Increasing the Resilience of the Food Systems
In Islamic States in Face of Future Food Crises
104
Identifying Food Security Vulnerabilities in Indonesia
The Indonesian food system has a number of vulnerabilities that could significantly impact the
level of food security in the country.
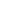
Table 55: Summary of Areas of Vulnerability in the Indonesian Food System (highlighted in
the table)
Availability
Access and Affordability
Utilization
Stability
Production
Transportation
Food Safety
Availability
Reserves
Market Infrastructure
Care & Feeding Practices
Access
Imports
Purchasing Capacity
Health & Sanitation
Utilization
Source: DinarStandard Analysis
Indonesia faces substantial environmental risks and is ranked 111
th
in the world in overall
natural resources and resilience,
423
due primarily to a particularly high risk of exposure to
significant climate change; here, the country ranked 102
nd
in the world.
424
It is expected that
global warming will adversely impact Indonesian agriculture, with temperatures expected to
rise by one to two degrees Celsius over the next 40 years, increasing precipitation. In addition,
Indonesia is one of 10 countries that experienced the highest number of natural disasters in
2016.
425
The risk of natural disasters facing Indonesia greatly affects agricultural its production.
Floods occur often, with a total of 506 incidents in 2019.
426
Another vulnerability is poverty. The number of impoverished people in Indonesia in 2018 was
high, at 25.9million, but the proportion of the poor to the national population shows a declining
trend since 2014 (11.25% to 9.82%). To overcome this, the Indonesian government has
implemented several programs to reduce hunger among the poor.
Toddler malnutrition conditions are still found in several regions of Indonesia. In 2017, the
incidence of stunting in toddlerswas 29.6%, which increased from the 2016 rate of 27.5%. East
Nusa Tenggara Province has the highest incidence of stunting, at 40.3% in 2017. However, an
intervention program initiated in 2018 is effectively addressing stunting in 100 priority districts
and cities throughout Indonesia.
427
The core of the vulnerability of Indonesia's food security is poverty; there are still many cases
in which household incomes cannot meet standard nutritional needs. The Indonesian
government has attempted to reduce poverty through several poverty alleviation programs.
423
“Natural resources and resilience rankings.” Global Food Security Index.
https://foodsecurityindex.eiu.com/Index/AdjustmentFactorRankings424
ND-GAINCountry Index. University of Notre Dam
e. https://gain.nd.edu/our-work/country-index/rankings/425
“Food Security and Vulnerability Atlas 2018.”
http://bkp.pertanian.go.id/storage/app/media/Pusat%20Ketersediaan/Bidang%20Ketersediaan/peta-ketahanan- kerentanan-pangan-2018.pdf426
https://bnpb.cloud/dibi/laporan5427
“Food Security and Vulnerability Atlas 2018.”
http://bkp.pertanian.go.id/storage/app/media/Pusat%20Ketersediaan/Bidang%20Ketersediaan/peta-ketahanan- kerentanan-pangan-2018.pdf