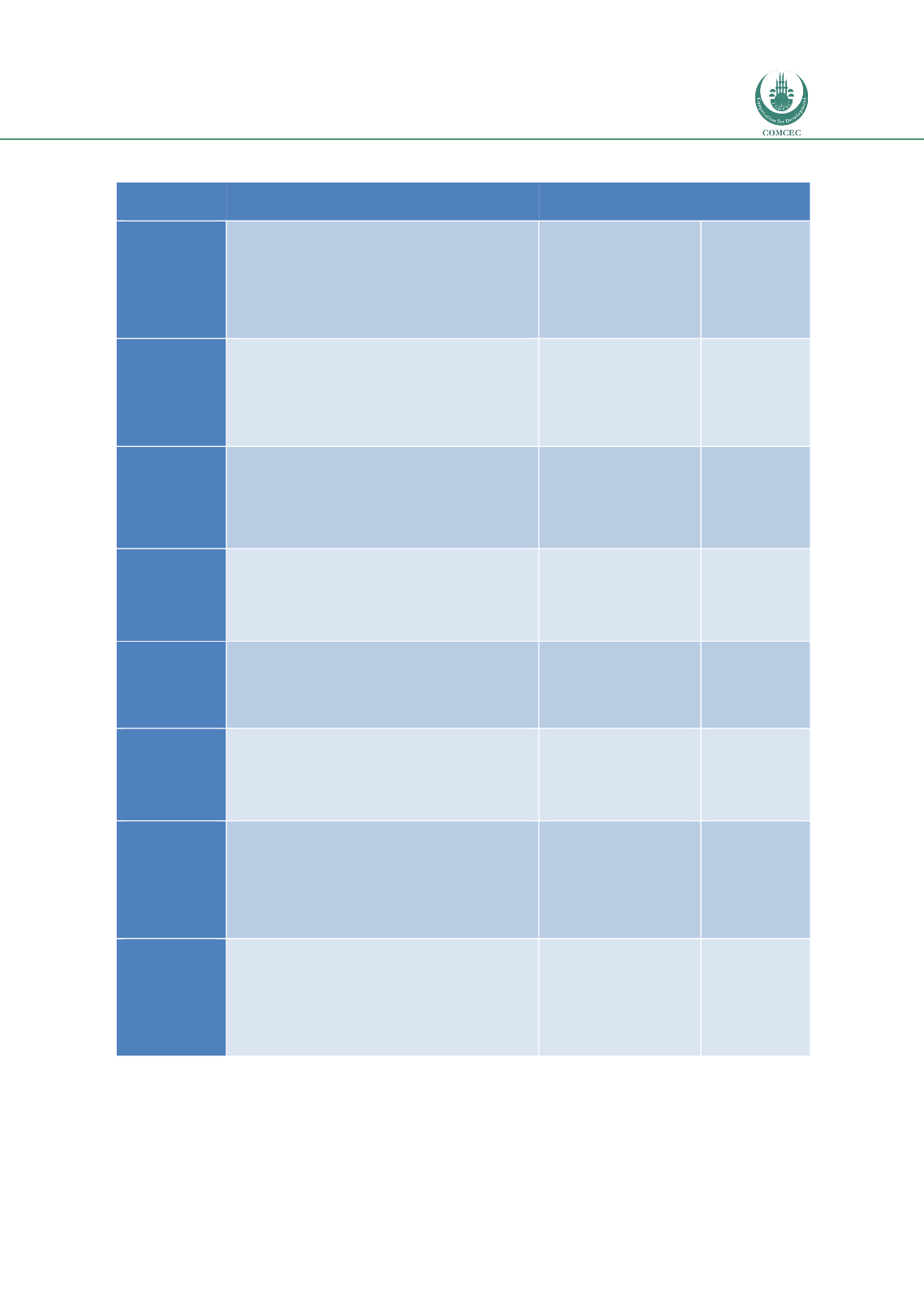
Table 22: Causes of PHLs reported for cereals and per postharvest step of the value chain
Postharvest
step
Maize
Rice
Sorghum
Harvest
Contamination through use of old sacks/containers:
cobs are often left on the ground for picking later,
which can cause contamination by fungus
Harvesting method; some crop left in field
Late harvesting; grain shattering, insect infestation
in field: harvesting method to improve
Rain during harvest; rotting or sprouting grains
Harvesting method; some
crop left in field
Late harvesting; grain
shattering, insect
infestation in field
Harvesting
method; some
crop left in field
Field drying
Placement on ground; contamination by fungi or
insect damage
Rain during drying; rotting, sprouting or mycotoxin
contamination
Theft by humans, birds, livestock or wild animals
Placement on ground;
contamination by fungi or
insect damage, mice and
other rodents
Rain during drying;
rotting, sprouting or
mycotoxin contamination
Theft by birds,
livestock or
wild animals
Transport
Delays due to poor infrastructure
High number of bribe payments required
Insect infestation due to use of contaminated
container
Spillage through use of unsuitable containers
Theft by humans
Spillage through use of
unsuitable containers
Spillage through
use of
unsuitable
containers
Further
drying
Contaminating grain by placing it directly on ground
Inadequate drying practice
Possible insect infestation
Lack of wind and high humidity during drying
Rain during drying
Contaminating grain by
placing it directly on
ground
Feeding by livestock and
pests
Rain during drying
-
Threshing/
shelling
Contamination with foreign matter (e.g. small
stones, dust)
Rough shelling/threshing methods; broken, cracked
grains
Scattering of grains
Rough shelling/threshing
methods; broken, cracked
grains
Scattering of grains
Scattering of
grains
Sorting/
grading
Labour intensive manual sorting methods
No price premium for high quality maize, so no
incentive for sorting
Labour intensive manual
sorting methods
No price premium for
high quality rice, so no
incentive for sorting
No price
premium for
high quality
sorghum, so no
incentive for
sorting
Storage
Ineffective grain protection: Insect damage
Rodents damage, ineffective grain protection
methods used and storage hygiene
Poor monitoring of stored products
Too high moisture content; mould growth and
increased risk of aflatoxin contamination All of the
above apply, as a consequence of poor monitoring
Insect damage, Rodent
damage, Weevil
infestation
too high moisture content
Poor monitoring of
stored products
Insect damage
Marketing
Cartel behaviour among traders
No financial incentive for farmers to produce and
sell high quality maize
Sales after harvest at low prices, due to urgent need
for cash
Weak marketing knowledge and limited collective
selling arrangements of farmers
No financial incentive for
farmers to produce and
sell high quality grain
Sales after harvest at low
prices, due to urgent
need for cash
Sales after
harvest at low
prices, due to
urgent need for
cash