Increasing Agricultural Productivity:
Encouraging Foreign Direct Investments in the COMCEC Region
9
with less than 1,000 m
3
per capita year while 13 of them suffer absolute water scarcity with
total water resources of less than 500 m
3
per year.
Clearly, lack of sufficient water is one of the biggest barriers to further developments in the
agricultural sector in the COMCEC Region. Irrigation techniques, such as sprinkler and localized
irrigation are a very powerful solution to allocate the right amount of water for a particular
(crop) production process. These are considered a relatively efficient irrigation technique, with
high water saving potential, however, the initial investments are considerable and the payback
period is relatively long.
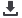
Figure 3: Irrigation Techniques in the COMCEC Member Countries (2011 or latest available)
Source: SESRIC, 2013.
Surface irrigation refers the group of application techniques where water is applied and
distributed over the soil surface by gravity. As illustrated in Figure 3, it is by far the most
common form of irrigation throughout the world and has been practiced in many areas virtually
unchanged for thousands of years. Surface irrigation is often referred to as
flood irrigation
,
implying that the water distribution is uncontrolled and therefore, inherently inefficient.
Localized irrigation systems apply water directly where the plant is growing thus minimizing
water loss through evaporation from the soil. Such localized irrigation systems include drip
irrigation, porous clay pots, porous pipes, and perforated plastic sleeves.
Irrigation sprinklers are sprinklers providing water to vegetation, or for recreation, as a cooling
system, or for the control of airborne dust. it is mainly used in areas that have a shortage of
water.
61,570 (93%)
2,989 (5%)
1,568 (2%)
surface irrigation (1000 ha)
sprinkler irrigation (1000 ha)
localized irrigation (1000 ha)