Reducing Postharvest Losses
In the OIC Member Countries
64
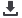
Table 24: Constraints to reducing PHLs reported for cereals and per step of postharvest
Postharvest step Maize
Rice
Sorghum
Harvest
Inadequate knowledge about technology and of
postharvest among farmers
Difficulties in the extension system
Inadequate knowledge on postharvest management
and poor harvesting methods. Pressure for money
makes farmers harvest the crop when it still has high
moisture content
Lack of training in postharvest for agricultural
extension officers
Poor training materials (trainers, equipment, etc.)
Insufficient
co-
operation between
farmers
Predominance
of
small scale upland
mixed
cropping
makes it impossible
to adopt even the
simplest mechanical
harvesting device.
-
Field drying
Lack of training in postharvest for agricultural
extension officers
-
-
Further drying
Climatic changes, lack of knowledge by farmers and
extension
Lack of local technical solutions for drying when rains
are late
Lack of training in postharvest for agricultural
extension officers
Reliance on mother nature (Sunshine)
-
-
Threshing/
shelling
Cost is too high for farmers
Cost of processing equipment
Lack of availability of cheap, locally made, technologies
Lack of training in postharvest for agricultural
extension officers
Lack of understanding of the danger of storing
damaged grain by farmers and extensionists
Low use of technology
Poor practices, use of hired labour
Lack of capital
Lack of awareness
on good practices
inadequate
infrastructure
facilities (energy)
Cost
and
organisation
Sorting/ grading
Labour intensive
Cost is too high for farmers
Lack of price differential that does not give incentive
Lack of training in postharvest for agricultural
extension officers
-
Training and
improved
marketing
arrangements
Storage
Availability and accessibility (up-front costs) of
improved storage options and knowledge of how to
properly store
Cost is too high for farmers
Lack of information and non-availability of hermetic
storage bags, ineffective storage structures
Low investment in storage and not being aware of
storage structures which can reduce losses
Low volumes
More space needed
Proper training is not widely available, proper
structures are needed
Weak understanding of insect life cycles and how
insects can decimate a new crop
Lack of knowledge by farmers and extension on
effective grain storage methods
Lack of capital, lack
of awareness on
good practices,
inadequate
infrastructure
facilities (roads)
Most farmers store
their rice grains in
their homes among
other household
items.
-
Marketing
At the start of the marketing season there is a glut on
the market due to oversupply. This takes farmers a
long time to dispose of their grain. Meanwhile grain
losses are incurred
Commodity staying long at the markets
Lack of market information
-
Need an
industrial
champion for
commercial
sorghum
consumption
Secondary
processing (e.g.
milling,
oil
extraction)
Lack of education
Lack of training or awareness of food safety issues
such as mycotoxins
Lack of capital
Lack of awareness
on good practices
Inadequate
infrastructure
facilities (energy)
-